
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 4 Dec 2024, 12:41 IST
The Unit of Measure (SI) is a metric unit that is widely used as a measurement standard. In science and technology development, SI units are extremely important. In physics, there are multiple SI units that are being used to express various values. Base units and derived units are two types of units that can be used to classify quantities. To minimize misunderstanding with the units, the SI unit is an international system of measurements that are used internationally in technical and scientific study.
It is critical to have a standard unit system because it allows people all around the world to interpret measurements in one set of units. It is made up of seven base units that define 22 derived units. The SI units can be stated as fractional numbers or as standard multiples. Prefix multipliers with powers of 10 ranging from 10-24 to 1024 are used to define these quantities.
Because they are generated by multiple actions on the base units, the derived units are limitless. The dimensions of derived units are represented in terms of the dimensions of base units. A blend of base and derived units can also be used to express derived units.
These were a few commonly used units, as well as their SI equivalents. Aside from these, there are a few other units that are often used in physics. These are some instances of such units:
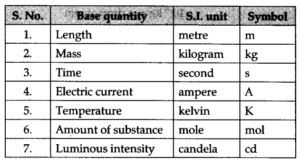
The SI units and Measurements in Physics NEET topics are intended to clarify and present the most likely questions that will occur on the exam. Two of the most pressing concerns are the propagation of errors and the parallax angle method. These can be explained in simple terms utilizing notes from experienced academics in the area, which are available on Infinity Learn online. If students have a thorough comprehension of the concepts presented in all portions of the subject, practicing multiple-choice questions is simple.
Units and Measurements Important NEET questions prepare students to reply to multiple-choice questions, which are common in the necessary test.


We choose many base units for a set of fundamental values in the coherent unit system and derive other units by dividing or multiplying any constant into it, yielding the same numerical and physical units. The whole set of base units are derived units with decimal multiples, and submultiples are referred to as SI units.
Kilometers, meters, and millimeters, for example, are SI units, as are meters per second and millimeters per second. Coherent SI units are “meter” and “meter per second” from this group.
In 1960, the SI unit was introduced.
The following are some of the reasons why the SI system is crucial: