
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 23 Jan 2025, 12:38 IST
Longitudinal waves are waves in which the medium’s vibration is parallel (“along”) to the wave’s travel direction and the medium’s displacement is in the same (or opposite) direction as the wave’s propagation. Because they create compression and rarefaction when moving through a material, mechanical longitudinal waves are also known as compressional or compression waves.
The wavelength is the distance between the two consecutive compression or rarefaction areas. Constructive interference occurs when the compression and rarefaction zones of two waves coincide, whereas destructive interference occurs when the compression and rarefaction regions do not coincide.
The vibrating motion of particles travelling across a conductive media produces a sound wave, which is an example of a longitudinal wave. The tuning fork is an example of sound waves travelling in a longitudinal direction.
The difference between the greatest pressure created by the wave and the pressure of the undisturbed air is the amplitude of the wave in sound waves. The type, content, and temperature of the medium through which sound travels determine its propagation speed.
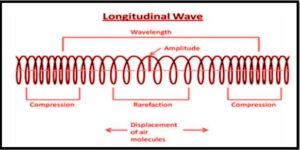
Compression is the portion of a longitudinal wave where the wave’s particles are closest to each other.
The Oscillations and Waves chapter, which accounts for 10% of the exam questions, covers a wide range of topics. All you have to do is grasp the concepts of each topic. If you stick to this plan, your Physics preparation would be spot on, and you’ll be able to pass this section with flying colours. As per the distribution of levels of difficulty in the previous year’s tests, basic and medium-level questions makeup roughly 83 percent of the JEE paper.


Sound waves, spring vibrations, tsunami waves, and so forth are examples of longitudinal waves.
Wavelength, amplitude, period, frequency, and wave speed are all parameters of longitudinal waves, just as they are for transverse waves. The key distinction is that longitudinal waves include compressions and rarefactions instead of crests and troughs.
Wave velocity is defined as the distance travelled in a motion per unit time in a cyclic or periodic fashion in any direction.