
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 21 Nov 2024, 15:29 IST
Even when they’re part of a complex, living, breathing being, atoms and molecules follow the laws of chemistry and physics. Even when the atoms or molecules are part of a living organism, you can learn in chemistry that some atoms tend to gain or lose electrons or establish bonds with one other. Simple interactions between atoms, repeated many times and in many combinations in a single cell or a bigger organism, are what allows life to exist. It’s possible to claim that everything you are, including your mind, is the result of chemical and electrical interactions between a massive number of non-living atoms!
The information about atoms, molecules, and elements from various physics-related articles is available here. Atoms and molecules are important topics in physics. Students who want to flourish in physics need to be well known about atoms, elements, and molecules to get deep knowledge about them to do well on their exams. The definitions and brief explanations are provided here to assist students in effectively understanding the respective topic. Continue to visit our website for additional physics help.
Every atom is made up of a nucleus and electrons that are bonded to it. The nucleus is made up of the same number of protons and neutrons (number of neutrons = number of neutrons). The nucleus contains 99.94 percent of an atom’s mass. Protons have a positive electric charge, electrons have a negative charge, and neutrons have no electric charge. The atom is electrically neutral if the number of protons equals the number of electrons. The charge is determined by the number of electrons and protons; if electrons outnumber protons, it will have a negative charge; if protons outnumber electrons, it will have a positive charge; otherwise, it will be called an ion.
In general, an element is a fundamental substance that is made up of only one sort of atom. Additionally, elements are formed up of smaller particles and might be synthetic or man-made. The periodic table is organized according to the number of protons counted in ascending order.
The smallest unit of a chemical substance is referred to as a molecule. It has the same chemical properties as the compound in concern. Because molecules are made up of atoms that are linked together by chemical bonds, there is a lot of room for size and complexity variation.
The atom is the tiniest structural unit of matter with chemical element characteristics. Every kind of matter, including solids, liquids, gases, and plasma, is made up of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are exceedingly small, measuring roughly 100 pm (a ten-billionth of a metre), and there are many other ways to quantify their size, all yielding similar results.
In chemistry, the molecule is said to be the smallest unit of a substance that holds the compound’s chemical properties. They are built up of atoms arranged in groups. When explaining an atom’s structure, it is also fragmented into smaller components. Protons, electrons, and neutrons are the sub-particles of an atom. The nucleus of the atom, which is surrounded by electrons, contains protons and neutrons.
Chemistry defines an element as a pure material consisting completely of atoms with the same number of protons in their nuclei. Chemical elements make up all of the baryonic matter in the universe. When separate elements undergo chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged into new compounds that are joined together by chemical bonds. Only a few elements, such as silver and gold, are discovered uncombined in relatively pure native element minerals. On the Earth, nearly all other naturally occurring elements exist as compounds or combinations. As we know, the air is mostly built up of the elements nitrogen, oxygen, and argon; however, it also contains carbon dioxide and water. Because atoms are far too small to be observed, studies to determine their structure and behavior must be carried out using a vast number of them.

The chemical or covalent bonds combine one or more atoms together to form molecules. Atoms can be represented as circle shapes with a nucleus in the center (containing protons and neutrons), surrounded by one or more concentric circles representing the ‘shells’ or ‘levels’ in which the electrons surrounding the nucleus of the atom are situated, and markings denoting the electron at every level. As we said before, the molecule is the smallest unit of a material that retains its identity. Chemical bonding holds two or more atoms together.
As already mentioned, protons, electrons, and neutrons are the three basic types of particles that make up an atom. Neutrons and protons have nearly identical masses; however, the mass of an electron is negligible. Protons have a positive charge, while neutrons do not, and electrons have a negative charge. Because an atom has the same number of protons and electrons as it does electrons, it has no charge. The nucleus of an atom is positively charged because it only contains protons and neutrons. The area or space around the nucleus is occupied by electrons. As a result, the nucleus contains the majority of the mass.
The nucleus of an atom is its core. Neutrons and protons make up the nucleus, which is responsible for an atom’s weight and positive charges. A neutron is a massless particle with one unit of mass. A proton is a one-unit mass particle with a single positive charge. The atomic number of an element is determined by the number of protons or positive charges in the nucleus. The atomic weight of an element is calculated using the total amount of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. An electron has a single negative charge. An element’s atom must have the same number of protons as electrons to have zero charges. These electrons are arranged in orbits around the nucleus of the atom, similar to the layers of an anion.
We can say that the molecule is the tiniest unit of a material that contains the chemical properties of the component. Molecules are composed of atoms arranged in groups. It can be said that an atom’s structure is further subdivided into smaller components when describing it. Protons, electrons, and neutrons are the sub-particles of an atom. The nucleus of the atom, which is surrounded by electrons, contains protons and neutrons. Electrons are negatively charged particles, whereas protons are positively charged. Neutrons are uncharged particles. As a result of the presence of protons, we can say that the nucleus is positively charged. The nucleus is the central bulk mass of an atom. Atoms are mostly empty. In general, the atomic number of each element is unique. The number of protons in an element’s nucleus is known as its atomic number, and it is denoted as Z. When we talk about the mass of atoms, we also have to consider the mass of their particles. Electrons have a mass of zero. As a result, the mass of an atom is equal to the sum of its protons and neutrons. A stands for the mass number. A molecule is the smallest unit (particle) of a compound, possessing all of the substance’s physical and chemical properties. This isn’t to say that molecules can’t be broken down into smaller bits, such as the atoms that make them up or the fragments of the molecule, each of which is made up of numerous atoms or sections of atoms.
Chemical species with at least two atoms of the same chemical element chemically linked to each other are known as molecular elements. Chemical compounds are distinguished by the presence of two or more atoms of different chemical elements in a chemical compound.

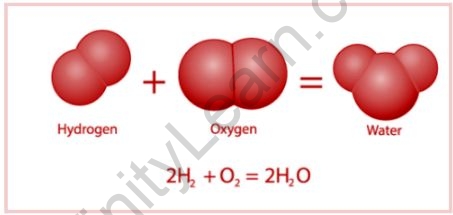
Compounds, such as water and methane, are made up of two or more atoms of different elements. The atoms are not depicted to size. The compound molecules consist of atoms from two or more distinct elements. Water, for example, has three atoms: two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen.
A positively charged nucleus composed of protons and neutrons is surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons in many atoms. An atom is a particle of matter that contains at least one proton at its most basic level. A few examples of atoms are as follows: hydrogen (H) neon (Ne).
A molecule is formed by the bonding of two or more atoms of the same or distinct elements. A molecule can be homonuclear, meaning it contains only atoms of one chemical element, such as oxygen, or heteronuclear, meaning it contains atoms from numerous chemical elements, such as water.
In its most basic form, glucose is a sugar molecule. Sugars come in a variety of forms, including table sugar, also known as sucrose in chemistry. Sucrose is a more difficult molecule to understand than glucose. Both are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.