
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 3 Jun 2025, 14:43 IST
Plant cells in eukaryotic cells differ in a number of important components from other eukaryotic organisms. Both plant and animal cells contain the nucleus and the same organelles. One of the unique characteristics of a plant cell is the presence of a cell wall other than the cell membrane.
The basic unit of life in all living things is known as the cell. Like animals and humans, an infinite number of cells form plants. The plant cell is surrounded by a cell wall responsible for providing the plant cell structure.Different cellular functions are associated with cell walls and other organelles. To better understand the similarities, let us take a closer look at a plant cell, its structure, and the functions of the different organisms in different plant cells.
The plant cell is rectangular and larger compared to the animal cell. Even though plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and consist of a few organelles, plant cells are very different compared to animal cells as they perform different functions. Some of these differences can be clearly understood when the cells are examined by an electron microscope.
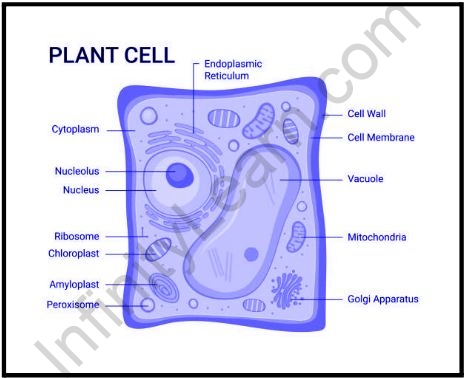
Like the various organs within a body, the structure of a plant cell consists of various parts known as cell organelles that perform various functions to support themselves. These organelles include:
It is a solid layer composed of cellulose, glycoprotein, lignin, pectin, and hemicellulose. It is found outside the cell membrane. It contains proteins, polysaccharides, and cellulose. The primary function of the cell wall is to protect and provide structural support to the cell. The cell wall of plants is also involved in protecting the cell from mechanical stress and providing the structure and structure of the cell. It also filters out molecules that enter and leave the cell.
The structure of the cell wall is regulated by microtubules. It consists of three layers, namely, primary, secondary, and medial lamella. The cell wall is made up of cellulose, which is secreted by enzymes.
It is a membrane that can easily penetrate the cell. It is made up of a thin layer of protein and fat. The cell membrane plays an important role in controlling the entry and exit of certain substances within the cell.

For example, cell membranes keep toxins from entering, while essential nutrients and minerals are transported across
The nucleus is a membrane-bound structure found only in eukaryotic cells. An important function of the nucleus is to store DNA or genetic information needed for cell division, metabolism, and growth.
Produces structures that produce proteins and ribosomes.
A nuclear membrane has holes called nucleopore that allow proteins and nucleic acids to pass through.
The cells of a mature, high-growth plant are specialised in performing certain vital functions. Few plant cells are involved in the transport of nutrients and water, and some are food storage. Specific plant cells include parenchyma cells, sclerenchyma cells, collenchyma cells, xylem cells, and phloem cells.
The following are some of the different types of plant cells:

Sturdy or sturdy cells play a key role in supplying plants where there is inhibitory growth in the plant due to the lack of a strong agent in the main walls.
These cells are much stronger compared to collenchyma cells and this is due to the presence of a strengthening agent. These cells are commonly found in all plant roots and are strongly involved in providing plant support.
Parenchyma cells play an important role in all plants. They are living cells of plants, involved in the production of leaves. They are also involved in gas exchange, food production, storage of organic products, and cell metabolism. These cells are usually more flexible than others because they are smaller.
Xylem cells are transport cells in vascular plants. They help to transport water and minerals from roots to leaves and other parts of plants.
Phloem cells are other transport cells in the vascular system. They deliver leaf-cooked food to different parts of the plant.
Plant cells are plant structures. Photosynthesis is a major function of plant cells.
Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts of a plant cell. It is a process of preparing food for plants, using carbon dioxide, sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. Energy is produced in the form of molecules (ATP) in this process.
Few plant cells help to transport water and nutrients from the roots and leaves to different parts of the plant.
They are organelles that bind to the membrane with their DNA. It is necessary to store the starch, to carry out the process of photosynthesis. It is also used to assemble many molecules, forming cell building blocks. Some of the important types of plastids and their functions are listed below:
They are found in the non-photosynthetic tissue of plants. They are used to store protein, lipid, and starch.
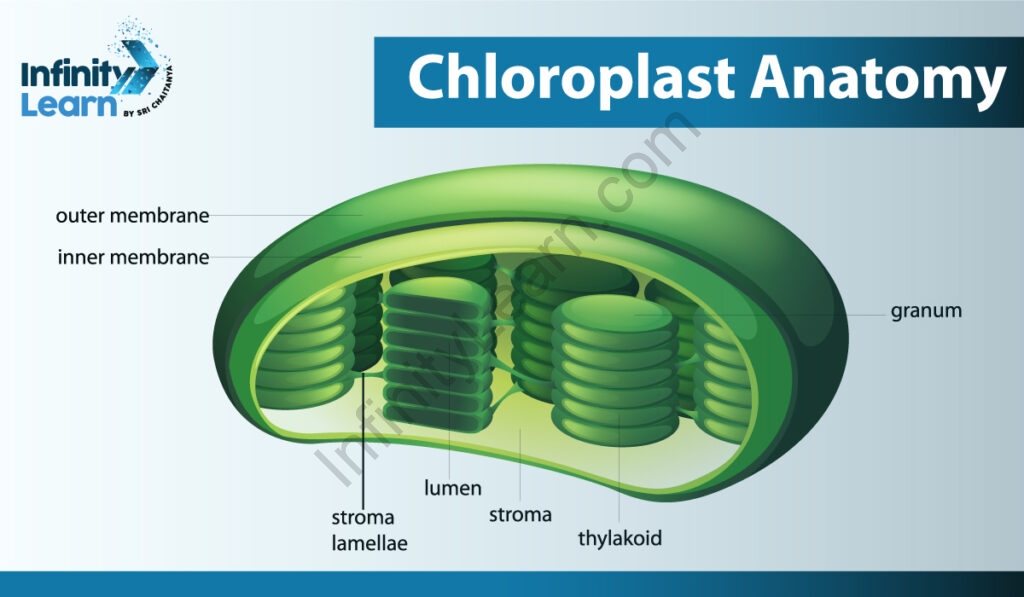
It is a long organelle covered with a phospholipid membrane. The chloroplast is disk-shaped and the stroma is the fluid inside the chloroplast that encompasses the round DNA. Each chloroplast contains a green pigment called chlorophyll needed for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll absorbs light from the sun and uses it to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars.
They are heterogeneous, colored plastids responsible for pigment formation and storage of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. Chromoplasts are red, orange, and yellow that gives color to all ripe fruits and flowers.
It takes up about 30% of the cell volume in a mature plant cell. Tonoplast is a layer around the central vacuole. An important function of a central vacuole outside storage is to support turgid pressure on the cell wall. The central vacuole contains cell sap. It is a mixture of salt, enzymes and other substances.
They are found in all eukaryotic cells involved in the distribution of macromolecules that are attached to different parts of the cell.
The tiny organelles that are attached to the membrane combine RNA and proteins. They are the building blocks of protein synthesis, hence, they are also called cellular protein industries.
They are two-pore organisms found in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. They provide energy by breaking down carbohydrates and sugar molecules, hence the name “Energy House of the Cell.”
Lysosomes are called suicide cells as they trap digestive enzymes in the closed membrane. They do the work of disposing of cell waste by digesting worn organelle, food particles and foreign bodies in the cell.
Photosynthesis is a major function of the Plant cell and is therefore known as plant structures
The nucleus is a membrane-based organelle found in eukaryotic cells.
Plant cells are commonly referred to as eukaryotic cells with their own nucleus and other special structures known as organelles. The structure of the plant cell is rectangular with a central vacuole taking up 30% of the volume of the cell.
Apart from the cell wall and cell membranes, parts called organelle to perform certain functions. Some of the most important organelles are as follows: