Table of Contents
Introduction: Biosynthetic Phase of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which autotrophs convert light energy into chemical energy, later used to stimulate cellular activity. Chemical energy is stored in sugar, which is formed from water and carbon dioxide.
Photosynthesis means that this process occurs in chloroplasts only through photosynthetic compounds such as chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotene, and xanthophyll. All green plants and a few other autotrophic species use Photosynthesis to synthesize nutrients through carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight. The product of the process of Photosynthesis is oxygen. Let’s take a closer look at the process, reaction, and importance of Photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis also applies to other organisms besides green plants. These include several prokaryotes such as cyanobacteria, purple bacteria, and green Sulphur bacteria. These organisms depict Photosynthesis like green plants. Glucose produced during Photosynthesis is then used to ignite various cellular functions. The product of this physio-chemical process is oxygen.
Algae also use Photosynthesis to convert solar energy into chemical energy. Oxygen is released as a product, and light is considered a significant factor in completing the photosynthesis process.
Photosynthesis occurs when plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen. The leaves contain cellular organelles called chloroplasts.
Each chloroplast contains a green pigment called chlorophyll. The chlorophyll molecules absorb light energy while carbon dioxide and oxygen enter the tiny stomata cavities in the leaf epidermis.
Another product of Photosynthesis is sugar, such as glucose and fructose.
The sugar is then transferred to the roots, stems, leaves, fruit, flowers, and seeds. In other words, this sugar is used by plants as a source of energy, which helps them to grow. These sugar molecules combine with other complex carbohydrates such as cellulose and starch. Cellulose is considered a structural element used in the walls of plant cells.
Photosynthesis process
At the cellular level, the process of Photosynthesis takes place in cell organelles called chloroplasts. This organelle contains a green pigment called chlorophyll, which is responsible for the green color of the leaves.
As already mentioned, Photosynthesis takes place in the leaves, and specialized cell organelles responsible for this process are called the chloroplast. Structurally, the leaf covers the petiole, epidermis, and lamina. Lamina is used to absorb sunlight and carbon dioxide during Photosynthesis.
Steps in Photosynthesis:
During the process of Photosynthesis, carbon dioxide enters through the stomata; water is absorbed by the root hairs from the soil and transported to the leaves by xylem vessels. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy from the sun to separate water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
Hydrogen from water molecules and carbon dioxide absorbed into the air is used to produce glucose. In addition, oxygen is released into the atmosphere by leaves as pollutants.
Glucose is a source of nutrients for plants that provide growth and development; some are stored in roots, leaves, and fruits for later use.
Pigments are part of basic Photosynthesis. Cells give color, absorb light at a certain wavelength, and repel light that is not absorbed. All green plants mainly contain chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoids in the thylakoid of chloroplasts. It is primarily used to absorb light energy. Chlorophyll-a is the primary color.
The process of Photosynthesis takes place in two stages:
- Light-based reactions or light reactions
- Light independent reaction or dark reaction
Light Photosynthesis (or) Light-based reaction
Photosynthesis begins with the reaction of light produced only during the day when there is sunlight. In plants, light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid layer of chloroplasts.
Grana membrane-bound sacs are located within the thylakoid function by collecting light and are called photosystems.
These photosystems have large pigment compounds, and protein molecules present within plant cells, which play a key role during the process of Photosynthesis.
There are two types of image systems: image system I and image system II.
Under light-dependent reactions, light energy is converted to ATP and NADPH, which are used in the second phase of Photosynthesis.
During light reactions, ATP and NADPH are produced by two electron-transport chains, water is used, and oxygen is produced.
The chemical equation in Photosynthesis can be reduced to:
2H2O + 2NADP + + 3ADP + 3Pi → O2 + 2NADPH + 3ATP
Dark Photosynthesis (or) Independent Light Reaction of Light
The black reaction is also called a carbon-fixing reaction.
It is an independent light process in which sugar atoms are formed in water and carbon dioxide molecules.
Dark reactions occur in the chloroplast stroma using NADPH and ATP light reaction products.
Plants emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere through the stomata and proceed to the Calvin photosynthesis cycle.
In the Calvin cycle, ATP and NADPH formed during light reactions triggering reactions and converting 6 carbon dioxide molecules into one molecule of sugar or glucose.
The chemical equation of the black reaction can be reduced to:
3CO2 + 6 NADPH + 5H2O + 9ATP → G3P + 2H + + 6 NADP + + 9 ADP + 8 Pi
Biosynthetic phase of Photosynthesis
The biosynthetic process of Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplast stroma. Light from the sun does not include this function. In this process, with the help of hydrogen ions formed during light-based Photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is reduced to sugar. ATP and NADPH are used in food synthesis in the biosynthetic process of Photosynthesis. CO2 is concentrated to create the effect of CO2 fixation.
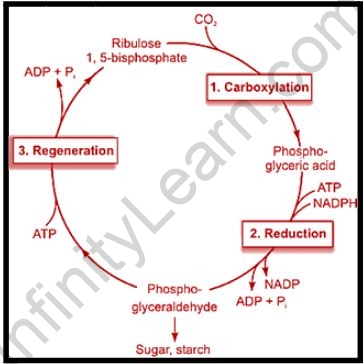
The cycle begins when carbon dioxide from the atmosphere reaches the plant cells. The first reaction creates an enzyme called rubisco, which binds CO2 to a specific 5-carbon molecule called ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP). A 6-carbon molecule is formed by this reaction, which then divides into two 3-carbon molecules. The carbon sequestration is called the cycle phase. This means that, like sugar, inorganic carbon is converted into living molecules.
Additional Information:
With biosynthesis or dark phases, there are two major mechanisms; the Calvin cycle and the C4 dicarboxylic acid cycle. CAM metabolism is the third method and is the link between the two methods. The plants with the Calvin cycle and the C4 dicarboxylic acid cycle are called C3 and C4 plants, respectively.
Note: – Light reaction cannot occur in the absence of light. It is noteworthy that even the biosynthetic process stops (albeit temporarily) after some time. This indicates that it indirectly depends on light and requires continuous light reaction products.
Biosynthetic Phase of Photosynthesis FAQs
What is Photosynthesis? Describe the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the biological process used by all green plants to combine their nutrients. The process of Photosynthesis requires solar energy, water, and carbon dioxide. The product of this process is oxygen.
How much is Photosynthesis?
During photosynthesis, oxygen gas is released into the environment and used by humans, animals, and other living things during the respiratory system.
List the factors that influence Photosynthesis.
There are several factors that affect the quality of Photosynthesis. Light energy, water, soil pH, carbon dioxide saturation, temperature, and other weather conditions are all factors that affect the level of Photosynthesis.
What are the different stages of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis occurs in two phases, namely light-based reactions, and independent light-response. Light-dependent reactions are also called light reactions and occur during the day. An independent reaction of light is also called a black reaction or a Calvinist cycle.
What is Calvin's cycle?
Calvin's cycle is also called a light-independent reaction. The complete Calvinist cycle occurs in the chloroplast stroma.







