
Courses

Nerve: In the peripheral nervous system, a nerve is an encapsulated, cord bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Electrical impulses are transmitted through a nerve. It is the most fundamental component of the nervous system. The electrochemical nerve impulses known as action potentials are transmitted down each of the axons to peripheral organs or, inside the case of sensory neurons, from the periphery back to a central nervous system, via a nerve. Within the nerve, each axon is an outgrowth of a single neuron, along with many other supporting cells like Schwann cells, which wrap the axons with myelin.
The epineurium, a thick sheath of connective space that covers each nerve, defends it from the environment. A layer of fat cells called the perineurium lies beneath this, forming a full sleeve around the bundle of axons. The nerve is divided into multiple bundles of fibers by perineurial septae, which extend into it. The endoneurium surrounds each such fiber. From the surface of the spine to the level where the axon synapses including its muscle fibers or ends in sense receptors, this forms an unbroken tube. The endoneurium is made up of a glycocalyx inner sleeve and a fine meshwork of collagen fibers on the outside. Because the neurons in a nerve have a lot of energy, they are bundled and commonly travel alongside blood vessels.
Molecules cannot penetrate the bloodstream into the endoneurial fluid as a result. The proportion of endoneurial fluid at the site of nerve irritation (or injury) may grow throughout the development of nerve edema. Magnetic resonance neurography (MR neurography) can detect this rise in fluid and hence diagnose nerve discomfort and/or damage.
Nerve cells’ shape, size, and structure are determined by their location and function in the body. The size of nerve cells is usually determined by the length of time that electrical impulses must be conveyed. Our nervous system is made up of nerve cells, which are specialized individual cells. A cell body, an axon, and dendrites are the three elements of every human body neuron. The parts of a nerve cell are as follows:
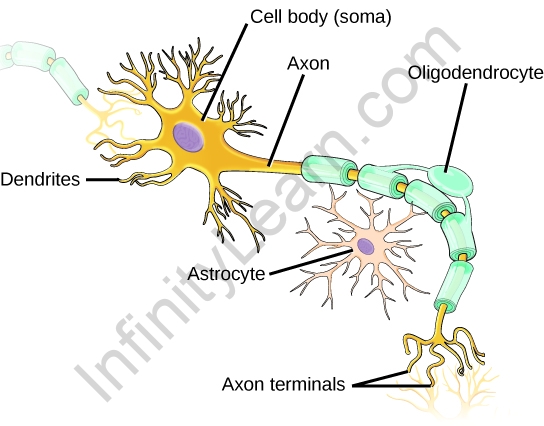
A nerve cell’s core is the cell body. It’s also known as soma. The nucleus of the nerve cell, as well as other specialized cell organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and other components, make up the cell body. A neuron’s cell body contains genetic information and is an important portion of the cell. It also aids in the maintenance of the cell’s general structure that provides energy for the cell’s functions.
An axon is a long tube-like feature that connects the cell body at a certain point in the nerve cell. The axon’s main function is to transfer electrical signals from the cell body to the neuron ending and then pass them to other nearby neurons.
They’re the root-like extensions on a cell’s body that help with message transmission and reception to and from other neurons. The electrical impulses received from the axon ends are processed and sent to the cell body by dendrites.
It is a nerve cell’s outermost layer. Its main job is to protect and coat the nerve fibers in the neurons.
It’s also known as the nerve junction or the termination of the nerve. Its principal role is to allow electrical impulses to pass from one neuron to the next.
Let’s look at the different sorts of neurons now that we’ve looked at the parts and lengths of nerve cells. Neurons can be divided into three categories based on their functions:

Sensory neurons are located in the human body’s sense organs, including the eyes, nose, skin, tongue, and ears. The chemical and physical stimuli of our surroundings, such as sound, heat, and light, activate these nerve cells. Sensory neurons allow sensory impulses to go from the sensory organs to a central nervous system. In the human body, there are around 10 million sensory neurons.
Motor neurons help transmit motor impulses from the central nervous system to various regions of the body. These neurons play an important role in both deliberate and involuntary bodily motions. The motor neurons are predominantly present in the human body’s glands and muscles.
Sensory neurons, motor nerves, and the nervous system all communicate through interneurons. They aid in the transfer of signals in a seamless manner. They aid in the smooth transmission of information between neurons and the central nervous system. Interneurons can be found in every part of the body; however, they are only located in the central nervous system.
Every nerve cell in the human body has one fundamental function: to relay signals. Nerve cells, on the other hand, are involved in various activities:
1) It aids the body’s response to external stimuli.
2) It aids the body’s metabolic operations to run smoothly.
3) It facilitates both voluntary and unintentional movement of body parts.
4) It enables the seamless transfer of messages between the central nervous system and the body parts, which aids communication.
To pass the NEET exam, pupils must have a comprehensive understanding of the entire subject. While all of the chapters are essential, and you should never skip any part of your syllabus, there is a handful that you should pay particular attention to. Because the NEET exam is a major accomplishment in every student’s life, selecting the best study material is crucial. Infinite Learning’s mission is to build confidence in our students. As a result, we designed the biology solutions to answer every question a student might have. Our solutions are in pdf format, so students may access them at any time as well as from anywhere.
Sensory neurons differ from motor neurons in that they have a separate set of functions. Sense neurons transmit electrical impulses or messages from the sensory organs to the central nervous system. The motor neuron, on the other hand, transports electrical signals from the brain system to other regions of the body, including sensory organs. In contrast to the axon of motor neurons, sensory neurons have a shorter axon. Sensory neurons have a single long dendron, whereas motor neurons have several dendrons. The sensory neurons are typically found in the body’s sensory organs. Motor neurons, on the other hand, are predominantly found in glands and muscles.
The nervous system of higher animals is made up of two types of cells: neurons and neuroglia. The main distinction between neurons and neuroglia is that neurons are engaged in nervous system signal transduction, whereas neuroglia is the neurons’ supporting cells.
Nerve cells have two major characteristics: they are responsive and react to various stimuli. It demonstrates conductivity by sending signals from one cell to the next. It is important in the transmission of messages via neurotransmitters.
Nerves transmit signals through electrical impulses called action potentials. These impulses travel along the axon of a neuron, aided by the myelin sheath, which speeds up signal transmission. At the synapse, signals are converted into chemical messages to cross to the next neuron or target cell.
Nerve damage can disrupt signal transmission, leading to symptoms like numbness, pain, weakness, or loss of function in the affected area. Depending on the extent of damage, recovery may occur naturally, or medical interventions like physical therapy or surgery may be needed.