CBSE Class 12 Geography Sample Paper With Solutions Set 12
[Time Allowed : 3 hrs.] [Max. Marks : 70]
Questions 1-7 (1 Mark), 8-13 (3 Marks), 14-20 (5 Marks), 21 and 22 (Map Question-5 Marks each)
Q.1.In which five year plan of India, were Hill Area Development Programme (HADP) initiated.
Ans. The Hill Area Development Programme was initiated in the fifth Five Year Plan. ”
Q.2. Name the iron and steel plant located in Chhattisgarh.
Ans. ‘Bhilai’ is the major steel plant located in Chhattisgarh.
Q.3. Name the types of iron-ore found in India.
Ans. Haematite and Magnetite are the two main types of iron-ore found in India.
Q.4. Why is the number of pastoral nomadic decreasing in the world? Mention any two
reasons. “
Ans. The two reasons responsible for the decline of pastoral nomadic are –
(i)Imposition of political boundaries.
(ii) New settlements plan developed and implemental by different countries. -T
Q.5. What is the meaning of retail trade services?
Ans. The retail trading services are confined to the direct sale of goods to the consumers. It is with fixed establishments which is related only to the selling of products.
Q.6. Name the inland waterway of Europe that connects Rotterdam and Basel.
Ans. The Rhine inland waterway of Europe connects Rotterdam (Netherland) and Basel (Switzerland).
Q.7. Name the headquarter of “OPEC” regional trade bloc.
Ans. Vienna, (Austria) is the headquarter of OPEC regional trade bloc.
Q.8. Explain any three characteristics of “Welfare Approach” of human development in the world.
Ans. The three main characteristics of ‘Welfare Approach’ of human development in the world are:
(i)The welfare approach is mainly associated with the development of human beings.
(ii)In this approach the government spends capital on the expansion of infrastructure like health, education other amenities.
(iii)The government is responsible for increasing levels of human development and the human being is the passive recipient of the welfare aspects.
Q.9. Write down any six characteristics of the Panama shipping canal.
Ans. The six characteristics of the Panama Canal are as follows :
(i)Panama canal connect the Atlantic Ocean in the east and Pacific Ocean in the west.
(ii)Panama canal has been constructed across the Panama isthmus.
(iii)About 8 km of area on either side of the Panama canal, is owned by the U.S. government.
(iv)It has reduced the distance between the eastern and the western coast of North and South America.
(v)The canal has lock system. Ships cross different level of canal through three locks, prior entering to the Gulf of Panama.
(vi)It has reduced the distance between New York (east) and San Francisco (West) by 13,000
km through Panama Canal.
Q.10. In the new industrial policy. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) has been seen as a supplement to the domestic investment for achieving a higher level of economic development. FDI benefits the domestic industry as well as the consumers by providing technological upgradation, access to global managerial skills and practices, optimum use of natural and human resources, etc. Keeping all this in mind, foreign investment has been liberalised and the government has permitted access to an automatic route for Foreign Direct Investment. The government has also announced changes in the industrial location policies. Industries are discouraged in or very close to the cities due to the environmental reasons.
Read the above paragraph and analyse the following :
(i)What are the benefits of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) ?
(ii)Why are the industries discouraged very close to the cities ?
Ans. (i) The benefits of Foreign Direct Investment are:
•Supplement to the domestic investment
•It alto benefits the domestic industry and consumer by technological upgradation
•Access to global managerial skills and practices
•Optimum use of natural and human resources
(ii)The Industries are discouraged very close to the cities, due to the environmental reasons, as the large scale industries are also stated as ‘Smokestask’.
Q.11.Name two different techniques of rain water harvesting followed in India.
Ans. Different techniques of rain water harvesting are:
(i)Recharge through abandoned tuber wells.
(ii)Construction of percolation pits and trenches.
(iii)Bunds and stop dams on small rivulets. (any two)
Q.12.How will the use of Bio-Gas help rural population to depend less on Government supply of L.P.G? What values does the use of Bio-Gas promote?
Ans. The use of Bio-Gas will enable the rural population in:
(i)Waste management
(ii)Used as fuel as well as manure
(iii)Cheap source of fuel
Values promoted from the use of Bio-Gas are:
(i)Environmental Concern
(ii)Self Reliance of rural households
(iii)Management of natural resources
Q.13. Tourism is a highly labour intensive activity of a unique kind in the world”. Support this statement with examples.
Ans. Tourism is a highly labour intensive activity of a unique kind in the world :
(i)Tourism the only sector of the tertiary sector which provide employment to the 250 million population in the world.
(ii)Tourism in the service sector contribute 40 percent of the total GDP.
(iii)Tourism is not only labour intensive about also support in the infrastructural industries in the form of roadways, hotels, motels, security and entertainment, etc.
Q.14. Describe any five features of the composition of India’s import.
Ans. The main features of changing patterns of the composition of India’s import are as follows :
(i)Food grains was the major item of import during 1950s and 1960s.
(ii)The import of food grains was discontinued after 1970s as the country has become self- reliant in foodgrains.
(iii)Fertilisers, pesticides and petroleum dominated our imports.
(iv)Machinery and equipment, special steel, edible oil, and chemical became the major items of import.
(v)Capital goods, like transport equipment, also became the major items of import.
(vi)Pearls, semi-precious stones, gold and silver, etc. also were the major items of import, (any five)
Q.15.Describe in brief the demographic consequences of migration in India?
Ans. The demographic consequences of migration in India are as follows :
(i)The migration of working age group (15-59) to the urban areas creates serious unemployment problem whereas there will be a great imbalance in the participating age group in rural areas.
(ii)Migration, declines the male sex in the rural areas because rural to urban migration is male dominated and it outnumber male population in the urban centres.
(iii)The rural to urban population also enhances the population of urban areas.
(iv)It leads to regional disparities in term of natural resources.
(v)Certain areas remain devoid of productive population.
Q.16. What benefits to nations get by forming trading blocs?
Ans. The international trade has become very complex with a high degree of specialisation in
agricultural and industrial production. It has become an important component of the world
economy. .
•The global trade has grown much more rapidly over the past 25 years.
•The average annual growth rate of the value of the world exports was twice that between 1955 and 1995.
•Today roughly 25 per cent of the world’s total output is traded among nation-states.
•Most of the world’s trade has been taking place within the blocs as a result of the effects of distance, the legacy of colonial relationship and geographical alliances.
Q.17.Define Market gardening and Horticulture? Describe any four of their characteristics.
Ans.The market gardening and horticulture is one of the most specialised forms of cultivation of
vegetables, fruits and flowers, which has high value and have great demand in urban market.
The four features of market gardening and horticulture are :
(i)It requires good and quick transportation system as fruits, vegetables and flowers are perishable in nature. Hence this farming is also stated as ‘truck farming’.
(ii)This type of farming is capital as well as labour intensive.
(iii)More stress is given on the optimum use of HYV seeds, pesticides, fertilisers, other means of irrigation and greenhouses for artificial heating in colder regions.
(iv)It is more common in the densely populated industrial regions of developed countries (North-west Europe, north eastern regions of the USA and Canada, Southern Europe, etc).
Q.18. Describe any five factors influencing industrial location in the world?
Ans. Following factors favour the localisation of an industry :
•Nearness of Raw Material: The heavy and basic industries are mainly localised near the source of raw material, as the raw material is the soul of the industries. They are established in the area surrounding the raw material to minimise the transport cost. The sugar industries are located near the raw material, as sugar cane is a perishable’ product and delays in transport affect the production. The heavy raw material based industries are found generally near the availability of the raw material. The paper and pulp industries and saw mills are located in the coniferous forest region due to easy availability of the raw material.
•Power Resources: Coal, petroleum and hydro-electricity are the chief sources of power. The heavy industries need power in abundance. These industries are generally localised near the areas where power is easily available. The Damodar valley in India and the Rhur valley in Germany are the main industrial centres due to coal and hydro-electric power. The iron and steel industry, fertiliser, aluminium and copper smelting are power intensive industries, hence located near the sources of power.
•Means of Transport: The means of transport are the ‘arteries and veins’ of industries, as these connect the producer to consumer. Hence industries are set up in those places which are endowed with cheap, quick and abundant means of transport.
•Suitable Climatic Condition: Climate plays an important role in their establishment. The cold climate affects health and ultimately the efficiency of work and the damp climate is helpful to the cotton textile industry. The dry atmospheric conditions are helpful for the aircraft industry.
•Abundant and cheap Labour Force: The skill and technique of manufacturing something is very essential. The skilled labour and technique of appliances increases the quality and quantity of production. The manufacturing of watches in Switzerland, toys and electronics in Japan, glass work in Ferozabad and textile in Lancashire are famous due to skilled and specialised labour force.
Q.19 Describe the major challenges of agriculture in present India.
Ans. Agriculture is the main occupation of people of India. It is the source of living for about 70% of its working population. It is the base of Indian economy. Despite its dominant role, agriculture has not been able to provide the basic needs of the country. Our agriculture has been failed to meet the food grains required of the country.
Many factors have hindered the development of agriculture in India such are as follows :
•Pressure of Population on Land. Due to continuous increase in population, pressure of population on land is increasing. Due to over crowding, the per capita cultivated land in India has been reduced to only 0.3 hecter areas. It has resulted in shortage of foodgrains. The growth rate in agriculture is also low.
•Inadequate Irrigation Facilities. In India, agriculture depends on monsoonal rainfall. Due to uncertain and variable rainfall irrigation is necessary. Only 22% of cultivated land is irrigated. It is necessary to irrigate at least 50% of the cultivated land to make it a success. Moreover, irrigation is required to increase the yield productivity and the intensity of cropping to check the severe draught.
•Low productivity. In India, the yield per hectare of foodgrains and other crops is low as compared to other countries of the world. High yielding varieties have been introduced. But only 16% of the cultivated land is under high yielding varieties.
•Poor Techniques of Production; Due to continuous agriculture over a long period, the fertility of soils is declining. To maintain its fertility, the use of chemical fertilisers is necessary. Indian farmers have been using old inefficient methods due to which there is low productivity. Use of better quality seeds and pesticides can increase the productivity.
•Lack of Mechanised Farming. Agriculture is mostly intensive. Human labour is used to get maximum output. Use of modern machines is limited due to low purchasing power of farmers. The government has been taking some steps to remove the drawbacks of the agriculture. A new strategy have been adopted to bring many improvements in the economic, technical and organisational form of the agriculture in India.
♦The area under cultivation has been increased. The intensity of cropping has been increased. More than one crops are being obtained from the same field. It has resulted in increased agricultural production.
♦Many minor and major irrigation schemes have been completed to provide more irrigation facilities.
♦The use of better quality seeds and fertilisers has been encouraged. High yielding varieties are being introduced. Many research centres and agricultural universities have been set up to introduce new techniques.
♦Mechanised farming is being provided with the help of many government institutions. Modern agricultural implements like combines, tractors crushers etc., are being used.
♦Consolidation of land holdings had been done to check the fragmentation of landholdings. Ceiling of land holding had been introduced.
♦Many facilities have been provided in the field of marketing of agricultural products. Government fixes the support prices of the food grains every year.
♦The linkage between agriculture and industry had been strengthened by developing the cottage industries.
♦Green Revolution and package programmes have been started in many areas.
Q.20. Explain the five groups of towns in the world, which are being classified on the basis of their function.
Ans. The five types of towns on the basis of functions are :
•Administrative Towns. The main functions of administrative towns is to administer the country, state or a specific territory. It includes not only the capital cities of countries, but all the centres of provinces, states, districts and administrative divisions of the country. Mexico city, Buenos Aires and Bijing etc., are administrative towns.
•Defensive Towns. During the medieval period, most of the towns and cities used to be
developed on the defensive sites. Forts and garrisons used to be constructed at strategic sites.
The defensive towns have barracks, cantonments, training facilities for the armed forces,air fields and harbours for warships. Khadakwasla (India), Peshawar (Pakistan), Playmouth(England) and Nova-Scotia (Canada) have developed as the defensive towns.
•Cultural Centres. There are numerous towns and cities in the world, almost in each of the countries, which perform cultural functions. Oxford and Cambridge in England are educational towns. Varanasi (India) and Mecca (Saudi Arabia) are religious towns, whereas
Shimla (India) and Las-Vegas (USA) are recreational towns.
• Industrial Towns. Mining and manufacturing towns have developed in mining and manufacturing regions. Kalgoorlie, Coolgardie, Dhanbad and Khetri are industrial towns.
•Trade and Transport Towns. Many old towns were famous as trade centres. Dusseldorf ; in Germany, Winnipeg in Canada are trade and transport town.
Q.21. On the given outline map of the world, the following five features are shown. Identify these features and write their correct names on the lines marked near each feature.
(i) A Mega city of China (ii) Major sea port of Brazil 1 (iii) Major air port of England
(iv)The Highest HDI ranking country
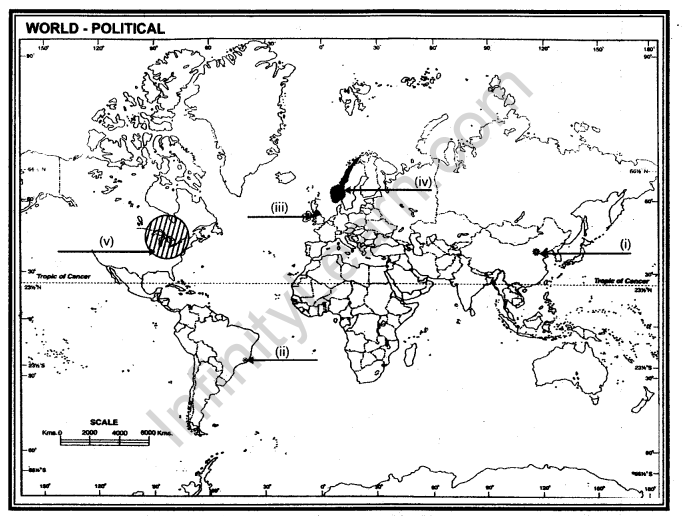
Ans. (i) Beijing (ii) Rio De Janerio (iii) London (iv) Norway (v) North East Lake Region of North America
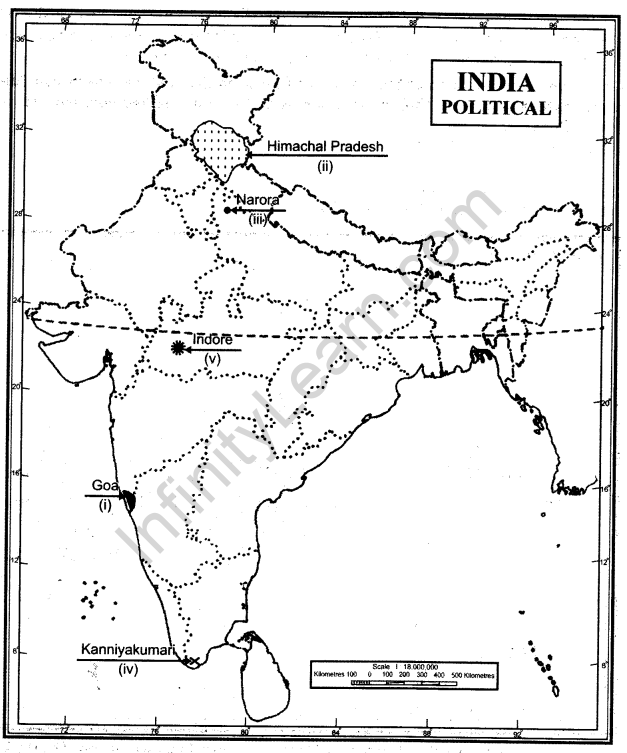
Q.22. On the given outline map of India, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols.
(i)The Smallest state in area
(ii)Hindu dominating state
(iii)Nuclear power plant of Uttar Pradesh
(iv)Southern terminal of North South corridor
(v)Software Technology Park in Madhya Pradesh
Ans.