










Courses

By Brijesh Sharma
|
Updated on 28 May 2025, 16:47 IST
P-block elements are a diverse group of elements found in groups 13 to 18 of the periodic table. These elements include metals, non-metals, and metalloids, each with unique properties and wide-ranging applications in everyday life, industry, and science. The term "p-block" refers to the filling of the p-orbital in the atoms of these elements as you move across the periodic table. Some of the most well-known p-block elements include carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and halogens, which play crucial roles in organic chemistry, environmental processes, and industrial applications.
P-block elements exhibit a wide variety of chemical behaviors, making them essential in various fields such as energy production, agriculture, medicine, and technology. They are involved in forming vital compounds like carbon dioxide, ammonia, sulfuric acid, and silicon dioxide, which are used in numerous industrial processes. Understanding the properties, uses, and important compounds of p-block elements is important for anyone studying chemistry and for those seeking to understand the elements that shape our world.
This group of elements also includes noble gases like helium, neon, and argon, which are known for their stability and non-reactivity. These gases have important applications in lighting, medical technologies, and creating inert environments in various industrial settings. The versatility of p-block elements in both chemical bonding and real-world applications makes them a key focus of study in chemistry and related sciences.
The periodic table is a classification of elements that share similar properties. One such classification is the p-block elements. These elements are located in groups 13 to 18 of the periodic table and are characterized by the filling of the p-orbital with electrons. The p-block elements include a wide range of metals, non-metals, and metalloids, making them an important part of the periodic table.
These elements are diverse in their chemical and physical properties. They play essential roles in various chemical reactions and are involved in many industrial and biological processes. The p-block elements consist of familiar elements like carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and halogens, all of which are crucial in different fields, from organic chemistry to environmental science.
The properties of p-block elements vary greatly depending on their group, but some general characteristics are shared among them:
Loading PDF...
The p-block elements have various uses across industries and daily life. Below are some of the most important uses:
The element in which the last electron enters the outermost p-subshell is referred to as a P block element. In the periodic table, the P block begins with the 13th group and ends with the 18th group.
When the total number of valence electrons, i.e. the sum of 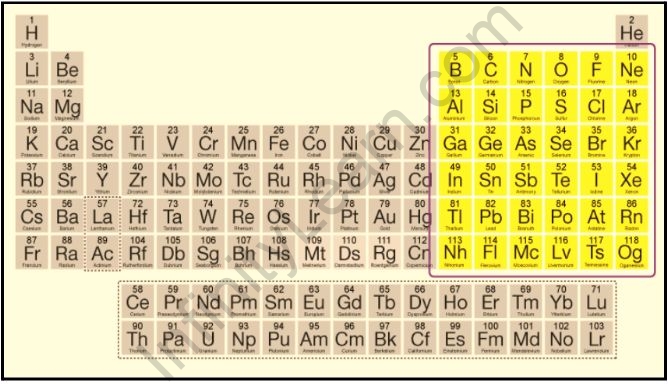 S and P electrons, is equal to a total number of valence electrons, the oxidation state of elements in the p – block is maximum. One of the most intriguing aspects of the p-block elements is the presence of both nonmetals and metalloids.
S and P electrons, is equal to a total number of valence electrons, the oxidation state of elements in the p – block is maximum. One of the most intriguing aspects of the p-block elements is the presence of both nonmetals and metalloids.

P-block elements also form a variety of important compounds that have wide-ranging applications. Some of these include:
Here is a table summarizing the important compounds of the p-block elements and their uses:

JEE

NEET

Foundation JEE

Foundation NEET

CBSE
| Compound Name | Formula | Uses |
| Carbon Dioxide | CO₂ | Photosynthesis, greenhouse gas, carbon cycle |
| Ammonia | NH₃ | Fertilizers, cleaning agents, refrigeration |
| Sulfuric Acid | H₂SO₄ | Fertilizers, detergents, petroleum refining |
| Hydrogen Fluoride | HF | Uranium production, aluminum manufacturing |
| Silicon Dioxide | SiO₂ | Glass manufacturing, construction, semiconductors |
Here are a few practice problems related to p-block elements that can help test and improve your understanding:
Problem 1: What is the general trend of electronegativity in p-block elements as you move across a period? Why?
Solution: Electronegativity increases as you move across a period in the p-block because the atomic size decreases, and the ability to attract electrons becomes stronger.
Problem 2: Identify the oxidation states of nitrogen in nitric acid (HNO₃) and ammonia (NH₃).

Solution: In HNO₃, nitrogen has an oxidation state of +5, while in NH₃, nitrogen has an oxidation state of -3.
Problem 3: What is the major use of chlorine in the chemical industry?
Solution: Chlorine is mainly used in the production of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) plastic and as a disinfectant in water treatment.
Problem 4: Which p-block element is commonly used in the production of solar cells and why?
Solution: Silicon is used in solar cells because it is a semiconductor that efficiently converts sunlight into electrical energy.
P-block elements are essential in various chemical, industrial, and biological processes. From the non-metals like oxygen and nitrogen to the metals like tin and lead, these elements contribute significantly to our daily lives and technological advancements. Understanding their properties, uses, and important compounds helps in the application of these elements across many fields.
No courses found
The p-block elements are the elements found in groups 13 to 18 of the periodic table. These elements include metals, non-metals, and metalloids, and they are characterized by the filling of the p-orbital with electrons.
P-block elements exhibit a range of properties, such as varying electronegativity, multiple oxidation states, and the presence of metals, non-metals, and metalloids. They also differ in physical states, from gases like oxygen to solids like silicon.
Some important compounds include carbon dioxide (CO₂), ammonia (NH₃), sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), hydrogen fluoride (HF), and silicon dioxide (SiO₂), which have wide applications in industries such as fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and construction.
P-block elements are used in a variety of ways, such as oxygen in respiration, nitrogen in fertilizers, fluorine in Teflon, and silicon in electronics and solar panels, making them essential to both daily life and technological advancement.
The oxidation states of p-block elements can vary greatly depending on the group. For example, elements in group 13 typically exhibit oxidation states of +3, while elements in group 17, like halogens, have oxidation states of -1. Additionally, some elements show multiple oxidation states.