
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 16 Jan 2025, 13:16 IST
The energy acquired by an object or particle due to its movement is known as kinetic energy. An object accelerates and creates energy when full force is applied to it. Moving objects or particles have this power as quality. In addition, movement affects not only the force but also the weight. The kinetic energy of an object is related to its square velocity. This means that doubling the speed of an object is four times its chemical strength. Kinetic Energy should always be zero or positive. The amount of kinetic energy scale is measured in Joules.
Kinetic energy is a measure of the work done by the body due to motion. Simple movements such as walking, running, throwing, and falling require kinetic energy. To accelerate an object, you need to apply a force. Work is done by force. When work is done by any object, energy is transferred and the object moves at a new speed. The energy transferred is called kinetic energy and it depends on the mass and velocity achieved.
An object’s kinetic energy is a measure of what an object can do as a result of its motion. Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity and can only be described fully as a quantity. The SI unit for Kinetic Energy is the joule and is equal to 1kgm2s-2. The CGS unit for Kinetic Energy is the Erg.
There are six types of energy included in kinetic energy:
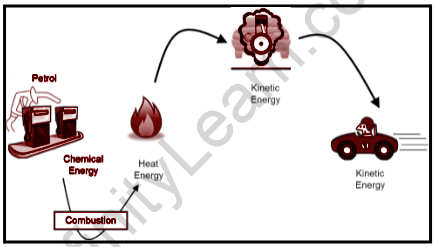
Energy can neither be created nor it can be destroyed, but it can be transferred from one object to another and changed from one form to another.
As kinetic energy depends on the mass and speed of the object for which the SI unit is the joule. This is a scalar value. The kinetic energy formula is expressed as where m is the mass of an object moving with speed v. If the mass is given in kilograms and the speed/velocity v is given in m/s, then the kinetic energy is in joules.
One joule is the energy when a force of 1 newton moves an object by 1 meter.
The Kinetic energy equation can be obtained by means of a basic function (W) of energy (F). If the force parallel to the surface is applied on the body of mass m it is pushed to the d distance on the surface, then the work done would be:

using the corresponding force, the work performed would be:
W=Fd
W=m.a.d
The acceleration in these calculations can be adjusted for the initial velocity (Vi) and final velocity (Vf). We find this in the kinematic equations of motion.
W=m.a.d
=m.d.(V²f-V²i)/2d

=½mV²f – ½mV²i
Initial velocity is zero because the body is at rest therefore the expression for kinetic energy is:
Kinetic Energy=½mV²
Hence, we can conclude that the total work done is equal to the change in kinetic energy. Therefore,
Wnet=∆k
Now, if the forces applied are large in magnitude, then also this has many applications. The equation derived is called as Work-Energy Theorem.
Some of the Kinetic Energy Examples are:
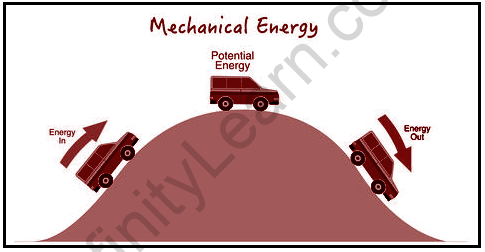

Kinetic energy is transferred between objects and can be converted into other forms of energy as well Yo-Yo is a good example of describing kinetic energy conversion. When we begin to play with it, we begin with letting it rest in our hands; at this point, all the energy is stored in the ball in the form of potential energy. When a person drops a yo-yo, the stored energy is converted into kinetic energy, which is the energy of movement. When the ball reaches the bottom of the yo-yo, all the energy is converted into kinetic energy.
Hence, we can say kinetic strength is the power of movement which directly depends on the weight of the moving body.
The quicker the frame passes the greater the kinetic energy is fashioned as a system of movement for example; when a bus goes up a hill down a hill, the strong current of the bus turns into K.E. There is not much potential energy at the bottom of the hill, but there is a large amount of kinetic energy.
Similarly, basketball shows kinetic strength, kinetic energy is equal to the weight of the ball and the square of its speed also if throwing the same ball twice immediately, the player does a lot of work and transmits four times more power.
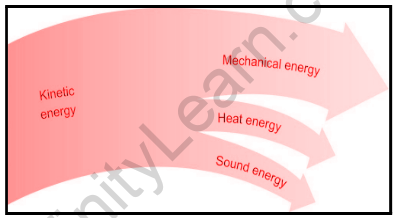
Examples of kinetic energy are windmills, moving vehicles, Yo-Yo, running water, etc. Kinetic Energy is expressed as,
Kinetic Energy=½mV²
Where m is the mass of the body and v is the velocity.
Energy can neither be created nor it can be destroyed, but it can be transferred from one object to another and changed from one form to another.
No, because the mass of the body cannot be negative and the square of velocity gives a positive number.
The energy possessed due to the position or state of the body is called potential energy and the energy possessed due to motion is called kinetic energy.
As kinetic energy directly depends on mass and velocity so as these two factors increase kinetic energy increases and when these two factors are at maximum kinetic energy is at maximum.
Electrical energy and sound energy are two main types of kinetic energy.