
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 11 Dec 2024, 17:55 IST
Autoclaves, also called steam sterilizers, are commonly used in healthcare or industry. They work by using steam under pressure to eliminate harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores from items placed inside a sealed container. These items are heated to a specific temperature for a certain duration to ensure sterilization. The steam’s moisture effectively transfers heat to the items, breaking down the protein structure of bacteria and spores.
Also Check: Atmosphere Layers Diagram
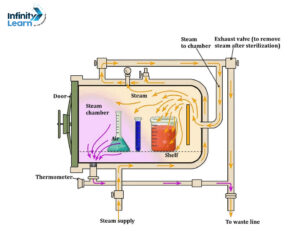
Autoclaves are machines used in hospitals to clean medical tools. Inside, there’s a special chamber where the tools go. Making sure the autoclave works well involves three important things: time, heat, and the quality of the steam.
The process of using an autoclave has three steps:
For the autoclave to work well, the steam needs to be just right. It should be mostly steam (vapor) with a little bit of water (liquid). This mix is best for killing germs efficiently. If there’s too little water in the steam, it’s called “superheated” or “dry” steam, and it doesn’t clean as well.
Also Check: Spirogyra Diagram
The size of the sterilizer changes depending on how much space it needs to cover. For instance, in places like a dentist’s office, a small sterilizer might be enough. It can just sit on a counter and sterilize small packs of tools. Near an operating room, they might need a tiny sterilizer that can quickly sterilize 1-3 trays of tools at once. But in most healthcare places, they have bigger machines that can handle more. These machines, usually found in the Sterile Processing Department (SPD), can handle 15-20 trays of tools per cycle. Some can even manage up to 625 lbs of tools per cycle, depending on their size.

For manufacturing, the sterilizers are even bigger. Some are as big as a semi-truck or airplane.
Autoclaves are machines that use steam, pressure, and time to clean and sterilize things. They get really hot and squashy to kill germs and tiny life forms. People use them to clean up biological messes and make lab stuff super clean. It’s important to use autoclaves to kill off any bacteria or viruses in medical waste before throwing it away.

Autoclaves are used to sterilize equipment and materials by subjecting them to high pressure and steam.
The principle of autoclave is to use steam under pressure to kill bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms.
121 degrees Celsius is used because it's the temperature at which steam under pressure can effectively sterilize materials.
The three stages are heating, sterilizing, and cooling.
The principle is steam under pressure, and the purpose is to sterilize equipment and materials.
Typically, materials are sterilized at 121 degrees Celsius for about 15-20 minutes.
Autoclaving disinfects by using high-pressure steam to kill microorganisms.
The main function is to sterilize equipment and materials in laboratories, hospitals, and other settings.
Autoclave 5 is typically used for sterilizing larger items such as laboratory glassware and medical instruments.
The working principle involves using high-pressure steam to kill microorganisms on equipment and materials.
An autoclave is a pressure chamber used to sterilize equipment, typically with a door that seals tightly.
An autoclave works by heating water to produce steam, which is then pressurized to sterilize materials inside the chamber.
Autoclave PDFs are documents providing information on autoclave operation, maintenance, and safety protocols.
The basic principle is to use steam under pressure to sterilize materials and equipment.
The autoclave works by using steam under pressure to kill microorganisms on equipment and materials.
The purpose is to sterilize equipment and materials to prevent contamination and ensure accurate experimental results.
Autoclaves are used in laboratories, hospitals, dental offices, and other settings where sterilization is essential.
The use is for sterilization, and the principle involves using steam under pressure to kill microorganisms.