
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 3 Jan 2025, 17:58 IST
Human Brain Diagram Class 10 Biology: The human brain serves as the command center of the nervous system and is an intricate organ responsible for controlling various bodily functions and cognitive processes. Understanding the labeled diagram of the human brain is essential for excelling in class 10 examinations.
When it comes to studying the brain, it’s a fascinating subject in biology. In this article, we’ll see some easy steps of Human Brain Diagram Class 10, breaking it down into easy-to-understand bits.
The human brain is one of the most intricate and fascinating organs in the body, responsible for controlling everything we think, feel, and do. At first glance, its structure may seem complex, but breaking it down simplifies its understanding. In this article we will have a look
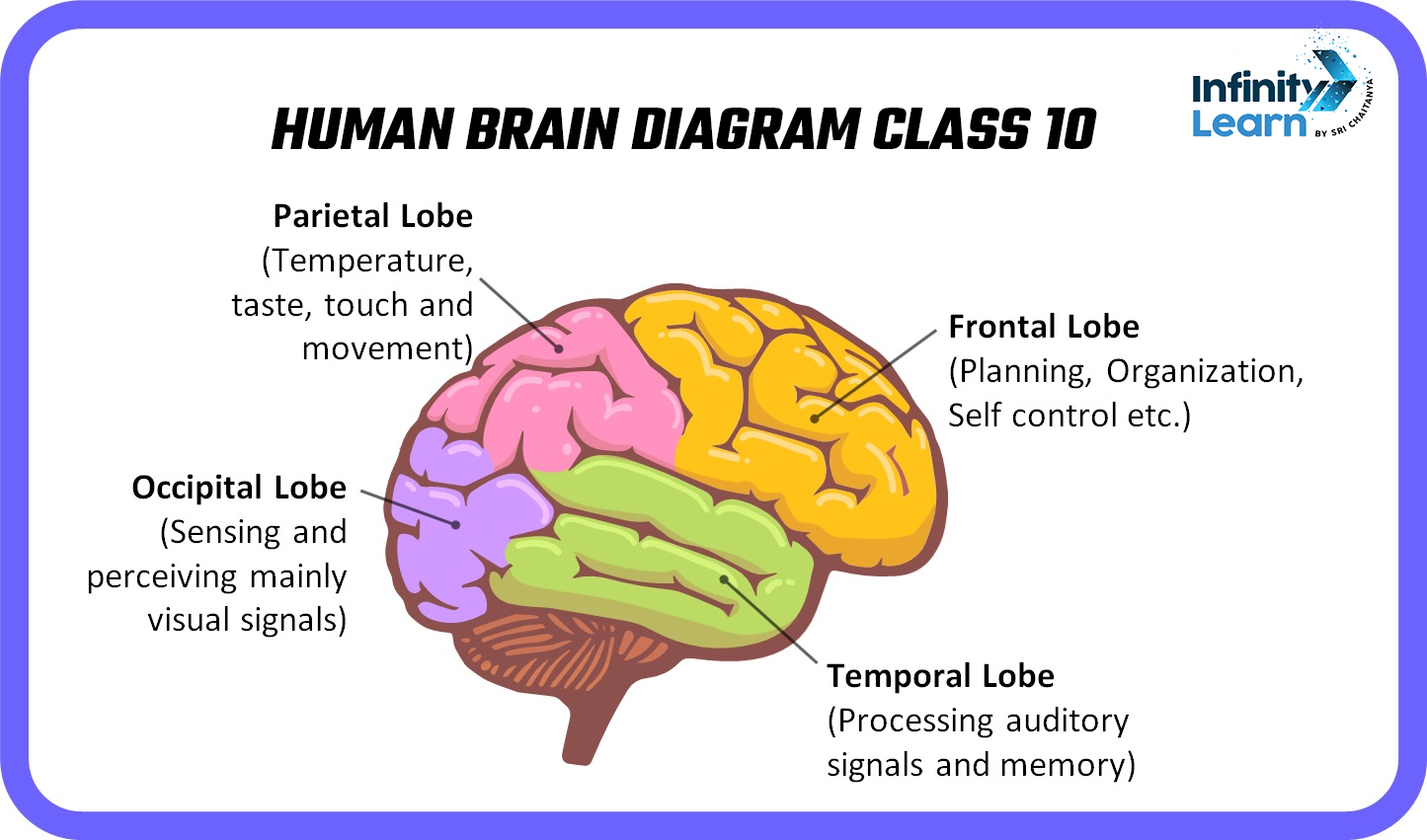
A human brain diagram serves as a visual representation of the brain’s structure, depicting its various parts and functions. Typically, it’s divided into different regions, each with specialized roles that contribute to overall cognition, behavior, and bodily functions.
The human brain comprises three primary sections: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain, each composed of various smaller components.
1. Forebrain:
Also known as the prosencephalon, the forebrain encompasses crucial regions such as the cerebral hemispheres, thalamus, and hypothalamus, playing a pivotal role in functions like learning and emotion regulation. Further divided into the diencephalon and telencephalon, it includes structures like the olfactory system, optic nerves, and cranial nerves.
The cerebrum, the largest section of the brain, is primarily responsible for housing crucial components like the cerebral cortex and subcortical elements. Distinct lobes—frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal—divide it, each bearing its own set of functions such as speech, vision, and auditory processing.

2. Midbrain:
Referred to as the mesencephalon, the midbrain, though small, is significant, situated between the cerebral cortex and hindbrain. It comprises the tectum, cerebral peduncle, and substantia nigra, among others, governing functions like hearing, vision, and body temperature regulation. The substantia nigra, housing dopamine-producing neurons, is associated with Parkinson’s disease.
3. Hindbrain:
Known as the rhombencephalon, the hindbrain, located at the bottom rear of the brain, includes the cerebellum, pons, and medulla. The cerebellum, second in size, coordinates voluntary movements and maintains balance. The medulla oblongata regulates autonomic functions like breathing and heart rate, while the pons acts as a relay between different brain regions, controlling sleep cycles and facilitating sensory experiences.
The human brain serves as the central hub for processing information and orchestrating the body’s functions, acting as a sophisticated ‘command and control system’. It regulates both voluntary actions, such as movement, and involuntary processes like those of the lungs, heart, and kidneys.
In addition to these vital functions, the brain also manages:
Here’s a simplified overview of the parts of the human brain:

The human brain comprises three main parts: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain includes the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus. The midbrain coordinates sensory information and motor responses, while the hindbrain consists of the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata, regulating vital functions like breathing and coordination.
The brain functions by receiving and processing sensory information, coordinating motor responses, regulating bodily functions, and controlling emotions and thoughts. Neurons, the brain's nerve cells, transmit electrical signals, enabling communication between different parts of the brain and the rest of the body.
To draw a simple brain diagram, start by outlining the basic structure of the brain, including the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. Then, add details such as the lobes of the cerebrum, the brainstem's components (medulla, pons), and the cerebellum's distinctive shape.
The three main functions of the brain are sensory processing (receiving and interpreting sensory information), motor coordination (controlling muscle movements and responses), and regulation of vital functions (such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion).
The hindbrain, consisting of the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata, regulates essential bodily functions like breathing, heart rate, and coordination of voluntary movements. It also helps maintain balance and posture.