










Courses

By Karan Singh Bisht
|
Updated on 18 Apr 2025, 16:33 IST
Zener diodes are the devices that facilitate current flow in both forward and reverse directions. As ubiquitous semiconductor diodes, Zener diodes hold pivotal significance in electronic circuits.
Therefore, read the article below to know what is Zener diodes, their definition, reverse bias operation, breakdown mechanisms (including avalanche breakdown and Zener breakdown), Zener diode symbols, V-I characteristics, and applications of Zener diode.
Zener diodes are the devices that facilitate current flow in both forward and reverse directions. It's special because it works backwards, unlike most electronic parts. When you flip the electric power, and it reaches a certain point (the Zener Voltage), it lets the electric current go the other way. This special thing is called the Zener Effect, and it makes Zener Diodes handy in electronics for specific tasks.
A Zener diode is a special semiconductor gadget made to work the opposite way. It's supercharged with various Zener voltages (Vz), and some types can even be adjusted to control different voltages.
These are like a tool in electronics that can handle things going backwards and has a range of voltage superpowers, making it useful for controlling and adjusting voltages in different electronic devices.
How does zener diode work in reverse bias? A Zener diode operates akin to a conventional diode in forward-biased mode. However, during reverse-biased conditions, a nominal leakage current traverses the diode. The diode begins to conduct current as the reverse voltage escalates and attains the pre-established breakdown voltage (Vz). This current achieves a maximum level dictated by the series resistor and stabilises, persisting consistently over a broad spectrum of applied voltages.
Loading PDF...
When exposed to elevated reverse voltage, avalanche breakdown can manifest in both standard diodes and Zener diodes. Free electrons acquire sufficient energy to accelerate at heightened speeds when applying a substantial reverse voltage across the PN junction. These accelerated electrons undergo collisions with other atoms, leading to the liberation of additional electrons.
This continuous collision generates many free electrons, precipitating a swift surge in electric current through the diode. In the case of a conventional diode, this abrupt escalation in current could inflict permanent damage.
However, a Zener diode is meticulously engineered to endure avalanche breakdown and manage the abrupt spike in current. Avalanche breakdown typically transpires in Zener diodes with a Zener voltage (Vz) surpassing 6V.
As the reverse bias voltage applied to a Zener diode nears its Zener voltage, the electric field within the depletion region becomes potent enough to pull and detach electrons from their valence band.

These energised valence electrons, influenced by the intense electric field, detach from their parent atoms. This occurrence unfolds in the Zener breakdown region, where even a minor uptick in voltage triggers a swift upsurge in electric current.
The Zener effect is more noticeable at voltages up to 5.6 volts, and beyond that point, the avalanche effect becomes more prominent. While both effects share similarities, the key difference is that the Zener effect is a quantum phenomenon, whereas the avalanche effect involves the movement of electrons in the valence band, akin to an electric current. The avalanche effect enables a larger current to pass through the diode compared to what a Zener breakdown would allow.

JEE

NEET

Foundation JEE

Foundation NEET

CBSE
Zener diodes are available in various packaging options as per their power dissipation needs. From those designed for high-power applications to surface mount formats, the packaging varies. The commonly used Zener diode is housed in a small glass enclosure featuring a distinctive band to indicate the cathode side of the diode.
The symbol representing a Zener diode in circuit diagrams resembles that of a regular diode but with a unique addition. It includes a triangle or arrowhead pointing towards the cathode side (the side with the band) of the diode.
This triangle is accompanied by two perpendicular lines at the cathode end – one extending upwards and the other downwards. These lines convey the specific behaviour of the Zener diode, differentiating it from other diode types in circuit diagrams. This symbol serves as a visual cue, helping engineers and technicians easily recognise and comprehend the presence of a Zener diode in a circuit.

The V-I characteristics of a Zener diode illustrate its behaviour under different voltage conditions. When reverse-biased voltage is applied, the Zener diode allows only a small leakage current until the voltage is less than the Zener voltage.
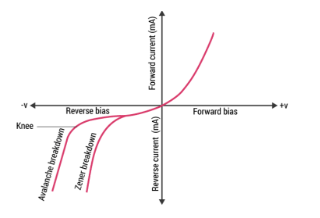
The forward characteristics of a Zener diode describe how the diode behaves when it is forward biased (i.e., when the positive terminal is connected to the anode and the negative terminal to the cathode).
Forward Voltage Drop: In the forward bias condition, the Zener diode behaves like a regular diode. Initially, the current through the diode is very small. As the forward voltage increases, the current increases rapidly once the threshold voltage is reached, typically around 0.7V for a silicon Zener diode.
Under reverse voltage, a small reverse saturation current (Io) flows due to thermally generated minority carriers. As the reverse voltage increases, there's a sharp rise in reverse current, indicating breakdown. This voltage is termed the breakdown voltage or Zener voltage (Vz).
Zener diodes are semiconductor devices that find various applications due to their unique ability to regulate voltage. Here are some common applications of Zener diodes:
No courses found
A Zener diode is a type of diode that allows current to flow normally in the forward direction but also permits reverse current flow when the voltage exceeds a certain value, known as the Zener breakdown voltage.
The main use of a Zener diode is voltage regulation. It maintains a stable output voltage despite variations in the input voltage, often used in power supplies and surge protectors.
Zener breakdown occurs in Zener diodes when the reverse voltage reaches a critical point, causing the diode to conduct in the reverse direction. Avalanche breakdown happens at higher voltages, where the reverse current increases rapidly due to the breakdown of the diode's junction.
A Zener diode is primarily used for voltage regulation, protecting circuits from voltage spikes, and in applications that require precise voltage control in reverse bias.
A Zener diode can be identified by its symbol, which is similar to a regular diode but with two additional lines at the cathode side to represent the breakdown region. Additionally, its reverse breakdown voltage is marked on the diode’s package.
The Zener effect refers to the phenomenon where a Zener diode conducts current in the reverse direction when the reverse voltage exceeds a specific value, causing the diode to maintain a stable voltage.
A Zener diode is used for voltage regulation, protecting circuits from overvoltage, clipping, and shunt voltage regulation in power supplies.
A Zener diode is used in DC circuits, especially for regulating the voltage in reverse bias conditions. It is not typically used in AC circuits unless it is part of a rectifying or protection system.
A Zener diode is a special-purpose diode, designed for reverse breakdown operation at a specific voltage, often used in voltage regulation and protection applications.