Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Asexual Reproduction
- Vegetative Propagation
- Stems
- Suckers
- Leaves
- Bulbs
- Tubers
- Summary
- What’s Next?
In the previous segment, we learnt about Reproduction and its types. In this segment, we will learn about vegetative propagation
What is Asexual reproduction?
- The reproduction that Does Not Involve Gametes is called asexual gametes.
- In asexual reproduction, a part of the parent body is capable of developing into a new organism.
- There are four types of asexual reproduction in plants: vegetative propagation, fragmentation, budding, and spore formation.
What is Vegetative propagation?
Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction, where a vegetative part of the plant gives rise to offspring.
The five major parts of the plants that are used for vegetative propagation are stems, sucker, leaves, bulbs, and tubers.
Stems
Stems of the plants can give rise to new plants with the help of two structures: stolons and rhizomes.
Stolons
-
-
- Stems of the plants have structures called Stolons or Runners.
- Stolons run along the ground and can develop roots which help in the formation of a new plant.
-

Stolon
– For example, strawberries and silverweed reproduce through stolons.
Rhizome
-
-
- The rhizome is a Horizontal Stem, but it grows underground.
- It is capable of giving rise to new roots below it and even shoots above the surface of the soil.
-

Suckers
Rhizome
For example, ginger and turmeric reproduce through rhizomes.
-
- Suckers are the Extensions or Growths that arise from the base of the stem.
- These extensions can develop roots and shoots, giving rise to a new plant.
For example,
The new banana tree grows attached to the older one because the parent tree develops suckers that further develop roots and shoots to form a completely new plant.
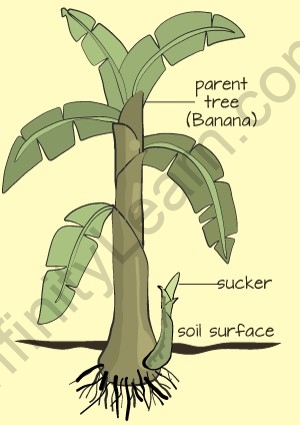
Sucker
Leaves
-
- The leaves are the part of the plant that are primarily responsible for photosynthesis. But in certain cases, they help in vegetative propagation.
For example,
Bryophyllum is the plant that has leaves which bear extremely small plantlets in the fringes or the margins of the leaves. When the leaves fall off, the plantlets firmly root themselves and can develop into new plants.







