
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 15 May 2025, 17:15 IST
Anatomy of Flowers: The anatomy of flowers is the study of the internal structure of organisms. It includes the association and design of the tissues. The group of tissues is interdependent identical or non-identical cells along with an intercellular substance having a common origin to perform a specific (definite) function in multicellular organisms called a tissue. The purpose of a flower is for a factory to be suitable to reproduce sexually. The manly part of the flower (stamen) consists of hair and an anther. The anther contains pollen. Other flower corridors include petals, sepals, bracts, pedicels, and containers. It may deliver flowers that are perfect or amiss and may have flowers that are complete or deficient. Shops may be classified as monoecious or dioecious.
Monocots have flowers with flower corridors in multiples of three. Dicots have flowers with flower corridors in multiples of four or five. An inflorescence may be determinate or indeterminate. Common inflorescence types are cyme, shaft, raceme, panicle, corymb, umbel, spadix, catkin, and head.
Also Check: Monocot Dicot Plants Anatomy
Flowers are composed of sets of essentially modified leaves arranged in curls. The remotest spiral of a flower is called the calyx and is composed of sepals. Inside the calyx is the corolla, which is composed of petals. Together, the calyx and corolla are anointed perianth. Inside the perianth is the androecium (house of man), a spiral composed of stamens. Each stamen has long hair holding up pollen sacs called anthers. Inside the androecium is the gynoecium (house of a woman), composed of carpels. Each carpel has an ovary at the base where ovules are sheltered. The style emerges from the ovary and is outgunned by the smirch. Pollen grains land on the smirch and grow a tube to reach the ovule and complete fertilization.
Anatomy refers to the study of the interior structure of an organism. The study of the factory anatomy of flowers includes histology- the study of the association and design of the tissue. Anatomy helps us know the structural tricks of different plants and indicates the structural adaptation to other surroundings.
A stem is one of a vascular plant’s two main structural axes. The part of the plant can be seen above the ground.
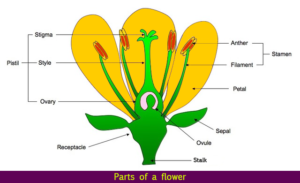
The womanish reproductive part of the flower consists of four major corridors.
The manly reproductive part of a flower consists of two major corridors.

Anatomy directs the study of the internal structure of an organism.
Marcello Malpighi, an Italian doctor, discovered the anatomy of flowers.
The center part of the flower Filled the pistil. It is made up of stigma style and ovaries.
The five main parts of the flower are Stigma, Stamen, Calyx, Pistil, Colas.