Table of Contents
To know the idea of the coefficient of friction, we should first understand friction, friction force, and friction type. A surface would be classified as frictional if it resists relative motion between two surfaces that are in contact, such as when sliding, rolling, or resting. Friction has been usually caused by rough surfaces. That is, if the surfaces are not designed for motion, the relative motion between them will cause friction. Surface roughness has always been directly proportional to friction. Rougher surfaces seem to be more prone to friction. Surfaces that really are smoother will have less friction than rough ones.
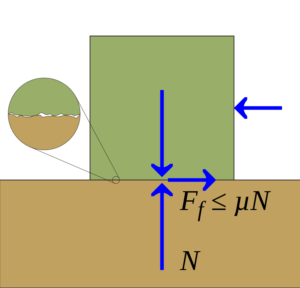
The coefficient of friction is indeed the ratio of the frictional force resisting motion between two surfaces in contact to the normal force pressing the two surfaces together. The Greek letter mu (μ) has been commonly used to represent it. Arithmetically, μ= F/N, in which F represents the frictional force and N represents the normal force.
The coefficient of friction between two surfaces indicates the amount of interaction between the two surfaces in terms of friction. The coefficient of friction value determines surface roughness. Whenever an object under observation is subjected to the normal force acting on it, friction occurs.
The coefficient of friction varies depending on whether the friction is static or kinetic. In static friction, the frictional force withstands the application of force to an object, and the object remains at rest until the force of static friction is overcome. Whereas In kinetic friction, the frictional force endures the motion of an object. For just a brick sliding on a clean wooden table, the coefficient of kinetic friction is around 0.5, implying that a force equal to half the weight of the bricks is required just to overcome friction and keep the bricks moving at a constant speed, and the coefficient of static friction is about 0.6. It is clear that the frictional force acts in the opposite direction of the object’s motion.
Dimensional Formula of Coefficient of Friction
The dimensional formula of coefficient of friction can be represented as:
[M0 L0 T0]
Here,
M = Mass
L = Length
T = Time
Derivation:
We have, Coefficient of friction (μ) = Frictional Force × [Normal Force]-1 . . . . (1)
As because, Force (F) = Mass × acceleration = Mass × velocity × [Time]-1
Similarly, velocity = Displacement × [Time]-1
Therefore, the dimensions of Force = [M] × [LT-1] × [T]-1 = [M1 L1 T-2] . . . . (2)
Now, when substituting equation (2) in equation (1) we get,
Coefficient of friction (μ) = Frictional Force × [Normal Force]-1
That is, μ = [M1 L1 T-2] × [M1 L1 T-2]-1 = [M0 L0 T0].
Thus, the coefficient of friction has been dimensionally represented as [M0 L0 T0].
Also read: Dimensions of Charge
FAQs
What do you mean by friction?
An external force trying to oppose the relative motion of two surfaces causes friction. The friction between the two substances occurs at the point of contact. The movement of one object relative to another is referred to as relative motion.




