
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 24 Jul 2025, 13:02 IST
Class 9 Science is an exciting subject that covers various topics like physics, chemistry, and biology. It helps students understand the natural world and the laws that govern it. One essential aspect of learning science is understanding and drawing diagrams. Diagrams play a crucial role in helping students visualize concepts and understand complex scientific ideas. In this blog, we will discuss the importance of diagrams in Class 9 Science and the list of important diagrams for Class 9 Science students.
Class 9 Science is a foundational course that introduces students to basic scientific concepts. It covers a wide range of topics, including physics, chemistry, and biology. The goal of Class 9 Science is to lay a strong foundation for students to understand more advanced scientific concepts in higher classes. It helps students understand the natural world and the laws that govern it.
Diagrams in Class 9 Science play a crucial role in helping students visualize and understand complex scientific concepts. They are visual representations of scientific ideas and processes, making it easier for students to grasp the subject matter. Diagrams are used to illustrate various topics in physics, chemistry, and biology, such as the structure of atoms, the human digestive system, the water cycle, and much more. By studying and drawing diagrams, students can gain a deeper understanding of the natural world and its workings.
Here are some key reasons why diagrams are important in Class 9 Science:
Also Check: CBSE Notes Class 9
Below is a list of the important diagrams for Class 9 Science. These diagrams are essential for understanding key concepts in Class 9 Science and are often included in exams and textbooks. Mastering these diagrams can help students excel in their science studies.
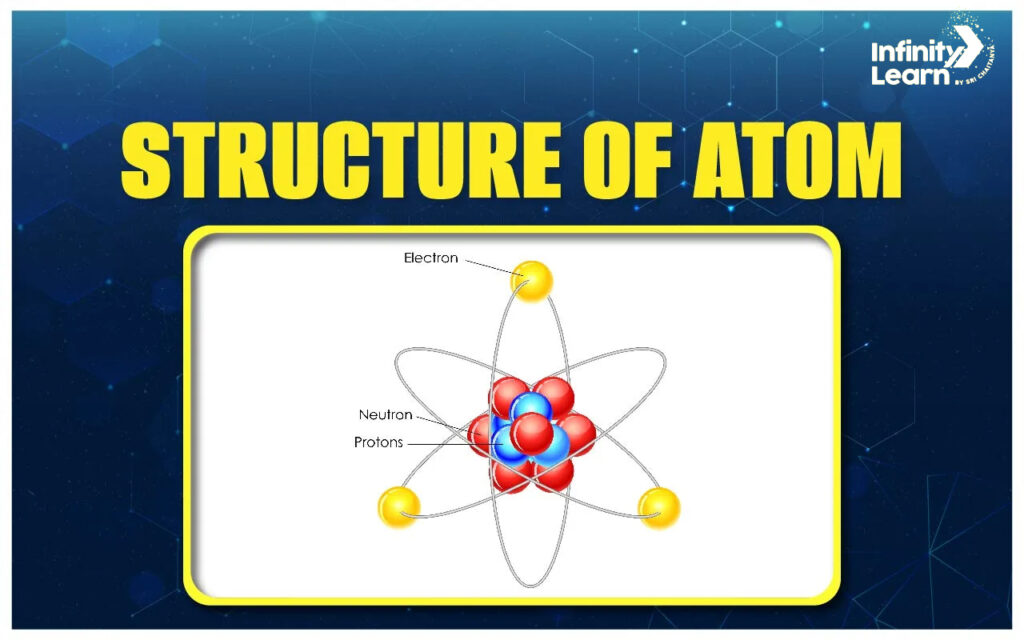
1. Structure of an Atom: The structure of an atom consists of three main components: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus at the center of the atom, while electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels or shells. The number of protons determines the element’s identity, while the number of neutrons and electrons can vary, forming different isotopes and ions.

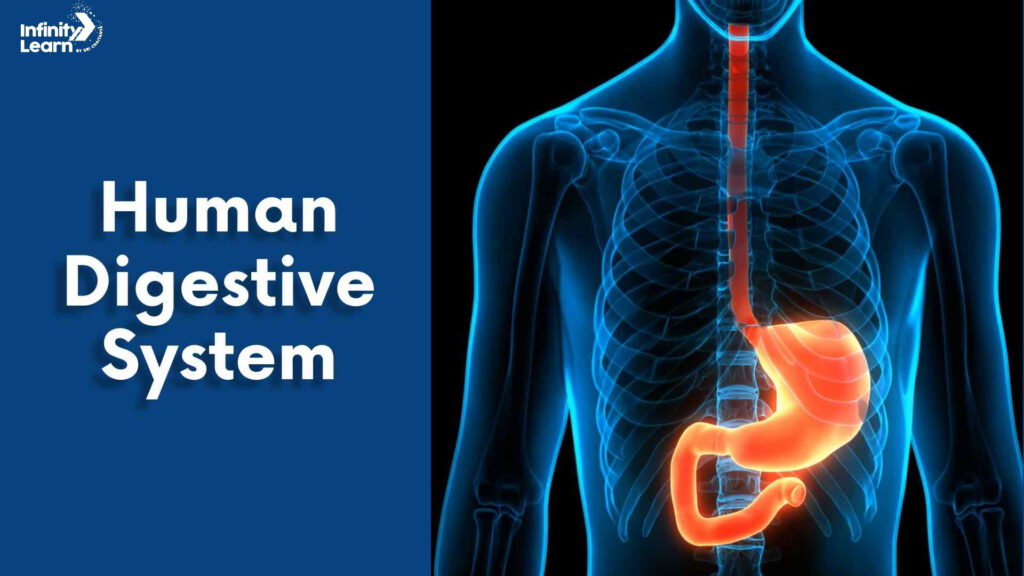
2. Human Digestive System: The human digestive system is a series of organs that work together to break down food into nutrients that can be absorbed by the body. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. Each organ has a specific role in the digestion process, such as breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste.

JEE

NEET

Foundation JEE

Foundation NEET

CBSE
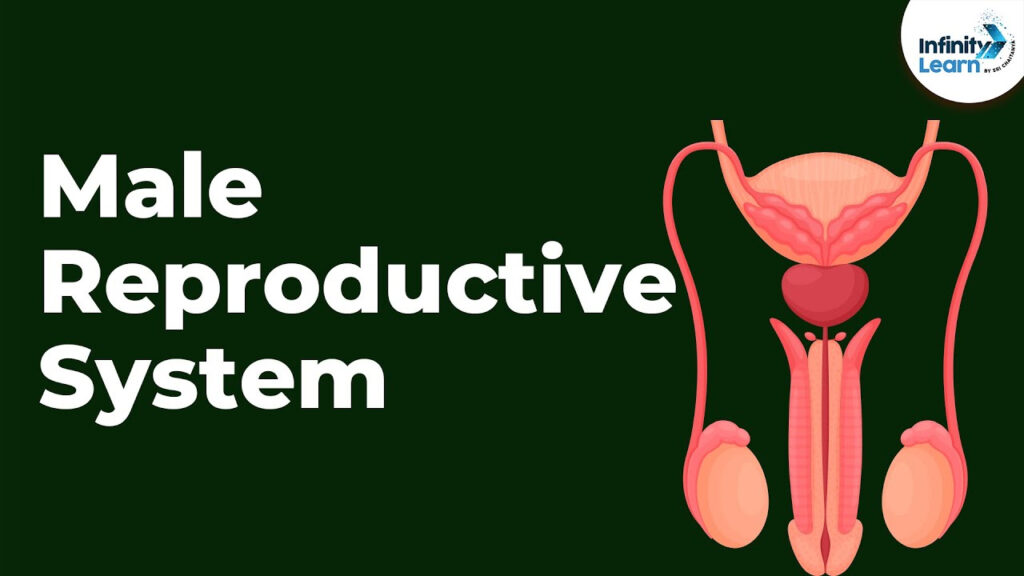
3. Male Reproductive System: The male reproductive system consists of organs that work together to produce and deliver sperm. It includes the testes, where sperm is produced, the epididymis, where sperm is stored and matures, the vas deferens, which carries sperm from the epididymis to the urethra, and the penis, which delivers sperm to the female reproductive system during intercourse.
4. Female Reproductive System: The female reproductive system is responsible for producing eggs, receiving sperm, and nurturing a developing fetus. It includes the ovaries, where eggs are produced, the fallopian tubes, which carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus, the uterus, where a fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus, and the vagina, which receives sperm during intercourse.

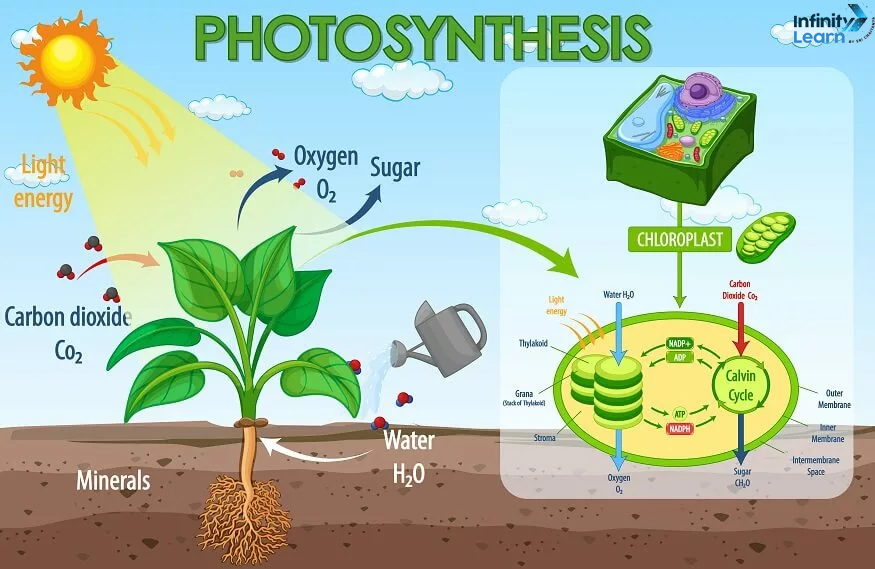
5. Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose. It takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells and involves the absorption of light by chlorophyll, the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, and the release of oxygen as a byproduct.

6. Cell Structure: Cells are the basic units of life and have a complex structure that allows them to carry out various functions. A typical cell consists of a cell membrane, which encloses the cell and regulates the passage of substances in and out of the cell, cytoplasm, which contains organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum, and a nucleus, which contains the cell’s genetic material.
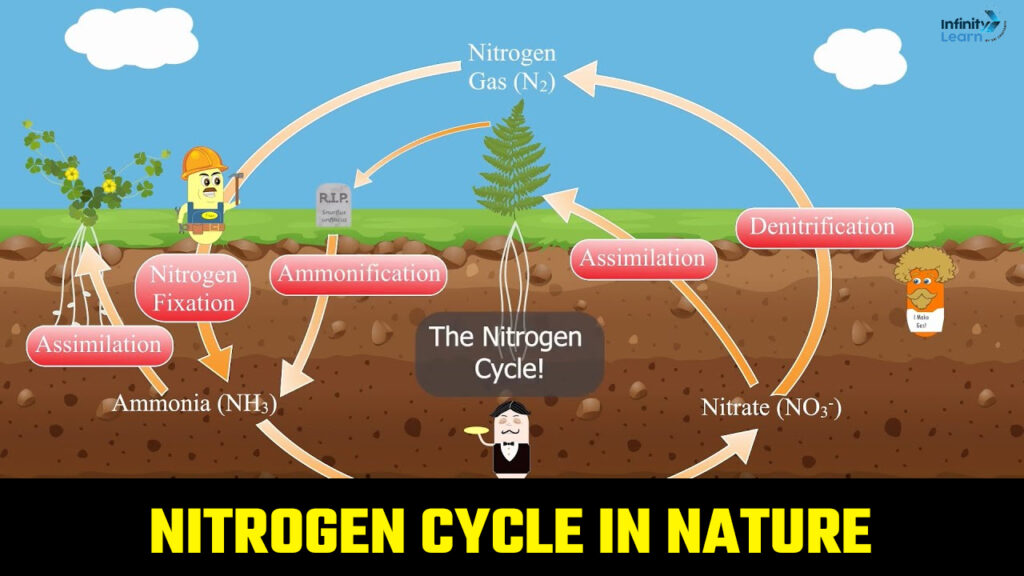
7. Nitrogen Cycle in Nature: The nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen is converted between its various chemical forms in the environment. It involves several steps, including nitrogen fixation, where nitrogen gas is converted into ammonia by bacteria, nitrification, where ammonia is converted into nitrites and then nitrates by other bacteria, and denitrification, where nitrates are converted back into nitrogen gas by denitrifying bacteria.
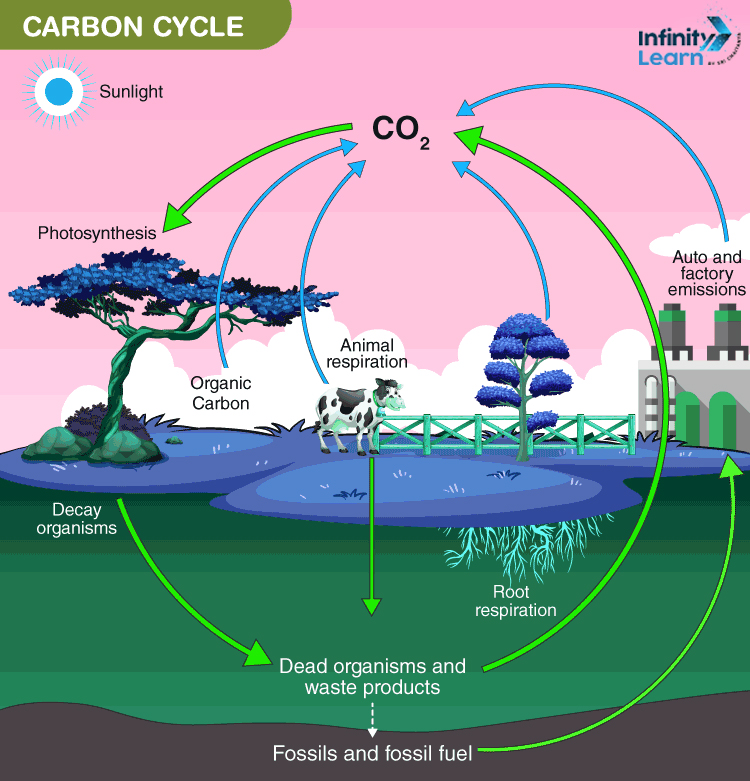
8. Carbon Cycle: The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon is exchanged between the atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living organisms. It involves several processes, including photosynthesis, where plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into glucose, respiration, where living organisms release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere, and decomposition, where dead organisms are broken down, releasing carbon back into the soil.
In conclusion, diagrams are an essential part of learning Class 9 Science. They help students understand complex concepts and retain information better. By mastering the top 10 must-know diagrams, students can enhance their understanding of science and excel in their studies.
The importance of chapters can vary for different students. However, chapters like Matter in Our Surroundings, Is Matter Around Us Pure, and Natural Resources are often considered important as they form the foundation for higher classes.
Important diagrams in biology include diagrams of the human digestive system, respiratory system, circulatory system, plant cell, animal cell, photosynthesis, and reproductive systems.
Diagrams in science are visual representations of scientific concepts, processes, or structures. They help in understanding complex ideas and improve retention of information.
Diagrams in physics help visualize abstract concepts, such as forces, circuits, and waves, making it easier to understand and solve problems.
In Chapter 1 of Class 9 Science, Matter in Our Surroundings, important diagrams include the particle arrangement in solids, liquids, and gases, and changes of state.
Important diagrams for Class 9 tissues include diagrams showing different types of tissues like epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue, along with their functions and locations in the body.