
Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 19 Nov 2024, 16:34 IST
The refractive index is said to be the ratio of the speed of light in a medium to the speed of light in a vacuum. Once light travels in a medium other than the vacuum, the atoms of that medium absorb and re-emit light particles, slowing the speed of light.
The phrase refractive index can also refer to the refraction index or index of refraction. The flow rate of light in a medium has been determined by the medium’s properties. The rate of motion of electromagnetic waves is determined by the optical density of the medium. The desire of atoms in a material to restore absorbed electromagnetic energy is referred to as optical density. The slower the speed of light, the more optically dense the material. The refractive index is one such indicator of a medium’s optical density.
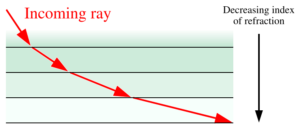
In fact, glass has a refractive index of 1.52 and water has a refractive index of 1.33. Because glass has a higher refractive index than water, the speed of light in water is faster than the speed of light through glass. When the refractive index of one medium exceeds that of another, the first medium is said to be optically denser. The majority of the substances we know have a positive refractive index with a value greater than zero. When a material has negative permittivity and permeability, it has a negative refractive index. The refractive index measures the relative speed of light in various media.
We can say that the refractive index has no dimensions. This is a number that represents how many times slower a light wave would be in the material than it would be in a vacuum. The refractive index, symbolised by n, is the ratio of light velocity in vacuum to light velocity in a medium and it is calculated using the formula n = c/v.
The dimensional formula refractive index can be represented as:
[M0 L0 I0 T0]
Here,
M = Mass
L = Length

T = Time
We have, Refractive Index (n) = speed of light in vacuum × [speed of light in medium]-1
As because, Speed = Distance × [Time]-1
Therefore, the dimensional formula of speed = [M0 L1 T-1]
Since the refractive index is the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum and medium.
Now, the Refractive Index (n) = [M0 L1 T-1] × [M0 L1 T-1]-1
Thus, the refractive index has been dimensionally represented as [M0 L0 I0 T0].
Refractive Index (RI) has no unit because it is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a medium. Since both speeds are measured in the same units (e.g., meters per second), the units cancel out, leaving the refractive index as a pure number without any dimensions or units.
The refractive index (n) can be calculated using the formula:
n = c / v
where c is the speed of light in a vacuum, and v is the speed of light in the medium. Alternatively, for light passing between two media, the refractive index can also be
calculated as the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction:
n = sin i / sin r
where i is the angle of incidence, and r is the angle of refraction.
The refractive index is a dimensionless quantity because it is the ratio of two quantities (speeds) with the same dimensions. Hence, the dimensional formula for the refractive index is:
[RI] = [M0L0T0]
Refractive index is dimensionless because it is derived as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a medium. Since both speeds have the same dimensions ([LT-1]), the ratio has no dimensions, making it a pure, dimensionless number.
The refractive index of glass, like any other material, is dimensionless. Its dimension is represented as:
[M0L0T0]
This is because the refractive index is a ratio of similar physical quantities and does not carry any inherent dimensions.