
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 4 Dec 2024, 18:05 IST
Identification of Primary Alcohol: These alcohols are water derivatives in which one of the hydrogen atoms is replaced by an alkyl group, which is an organic structure is commonly indicated by the symbol R. Alcohol is also available in a variety of shapes and forms. Fundamental alcohol is one in which the hydroxyl group is attached to a single carbon atom. It’s also referred to as a molecule with a “–CH2OH” group. Secondary alcohol, on the other hand, has the formula “–CHROH,” while tertiary alcohol has the formula “–CR2OH,” with “R” indicating a carbon-containing group. Ethanol and 1-butanol are examples of main alcohols. Methanol is also considered primary alcohol by most people.
Also Check: Algae -Important Topic Of Biology NEET 2025
Alcohols are classified according to whether or not they have a hydroxyl group connected to them. The physical and chemical properties of any alcohol are affected by the placement of this hydroxyl group. There are three different kinds of alcohol. Alcohols are divided into three categories: primary, secondary, and tertiary.
The hydroxyl group is classified according to where an alkyl group’s carbon atom is connected to the hydroxyl group. At room temperatures, the majority of alcohols are described as colourless liquids or even solids. Alcohols with a low molecular weight are considered to be highly soluble in water, while those with a higher molecular weight become less soluble and have higher vapor pressures, boiling temperatures, densities, and viscosities.
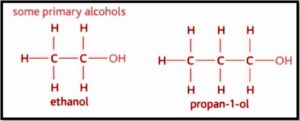
The primary alcohol is the one in which the hydroxyl group’s carbon atom (OH) is connected to only one alkyl group. Methanol (propanol), ethanol, and other main alcohols are examples. The intricacy of this alkyl chain has nothing to do with the classification of any primary alcohol. The fact that there is just one link between the –OH group and an alkyl group classifies every alcohol as a primary.
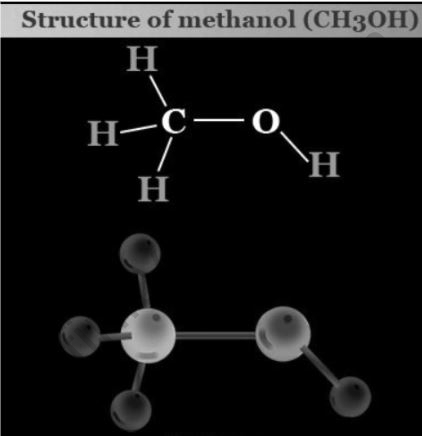
CO + H2 (synthetic gas) = CH3OH (Methanol) (in the presence of catalyst)
Also Check: Elementary Idea of Quaternary Structure of Proteins

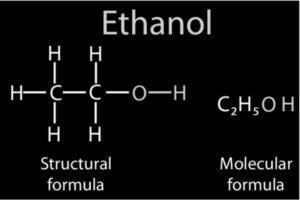
Since prehistoric times, ethanol (ethyl alcohol) has been created primarily through the fermenting of fruit juices. The matured juice could be stored in a closed container throughout the winter, and this rudimentary wine was safe to drink.
The sugars and starches that are broken down into simpler chemicals during fermentation might come from a variety of places. Grain alcohol refers to ethanol that is manufactured from grains such as corn (maize), wheat, rye, and barley.
The grain is boiled in water to make the mash, which is then fermented with malt (sprouted barley) to make the wort. Malt contains diastase, an enzyme that transforms starches in grains to sugar maltose.
C6H12O6 (glucose) with zymase enzyme = 2CH3CH2OH + 2CO2
Because higher alcohol concentrations are hazardous to yeast cells, fermentation creates a solution that is only approximately 12–15 percent alcohol. However, this solution could be distilled to increase the ethanol level to up to 95%.

Alcohol could be used in a range of methods.
The Identification of Primary Alcohol of alcohol is the subject of science. The NEET test covers these districts. They’re covered all around in the NCERT science understanding material, which was developed expressly for the NEET test.
Students can find out concerning such thoughts as well as the surmising of a couple of plans associated with them by visiting the infinity learn site. In the segment’s exercises, there are moreover unique issue issues to help you practice and get the topic’s application. Students can in like manner focus on other distributers’ science understanding material.
Primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols can be identified using a variety of methods. In organic chemistry, the diverse features of alcohol types can be utilized to distinguish the different forms of alcohol. Other qualitative tests, as well as alternative instrumentation analysis techniques, such as nuclear magnetic resonance, can be performed (NMR). Alcohol can be detected by combining these assays, just like ketones and aldehydes.
The majority of common alcohols are colourless liquids at room temperature. Ethyl alcohol, methyl alcohol, and isopropyl alcohol all have fruity scents. The majority of higher alcohols are greasy in texture and have a pronounced fruity fragrance. Alcohols with four to ten carbon atoms have a viscosity of four to ten.
Alcohol is an acidic substance. Metals like sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium react with it. A hydroxyl group has a polar connection between hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The primary state of alcohol is more acidic than the secondary and tertiary stages.