Table of Contents
Let’s take a look at the concept of Addison’s Disease. It is a disease of the glands. The adrenal gland’s condition known as Addison’s disorder is a rare but serious condition in which the body fails to produce the essential hormones cortisol and aldosterone. Those with Addison’s disease need treatment instead of living a life.
What is Addison’s disease?
Addison’s disease is characterized by inadequate production of cortisol and aldosterone by the adrenal glands. Cortisol helps the body respond to illness, injury or surgical stress. This affects blood volume and blood pressure by regulating the amount of fluid excreted by the kidneys as urine.
What causes Addison’s disease?
The autoimmune reaction causes Addison’s disease, which occurs when the immune system (which protects it against infection) attacks its organs and tissues. The outer part of the adrenal gland (cortex), where cortisol and aldosterone are produced, is affected by Addison’s disease.
Addison’s gland can also cause:
- Adrenal disease.
- Related infections and fungal infections.
- Amyloidosis is a disease in which amyloid proteins accumulate in the body.
- Errors in the genetic code.
What are the specific symptoms and symptoms of Addison’s disease?
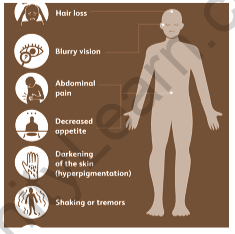
Damage to the adrenal gland accumulates over time and symptoms gradually appear. The symptoms are:
- Abdominal pain
- Abnormal menstrual cycles
- Craving for salty foods
- Dehydration
- Depression
- Uhud
- Annoyance
- Light head or dizziness while standing
- Loss of food
- Low glucose levels
- Blood pressure is low
- Muscle degeneration
- Nausea
- Dark skin spots
- Cold sensitivity
- Vomiting
- Increased fatigue (extreme fatigue)
What is the process of diagnosing Addison’s disease?
Your doctor may use the following tests to determine if you have Addison’s disease:
Physical and History:
Your doctor will review your symptoms and a physical examination will be done. Dark spots on your skin may indicate to your doctor that you should be tested for Addison’s disease.
Insulin Hypoglycemia Testing: Blood tests will be performed by the simulation to detect sodium, potassium, cortisol, and ACTH in the blood. Your doctor may recommend this test if you suspect that you are having a deficiency.
To perform this test, the patient is first given an insulin injection and then tested for glucose and cortisol levels. These tests will show low glucose levels and elevated cortisol levels in anyone who is healthy. If not, one needs to see a doctor immediately.
ACTH Incentive Test:
This exam evaluates the adrenal glands by balancing the ACTH activity. If the adrenal glands are born more harmless than cortisol due to shooting, they can remain inactive.
X-rays: To diagnose Addison’s disease, doctors may suggest an X-ray regarding the deposit of calcium in the adrenal glands. A person may develop Addison’s disease if calcium deposits are found.
Computed Tomography (CT scan): Computed tomography incorporates several X-ray images into various computerized images. It can reveal whether the adrenal gland is infected or not.
What is the treatment for Addison’s disease?
Your doctor may prescribe hormones similar to those needed for adrenal glands that mimic Addison’s treatment, such as hydrocortisone pills in combination with cortisol instead.
What is the prediction for people with Addison’s disease?
To live a normal but healthy life, people with Addison’s disease should take medication regularly. Additionally, you should consult your doctor about glucose levels and cortisol levels in the body from time to time. With this, your doctor may suggest an insulin-induced hypoglycemia test or an ACHT test at some point.
Adrenal dysfunction
The adrenal glands stop functioning normally for a variety of reasons. The two main reasons are a lack of primary and secondary adrenal glands. Let us consider the two reasons below.
Basic adrenal insufficiency – When the cortex does not function properly and does not produce enough adrenocortical hormones, it becomes less adrenal deficient. For unknown reasons, your body shows weakened immune systems and suffers from some autoimmune diseases. Other causes of adrenal gland dysfunction include TB (Tuberculosis), adrenal gland disease, adrenal gland cancer, adrenal gland bleeding or more. In severe cases, you may have adrenal insufficiency, with no previous symptoms.
Second adrenal insufficiency – When the pituitary gland does not function properly and does not produce enough adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), it becomes less than a second adrenal insufficiency. Most of the symptoms of secondary adrenal insufficiency are similar to primary adrenal insufficiency. People who suffer from adrenal insufficiency are more likely to have low blood sugar levels.
Foods to eat and avoid if you have Addison’s disease:
People with Addison’s disease and low levels of aldosterone hormone can eat foods high in sodium. The hormone aldosterone regulates the balance of sodium-potassium in the body. Some high-sodium foods include:
- Products made of grains
- Eggs
- Cheese
- Chicken soup
- Tiny tuna
- Beans in a tin
- Peanuts are salty
- Sesame seeds with salt
In addition, treatment for Addison disease involves an increase in doses of corticosteroids leading to other health problems such as osteoporosis and osteoporosis, so you need to check with your doctor to measure vitamin D levels and calcium levels, and dietary corticosteroids.
Emergency Treatment:
In an emergency, you and a colleague or family member can be trained to administer hydrocortisone injection. This may be necessary if you are nervous after an injury or vomiting or diarrhea and are unable to take oral medication. For example, this can happen if you are pregnant and sick in the morning. Your endocrinologist will discuss this with you when an injection is needed.
If you need to give emergency hydrocortisone, call your doctor right away. Check to see what resources are available after hours of work in your area if an emergency arises outside of normal working hours.
Also read: Important Topic Of Biology: Hyperactivity Disorder
FAQs
What is the main cause of Addison's disease?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a major cause of Addison's disease. If you have TB, there is a chance of adrenal insufficiency.
If you have Addison's disease, what happens next?
It is possible that people with Addison's disease or adrenal glands who are injured will not be able to produce enough cortisol. Cortisol deficiency can lead to weakness, fatigue, and low blood pressure.
What is the role of cortisol in our body?
Cortisol helps our bodies respond to problems such as illness, injury, or surgery. Therefore, people with Addison's problem should check their cortisol levels regularly.



