Table of Contents
There are a variety of medical conditions that you may not have the option to detect if they occur to you. A cough or fever is noticeable, as the pain is associated with a stomach ache after a lousy party. However, something like tetany can throw people tp who don’t have a normal feeling – and even doctors take time to process the problem. Tetany involves excessively stimulated neuromuscular movements.
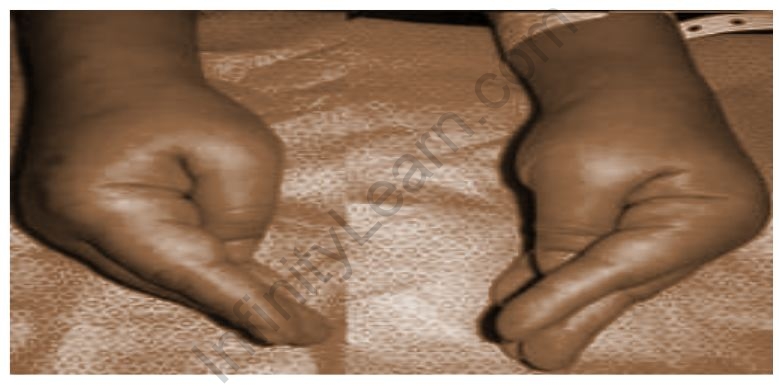
Tetany is a condition that occurs due to low blood calcium (hypocalcemia) and is characterized by tingling in the hands and feet, cramps, palpitations, and overactive nerves. Tetany is generally considered to be the result of very low calcium levels in the blood. Tetany may also be the result of a decrease in the ionized portion of plasma calcium without marked hypocalcemia, similar to the case of dangerous alkalosis.
What causes tetany?
- Parathyroid hormone deficiency. Your parathyroid is a small organ in the back of the thyroid that releases a chemical or parathyroid hormone. This hormone helps regulate calcium levels between your blood and bones. Without adequate parathyroid chemicals, your calcium levels may drop.
- Parathyroid organs can be injured as a result of thyroid surgery or infection – when your unaffected system attacks your organs or your calcium-sensitive proteins.
- High parathyroid chemicals. Your parathyroid can bring a lot of parathyroid chemicals, which can cause calcium problems. Undeniable levels can be made.
- Ongoing kidney disease
- Insufficient vitamin D – because you did not get enough sunlight or you have kidney or liver disease
- Pseudoparathyroidism – a genetic condition that causes your body to resist the parathyroid hormone
- Idiopathic pseudoparathyroidism – in which parathyroid organs are missing or dying
There are a few different causes of hypocalcemia.
What are the possible causes of hypocalcemia or tetany?
Degree of parathormone-Parathormone (PTH) hormone produced by the parathyroid organ. PTH strength is related to serum calcium levels by maintaining its effect on bones, kidneys, and the digestive system. In fact, its main function is to increase the levels of calcium in the plasma.
Initially, calcium absorbs or activates calcium from the bones to the plasma.
In addition, it can increase the retention of calcium present in food through the digestive tract to build up calcium in plasma.
Finally, it can increase plasma calcium levels through the regeneration of calcium from the kidney tubes and increase the levels of calcium in the blood plasma and reduce urination.
Accidental parathyroid injuries, immune problems, congenital malformations can also cause a decrease in PTH secretion.
- Low levels of vitamin D can cause hypocalcemia like vitamin D.
- Lower degrees of magnesium-As magnesium is very important in the synthesis of PTH.
Alkalosis – Increased blood pH causes egg whites, blood proteins, to bind free calcium to plasma. This results in reduced access to free calcium particles. Severe alkalosis may cause tetany. Alkalosis can also be caused by continuous vomiting (loss of stomach acids), increased intake of antacid foods, and so on.
Clostridium tetani is a bacterium that causes Tetany disease. Clostridium tetani invade the body and produce a neurotoxin that blocks the arrival of ‘synapses’. This can trigger extended muscle tone and muscle spasms. Such an infection is called a lockjaw (jaw spasming sickness)
Hypokalemia – This refers to the correction of reduced potassium (K +) in the blood. As we probably know, potassium is essential for the regeneration of nerve cells, a decrease in potassium levels can cause a different sign of tetany.
Also read: Important Topic of Biology: Muscular Dystrophy
Examples of Tetany
Low blood protein levels, septic shock, and blood transfusions can also contribute to lowering calcium levels in the blood. Sometimes, toxins can cause tetany. Another example is botulinum toxin found in a variety of contaminated foods or microorganisms in the soil that enters the body through wounds or bruises. Two types of tetany are visible: manifest and latent (spasmophilia). Previously, due to hypocalcemia, it is usually uncommon and often after surgery (parathyroid tetany), while the most common latent form of tetany or spasmophilia involves excessive ventilation and magnesium deficiency. Unconscious tetany is especially prevalent among young women. There are many symptoms of spasmophilia, but they are not clear, so this pathology is difficult to diagnose.
How is tetany treated?
Your doctor will determine the cause of the tetany, giving them the ability to treat the condition at its source.
In the meantime, the goal of treatment is to address inequality. This may include enrichment with calcium or magnesium, for example. Incorporating calcium directly into the circulatory system is a well-known method. In any case, oral calcium intake (and kit D for preservation) may be necessary to prevent a recurrence.
When a doctor finds out what was the basis for tetany, they may consider additional physical therapies. For example, it is thought that cancer in the parathyroid should be flawed, not directly removed.
Occasionally, for example, kidney disease, further treatment with calcium supplements may be needed to diagnose the condition that led to tetany.



