Table of Contents
Frame of Reference
A frame of reference, or reference frame, is a perspective that one uses to determine if an object is moving. A frame of reference consists of an object or terrain that’s considered to be stationary. Generally, the bystander is at rest in the reference frame; in this environment, the term is” experimental frame of reference.”
For illustration, when you see a ball roll down a road, you can tell the ball is moving because the frame of reference is the thoroughfares, whatever may be on the side of the roads, or the Earth. All of these are frames of reference.
All measures of stir will be compared to a frame of reference. Thus, the most generally used frame of reference is Earth itself, indeed though it moves. Stars are used as a frame of reference when agitating the movements of the Earth.
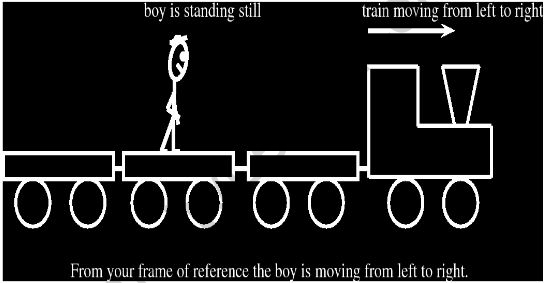
When we walk from one side of a boat to the other, our frame of reference is the boat; whether the boat is moving doesn’t apply to that frame of reference.
Various units of frame of reference of physics-related articles are available here. There are many materials and quantities in physics. Distinct units can be used to express different quantities in physics. Students who want to flourish in physics need to be fluent in measurement and want to learn about references caused while measuring can get complete knowledge from this article. The comprehensive unit of frame of reference is provided here to assist students in effectively understanding the respective topic. Continue to visit our website for additional physics help.
Overview
The frame of reference consists of an abstract match system and the set of physical reference points that uniquely fix the match system and regularise measures within that frame.
Types of frame of reference
Inertial Frame of Reference
- Non-inertial Frame of Reference
- Inertial Frame of Reference
An inertial frame of reference
An inertial frame of reference is a frame where Newton’s law holds. That means if no external force is acting on a body, it’ll stay at rest or remain in an invariant stir. The term inertial frame is relative i.e., first, we assume a reference frame to be the inertial frame of reference. So a more general description of an inertial frame would be Inertial frame is at rest or moves with constant haste concerning my assumed inertial reference frame.
Non-inertial Frame of Reference
Now we can define a non-inertial frame as a frame that’s accelerated concerning the assumed inertial frame of reference. Newton’s law won’t hold in these frames. So in the below illustration, if I assume Earth to be an inertial reference frame, the moon becomes an anon-inertial reference frame as it’s in accelerated stir concerning the Earth.
Frame of Reference
In the proposition of reciprocity, the stir of a body is measured concerning a matching system called frame of reference. This is described below.
When someone says the machine is moving, we’d be certain that what’s being described is a change of position of the machine concerning the Earth’s face or any object (s) which is (are) fixed to the Earth. We accept the original surroundings-a collection of objects attached to the Earth and thus at rest relative to each other as our frame of reference.
A frame of reference is a well-defined match system, and concerning this, the state of rest or the stir of a body is described.
- Inertial frame of reference A frame of reference in which a body continues to be in a state of rest or a state of an invariant stir if no external force acts on the body is called an inertial frame of reference. Newton’s law obeys this frame of reference, hence it’s also called a Newtonian or Galilean frame of reference. A reference frame moving with invariant stir relative to an inertial frame is also an inertial frame. For illustration, a matching system fixed on the Earth having a spinning stir is an inertial frame of reference.
- A non-inertial frame of reference A frame of reference in which a body is accelerated without applying any external force is called an accelerated or non-inertial frame of reference. A body at rest in an inertial frame of reference possesses acceleration in the non-inertial frame of reference. Newton’s law isn’t applicable in a non-inertial frame of reference.
Inertial Frame and Galilean Metamorphoses
Galilean metamorphoses are used to transfigure many physical amounts similar to position equals, haste, acceleration, time, etc. from one inertial frame of reference to another frame of reference.
Suppose two spectators are observing the series of events similar to the position of the body of mass m as a function of time. One is performing the trial concerning inertial frame x, y, z, and the other bone is in the primed match system X, Y, Z. The primed match system is in relative motion concerning the inertial match system.
Still, if it is constant or in other words, the relative stir of a primed match is invariant. or
Therefore, the acceleration at a flyspeck in inertial frames of reference is the same, indeed if they’re moving with constant haste relative to each other.
The force is the same in both match systems. Therefore the equations of a stir in a system moving slightly concerning inertial systems are identical to those in the inertial system. All systems rephrasing slightly concerning inertial systems are identical. Or Second Law of Motion is steady under the Galilean Transformation.
Of course, the below arguments would be valid only if the relative stir of the primed match system is in no way similar to the haste of light. However, there would be several complications, If the system moves with haste similar to that of light. It would be bandied about later by following Einstein’s special proposition of reciprocity.
Still, also we can write,
If we choose the origin of match systems to coincide at t = 0.
These are known as Galilean metamorphosis
x’ = x – vt,
. y’ = y,
.z’ = z
t’ = t
This set of equations is known as the Galilean Transformation. They enable us to relate a dimension in one inertial reference frame to another.
Non-inertial frame and Fictitious forces
Fictitious force in some textbooks is called inertial force. The fictitious force endured in a slightly accelerating system is invariant and commensurable to the mass of the system, like a gravitational force. The fictitious forces appear from the acceleration of the match system and not due to commerce between bodies.
Galilean Transformation and Velocity of Light
The Galilean metamorphosis successfully explained the invariance of laws of Newtonian mechanics in the different inertial frames. No trial in drugs carried out in a single inertial frame can tell us that our frame is at rest or moving with invariant haste. Let me remind you that our Earth moves with the haste of 30 Km/ sec concerning space in a nearly indirect path around the sun. There’s no favored inertial frame for the laws of mechanics to hold.
According to Maxwell’s electromagnetic theorem, the haste of light in space is a constant and 3×108.
It was believed that light peregrination with below haste in a medium called ether, which is inertial concerning the sun.
According to Galilean metamorphosis (v’= v-V), for a bystander in an S’- frame moving with haste V would measure the haste of light palpitation ranging from c-V to c V depending upon the relative direction of c and V. But according to Maxwell’s equation, the haste of light is constant in space/ vacuum.
Importance of chapter for JEE main, neet, and board exams
The unit plays an important role as it plays a part in daily life too. The reference frame used in dynamics is known as match systems with axes ( lines) expiring from a point known as the origin. The position of a point moving parallel to an aeroplane ( aeroplane stir) can be described by two figures (1) either the distances of the point from two lines at right angles to one another on the aeroplane ( blockish equals) or (2) the length of a line with one end fixed at the origin and the other end at the moving point and the angle that the line makes with a fixed axis ( polar equals). Stir in three confines can be described by three blockish equals or by the length of a line expiring from the origin and two angles ( globular equals); one of these angles is original to degrees of longitude and the other to degrees of latitude. A line from the origin to the point is known as the position vector for the point in all cases. As the point moves, the position vector changes in both magnitude and direction, and the haste of the point is defined in terms of these changes.
FAQs
What is a frame of reference?
frame of reference consists of an object or terrain that's considered to be stationary.
Q.How many types of frames of reference are there?
Ans: There are two types of frames of reference :
: Inertial frames
: Non-inertial frames
How is the frame of reference related to motion?
Stir is defined as a change of position. How we perceive stir depends on our frame of reference. The frame of reference refers to a commodity that isn’t moving with respect to a bystander that can be used to describe a stir.
Does time depend on the frame of reference?
In the Special Theory of Relativity, Einstein determined that time is relative — in other words, the rate at which time passes depends on your frame of reference. The briskly a timepiece moves, the slower time passes according to someone in a different frame of reference.
Who introduced the frame of reference?
This conception of time and simultaneity was latterly generalized by Einstein in his special proposition of reciprocity (1905), where he developed metamorphoses between inertial frames of reference grounded upon the universal nature of physical laws and their frugality of Lorentz metamorphoses).
For more visit Frame of Reference





