
The microscope is a tool used to make things look bigger. People often use it in labs to study small things. Last time, we talked about different kinds of microscopes. Now, let’s dive into the compound microscope and learn more about it.
Also Check: Autoclave Diagram
A compound microscope is a type of microscope that has two sets of lenses, allowing it to produce a detailed image of the sample in two dimensions.
The term “compound” indicates that it uses multiple lenses. There are two main types of microscopes: compound and simple. The key difference between them is that a simple microscope has just one lens, while a compound microscope has multiple lenses.
Also Check: Nephron Diagram

This compound microscope diagram for class 9, 10, 11 and 12.
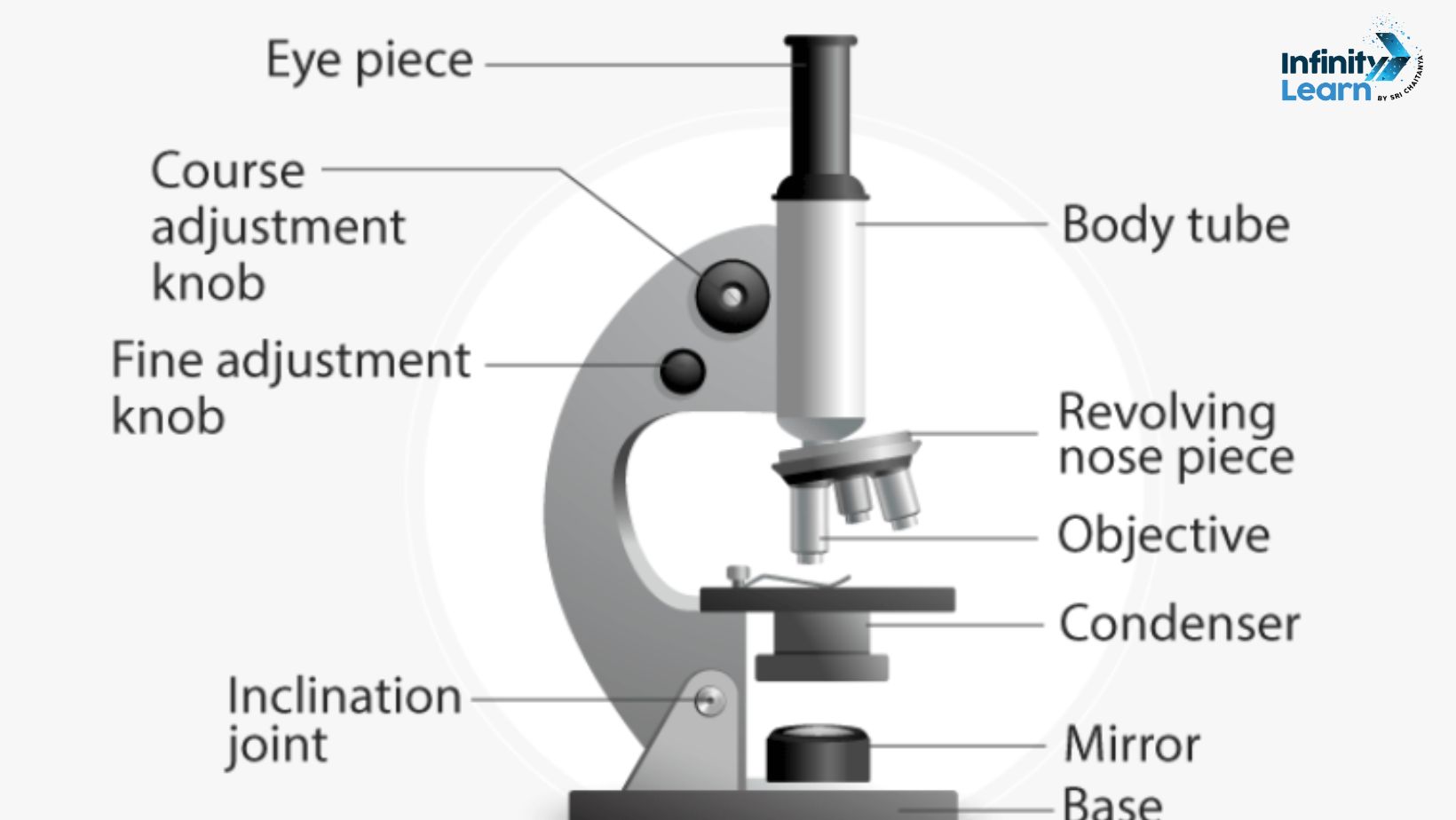

Also Read: Resolving power of Microscope
The compound microscope is mainly used for studying tiny details of cells, tissues, or parts of organs. It has two main parts:
Non-optical parts:
Optical parts:
There are different types of objective lenses for various levels of magnification and ocular lenses for different magnification strengths. Binocular head makes viewing easier with two eyepieces and special mirrors and prisms.
The mechanism involves light passing through the specimen, and the objective lens magnifies the image. The ocular lens further magnifies the image, which is then viewed by the user.
The compound microscope consists of two main lenses: the ocular lens (eyepiece) and the objective lens. It also has a mirror for illumination, a stage to place the specimen, and an arm and base for support.
The working principle is based on refraction. Light from the specimen passes through the lenses, bending at different angles to form a magnified image, which the eye perceives.
A concave mirror is typically used in a compound microscope to focus light onto the specimen for better illumination.