
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 17 Apr 2025, 11:41 IST
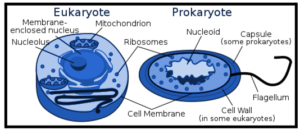
Eukaryotic cells have nuclei enclosed within a nucleus and form larger and more complex organisms. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They were divided under the Eukaryota empire.
They can store different areas in a single cell that allows them to perform different metabolic reactions. This helps them grow many times larger than prokaryotic cells.
The characteristics of eukaryotic cells are as follows:
The structure eukaryotic cell includes the following:
The cytoskeleton exists within the cytoplasm, which contains microfilaments, microtubules, and fibres to provide the complete cell structure, stabilise organelles, and stimulate cell movement.
It is a network of small, tubular structures that divide the cell surface into two parts: luminal and extraluminal.
The nucleus
Golgi Apparatus

Ribosomes
These are the major sources of protein synthesis and are made up of proteins and ribonucleic acids.
Mitochondria
Lysosomes
They are known as “suicide bags” because they contain hydrolytic enzymes that break down proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids.
Plastids
These are two-organ structures and are only found in plant cells. There are three types:
Eukaryotic cells divide during the cell cycle. The cell goes through different stages during the cycle. There are different checkpoints between each stage.
Quiescence (G0)
This is known as the resting phase, and the cell does not split during this phase. The cell cycle begins at this stage. Cells from the liver, kidneys, neurons, and stomach all reach this stage and can remain there for a long time. Most cells do not enter this phase and separate permanently during their lifetime.
At this stage, cells grow and absorb nutrients to prepare for division. It contains three
checkpoints:
Mitosis includes the following stages:
In the division, each cell of the daughter is exactly the same as the original cell.
Eukaryotic cells are found only in plants, animals, skins, protozoa, and other complex organisms. Examples of eukaryotic cells are listed below:
Prokaryotic cells are single-celled microorganisms known as the world’s first. Prokaryotes include Bacteria and Archaea. Photosynthetic prokaryotes include cyanobacteria that produce photosynthesis.
The prokaryotic cell contains a single cell and therefore, all reactions occur within the cytoplasm. They can be free-living or parasites.

Prokaryotic cells have different characteristics. The characteristics of prokaryotic cells are listed below.
The prokaryotic cell does not have a nuclear membrane. However, genes exist locally in the cytoplasm known as nucleoid. They may be round, rod-shaped, or round. The structure of the prokaryotic cell is as follows:
Prokaryotic cells have four main components:
Some prokaryotic structure cells have cilia and flagella that help to break out.
Prokaryote produces in two ways:
Binary Fission
The DNA of living organisms replicates and new copies are attached to the cell membrane.
Reassembling
In this process, genes from a single bacterium are transferred to the genome of other viruses.
It occurs in three forms — conjugation, conversion, transduction.
Examples of prokaryotic cells and structure are listed below:
Bacterial Cells
A prokaryotic cell is an old type of cell characterised by the absence of a nucleus. In addition, prokaryotes do not have cellular organelle bound to the membrane. Prokaryotes are not only unicellular.
Eukaryotic cells are cells that have a real nucleus and organelles bound to the membrane. Eukaryotes can be unicellular or multicellular.
A descriptive feature that distinguishes between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic nucleus. In prokaryotic cells, the true nucleus is absent, in addition, membrane-bound organelles are present only in eukaryotic cells. Another major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that prokaryotic cells are only unicellular, while the same does not apply to eukaryotic cells.