
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 3 Jun 2025, 15:02 IST
Nerve control and communication are important parts of the human body. The Neural System is a well-organized network of point-and-point communication in the human body that allows for rapid communication, while the endocrine system is responsible for the chemical synthesis of hormones.
Integration refers to the process by which two or more members share and fulfill the functions of another. For example, when we exercise, our oxygen supply and energy levels both increase as our muscle activity increases. When we stop exercising, our emotions, heart, lungs, and kidneys all return to normal. As a result, all organ functions are well integrated to perform body function and provide the right conditions during exercise.Similarly, in the human body, the brain and endocrine systems work together to coordinate and integrate all the functions of the organs to function in unison.
The sensory system of all animals is made up of highly specialized cells called neurons, which are responsible for identifying, receiving, and transmitting the many types of implants. The arrangement of the nervous system in small vertebrates, such as Hydra, is very simple, involving a network of neurons.
It is best adapted to insects, where the brain is made up of many ganglia and neural tissues. In addition to the central nervous system, ganglia are a group of cellular bodies. Vertebrates, on the other hand, have a highly developed nervous system.
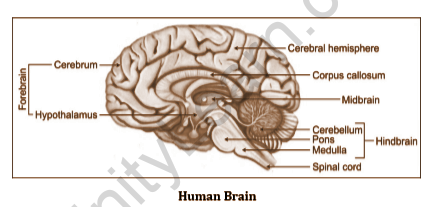
The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system. It is also known as the CNS and is where information and control are processed.
The midbrain, cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and medulla oblongata are all parts of the brain. The brainstem is responsible for important functions such as temperature control and assists the hypothalamus in its function. Memory and cerebellar functions are assisted by the cerebrum.
The body system and the autonomic nervous system (optionally) are both parts of the surrounding (voluntary) nervous system. It contains two types of nerve fibers found in the CNS, which are separate and different fibers.

The sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system are two subcomponents of the autonomic nervous system. The first one comes in when you are in combat, flight, or combat or flight mode (3F). The latter works when the body is resting or digesting food.
Neuron: Structural and Functional Unit of the Neurological System
A neuron is a small structure made up of three major parts: the body of the cell, the dendrites, and the axon. Neurons can be unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar.
Neurons can be divided into three types according to the number of axons and dendrites they have:
Functional cells are known as neurons because they transmit electricity. Their membranes are polarised, and the axolemma, or neural membrane, contains many types of ion channels. Different ions enter selectively from these ions.
The strength of the relaxing membrane of a neuron is a state in which it does not carry out any concepts. Potassium ions (K +) easily penetrate the axonal membrane, whereas sodium ions (Na +) cannot penetrate.

Neural Control & Coordination: Nerve control and communication are important parts of the human body. The Neural System is a well-organized network of point-and-point communication in the human body that allows for rapid communication, while the endocrine system is responsible for the chemical synthesis of hormones.
The cerebrum, the central nervous system, regulates temperature and initiates and regulates movement. Speech, judgment, thinking and reasoning, problem-solving, emotions, and learning are all powered by other parts of the brain.
For example, activities such as writing, dancing, cycling involve control and communication in the human body. As a result, the volunteer nervous system helps us to perform volunteer work under the direction of the brain.
Our activities are controlled by a central nervous system. The cerebrum is in control of our senses, our thoughts, and our emotions. The cerebellum is responsible for muscle contraction and movement.