
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 10 Dec 2024, 17:54 IST
Bohr model of the hydrogen atom was the first atomic model to effectively make sense of the radiation spectra of atomic hydrogen. Niels Bohr presented the atomic Hydrogen model in the year 1913. Bohr Model of the hydrogen atom endeavours to connect specific holes as proposed by Rutherford’s model. It holds a unique spot in history as it led to quantum mechanics by presenting the quantum hypothesis.
Also Check: JEE Organic Chemistry
All things considered, researchers actually had numerous unanswered inquiries, for example,
Bohr resolved this large number of inquiries utilizing an apparently basic suspicion: What assuming electron circles and energies, could display just explicit qualities? You can actually look at Atomic Theory to find out about the different atomic hypotheses set forward by researchers in the mid-twentieth century.
r(n)=n2 x r(1)
Where,
The Bohr’s radius has a value of r(1)=0.529 x 10-10m

Bohr determined the energy of an electron in the nth degree of hydrogen by considering the electrons in a roundabout, quantized circles as:
E(n)=-1/n2 x 13.6eV
Where,
Also Check: Identification of Primary Alcohol
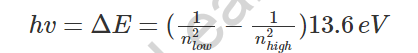
The Heisenberg’s vulnerability standard goes against actual electrons for Bohr existing in explicit circles with a known sweep and speed.
Albeit the advanced quantum mechanical model and the Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom might appear to be immeasurably changed, the key thought is something very similar in both. Traditional material science isn’t adequate to depict every one of the peculiarities that happen on an atomic level. Yet, Bohr was the first to understand the quantization of electronic shells by melding the possibility of quantization into the electronic design of the hydrogen atom and was effectively ready to make sense of the discharge spectra of hydrogen as well as other one-electron frameworks.

Summary:
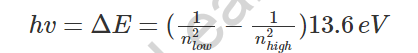
Question: State two limitations of Bohr’s model of the atom.
Answer:
Since hydrogen and hydrogen-like atoms have one electron and, in this manner, don't encounter electron relationship impacts.
The hypothesis noticed that electrons in atoms travel around a focal core in roundabout circles and can circle steadily at an unmistakable arrangement of good ways from the core in specific fixed roundabout circles. Such circles are connected with specific energies and are additionally alluded to as energy shells or energy levels.
Numerous changes have been acquainted with the Bohr model, most outstandingly the Sommerfeld model or Bohr - Sommerfeld model, which recommended that electrons move around a core in curved circles as opposed to round circles of the Bohr model. The Bohr - Sommerfeld framework was confused, adding to numerous mysteries.