Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Meristematic Tissue
- Types of Meristematic Tissue
- Development of Meristematic Tissue Function
- Summary
- Did You Know?
- What’s Next?
In the previous segment, we were introduced to the topic of Tissues. In this segment, we will learn more about the dividing type of tissues, also known as Meristematic tissues.
What is Meristematic tissue?
Meristematic tissue is a plant tissue that can divide and help the plant grow. Hence, these tissues are located at all the places where the parts of the plant show growth.
Meristematic tissue is a type of plant tissue that consists of undifferentiated cells that are capable of dividing and growing indefinitely. They are found in the growing regions of a plant, such as the tips of stems and roots, and are responsible for the growth and development of the plant. Meristematic tissue is made up of cells that are highly active and contain a high amount of cell division. This type of tissue is vital for the growth and development of a plant, as it enables new tissues to form and allows a plant to keep growing.
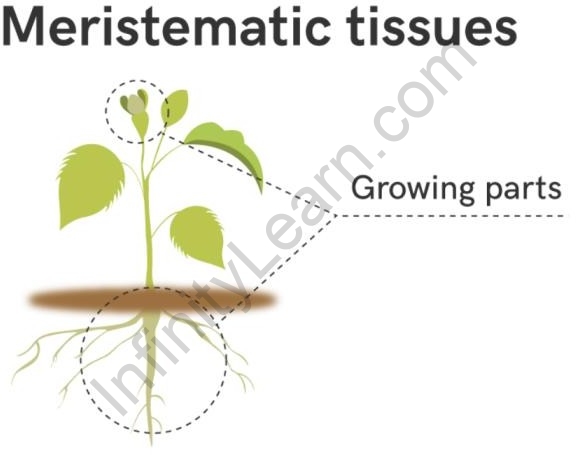
Meristematic tissues in plants
What are the types of meristematic tissues?
There are three main types of meristematic tissues in plants:
(i) Apical meristem – The apical meristem is found in the growing tips of the stems and roots. It divides and increases the length of the plant.
(ii) Cork cambium- The cork cambium is a layer of cells within the bark of trees that produces cork cells. This layer of cells, located between the inner bark and the outer bark, is responsible for producing the corky layer of cells that eventually becomes the protective layer of cork on the outside of the tree.
(iii) Intercalary meristem – Intercalary meristem is a type of meristem found at the base of leaves, between nodes of grasses, and at the tips of branches. It is responsible for growing additional internodes and is important in the process of elongation of stems.
Development of Meristematic Tissue Function
Meristematic tissue is an essential component of all plants, playing a key role in their growth and development. Meristematic tissue consists of undifferentiated cells that are capable of division to form new tissue. This tissue is responsible for the growth of plants, as it is able to divide and grow rapidly. Meristematic tissue is found in three different regions of a plant, the root, stem, and shoot apical meristem.
Root apical meristem is located at the tip of a root. This tissue is responsible for root elongation and root hair production, as well as lateral root growth. Root apical meristem is also responsible for the formation of lateral root primordia, which are the beginnings of lateral root production.
Stem apical meristem is located at the tips of shoots and branches. This tissue is responsible for the production of lateral and axial shoot growth, as well as the production of leaves and flowers. Stem apical meristem is also responsible for the production of lateral buds, which are the beginnings of branch growth.
Shoot apical meristem is located at the tips of leaves and flowers. This tissue is responsible for the production of leaf and flower primordia, which are the beginnings of leaf and flower production. Shoot apical meristem is also responsible for the production of lateral shoots, which are the beginnings of branch growth.
The function of meristematic tissue is essential for the growth and development of plants. This tissue is responsible for the continuous growth of plants, as it is able to divide and grow rapidly. Meristematic tissue is also responsible for the production of lateral and axial shoots, leaves, and flowers. Without the function of meristematic tissue, plants would be unable to grow and develop.
Summary
Meristematic tissue is a type of plant tissue composed of undifferentiated cells that are capable of dividing and growing. It is found in the root, stem, and shoot apical meristems, which are responsible for the growth of a plant. Meristematic tissue is composed of three types of cells—initial cells, undifferentiated cells, and meristematic cells—which can undergo cell division and generate new cells. Meristematic tissue plays an important role in plant growth and development, as it is responsible for the formation of new organs, such as leaves and flowers.



