





Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 28 Nov 2024, 12:46 IST
Mitochondria are known as the cell’s powerhouses. They participate in various cell activities such as respiration, differentiation, cell signaling, aging, controlling the cell cycle, cell growth, and other metabolic processes. They are rod-shaped and have a double membrane, found in both plant and animal cells.
The term ‘mitochondrion’ comes from a Greek word meaning threadlike granules, first described by German pathologist Richard Altmann in 1890.
Mitochondria are double-membrane-bound cell organelles found in most eukaryotic organisms. These organelles float freely within the cytoplasm of all living cells.
The diagram of mitochondria is useful for students in classes 10 and 12. It is one of the important topics, often asked in exams, with a high weightage of marks.
Also Check: Diagram of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
Also Check: Paramecium Diagram


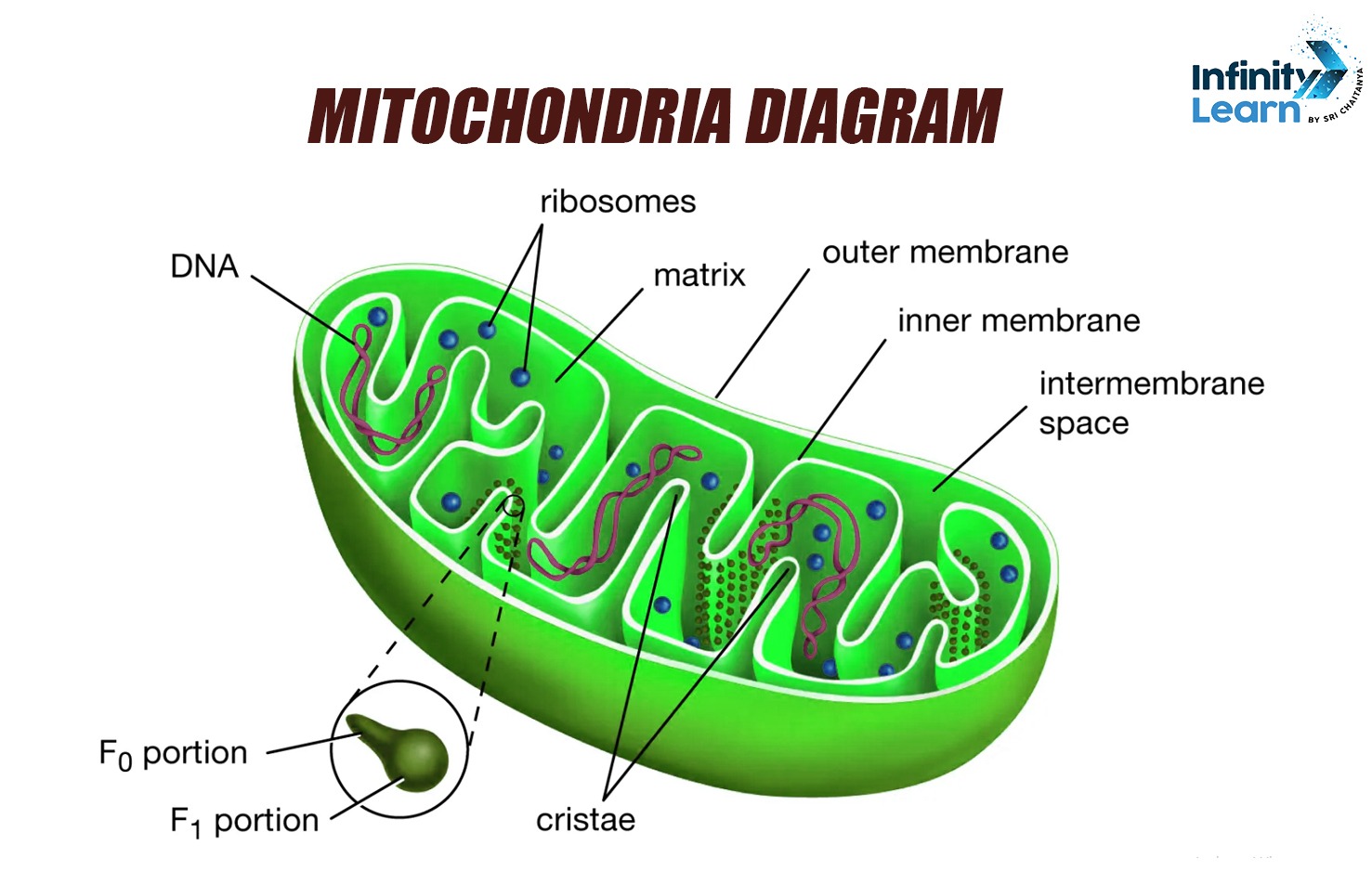
Mitochondria are cell organelles that produce energy. Here’s a simple diagram:
Mitochondria create energy for the cell by converting nutrients into ATP.
The three main parts are the outer membrane, inner membrane, and matrix.
Parts include the outer membrane, inner membrane, and matrix; they produce energy for the cell.
Mitochondria look like tiny, bean-shaped structures inside cells.