Table of Contents
Introduction:
Genetics is an excellent field of science where we focus on the various components of our genes. The most common genetic disorder in which genes are genetically modified is called domination. At a point where two unique genes show the different characteristics of a comparable asset, it is called codominance. In this section, we will focus on these unusual variables with models and discover how codominant alleles represent such properties. This allele material should be seen in all the vegetables of our nature.
What does Dominance mean?
To move forward in codominance, we will need to first determine and understand the meaning of domination. Consistent with the genetic specifications of the various true colors of a plant or an organism, there are at least two genetic variants for the expression of a particular trait.
In the discussion, let us consider two qualities of a certain character. Each character is linked to a specific quality or allele. When a parent contains both traits, the genes are passed on from one generation to the next.
It has been observed that only one of the attributes will be informed and the other will decrease. Two words are related to domination and affect the cause and effect of your relationship. These terms are provided below:
Rule – It is a feature that is defined in the description above.
Recessive – Another compressed element is known as recessive.
A strong gene should suppress the gene and thus the process is complete. The whole process of oppression and oppression is known as domination. Now, let’s get to understanding codominance.
Definition of Codominance:
Codominance is a natural process in which at least two factors are involved in the genetic code. It explains that the same traits will manifest themselves in all genes, reflecting on the formation of a visible character. This is a complex situation, which is why it is known as codominance. So far, we have not been able to comprehend this intricate phenomenon that we have seen everywhere but have not yet seen.
The law of codominance proves that there is a distinct relationship between the two genes in which both produce and display their properties at the same time. It also argues that the offspring will have the physical and mental characteristics of its father and mother.
What Is Imperfect Rule?
Another word closely related to codominance in the subject of inheritance is incomplete dominance. This is a natural phenomenon where the characteristics of the parent generation are brought together to form a new mixed element. For example, the exposure of many alleles during the fusion of a yellow flower plant and a red flower plant will produce an orange flowering plant.
In this example, you can easily understand the difference between codominance and imperfect governance. If it were the shape of a common feature, the flower would have yellow and red colors present at the same time. Once it has produced a new color, it is due to the incomplete dominance of both responsible alleles. Both the red and the yellow genes did not fully develop to produce a new orange color.
Examples of Codominance
A very good example is, in this case, the blood type of codominance. The ABO group is considered a cohesive blood group in which both the father and mother blood groups are represented. It means that blood group structures exist in the ABO type. The offspring carries the characteristics of both parents’ blood groups.
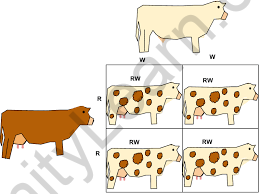
It can also be seen in cattle, dogs, etc. Puppies and calves have different hair colors when it comes to parents. It means that the phenotype measure will not be the same as the main one. In codominance genetics, a 1: 2: 1 ratio to the dominance phenotype will not exist.
Also read: Hardy-Weinberg’s principle
FAQs
How does domination occur in a living thing?
As we know, each character is connected by a certain quality or allele. To dominate the distinct genetic specifications of a plant or an organism, there are at least two genetic variants for a particular trait. When a parent contains both traits, the genes are passed on from one generation to the next. In the discussion, let us consider two qualities of a certain character. It has been observed that only one of the attributes will be informed and the other will decrease.
How does codominance occur in a living thing?
This is a complex situation, which is why it is known as codominance. It explains that the same traits will manifest themselves in all genes, reflecting on the formation of a visible character. Codominance is a two-dimensional object, requiring at least two characters and the genetics of both characters. The genetic makeup of a parent makes it possible for parents to have the same physical and mental similarities as that of the offspring. So far, we have not been able to comprehend this intricate phenomenon that we have seen everywhere but have not yet seen.
Explain how codominance and domination differ from each other.
If a strong gene has to press a repetitive gene then the process is completed. The whole process of oppression and oppression is known as domination. Although in codominance there is a unique relationship between the two genes in which both express and display their properties at the same time. It also argues that the offspring will have the physical and mental characteristics of its father and mother. Both are two different situations one is complex and the other is simple in its merits.





