










Courses

By Shailendra Singh
|
Updated on 23 Jul 2025, 17:12 IST
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 – Our Changing Earth help students learn how the surface of the Earth keeps changing all the time. This chapter explains that the movements of the Earth are caused by two types of forces – endogenic forces (from inside the Earth) and exogenic forces (from outside the Earth). Natural events like earthquakes and volcanoes are caused by endogenic forces and often lead to mass destruction.
On the other hand, slow processes like weathering and erosion continuously wear away the landscape. The Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 Questions and Answers cover all the important concepts in an easy way. These NCERT Solutions are prepared by experts to match the latest CBSE Class 7 Social Science syllabus. You can also download the FREE PDF of Our Changing Earth Class 7 to study anytime and clear your basics.
The movements of Earth are isolated based on the powers, which cause them. The powers, which act inside of the Earth are called Endogenic powers and the powers that work on the outer layer of the Earth are called Exogenic powers. Quakes and Volcanoes cause mass annihilation over the outer layer of the Earth.
The scene is in effect ceaselessly eroded by two cycles – enduring and disintegration. These NCERT Solutions for 7th Class Social Science Geography give students answers for every one of the inquiries spread out in the NCERT 7th Class Social Science Geography coursebook.
The NCERT Solutions for 7th Class Social Science Chapter 3 – Our Changing Earth help students understand how natural forces like earthquakes, volcanoes, and rivers shape the Earth's surface. These easy-to-follow answers explain tough topics in simple words, making learning fun and clear.
Students can use these NCERT Solutions to prepare better for exams and complete homework quickly. You can also download the PDF for all chapters for free and study anytime, anywhere. It’s a smart way to boost your knowledge and score well in Social Science. Simply Click link to download PDF.
Loading PDF...
Ques 1. Why do the plates move?
Ans. The Lithospheric plates move around because of the movement of the molten magma inside the Earth.
Ques 2. What are exogenic and endogenic forces?
Ans. Earth’s movements are divided on the basis of the forces which cause them. The ones that work on the Earth’s surface are called exogenic forces while the ones that works in the Earth’s interior are called endogenic forces. The erosional and depositional activities of wind and water are examples of exogenic forces. Earthquakes and volcanoes are examples of endogenic forces.

Ques 3. What is erosion?
Ans. Erosion is the weathering or wearing away of the landscape by different agents like wind, water, and ice.

JEE

NEET

Foundation JEE

Foundation NEET

CBSE
Ques 4. How are flood plains formed?
Ans. During its course through a plain, a river sometimes over flows its banks. This leads to the flooding of the neighbouring areas. As it floods, the river water deposits layers of fine soil and sediments on its banks. This leads to the formation of a flat, fertile flood plain.
Ques 5. What are sand dunes?
Ans. In deserts, when the wind blows, it lifts and transports sand from one place to another. When it stops blowing, the sand particles fall and get deposited in low hill-like structures called sand dunes.

Ques 6. How are beaches formed?
Ans. The erosional and depositional activities of the sea waves give rise to different coastal landforms. A beach is one such coastal landform. It is formed when the sea waves deposit sediments along the seashore.
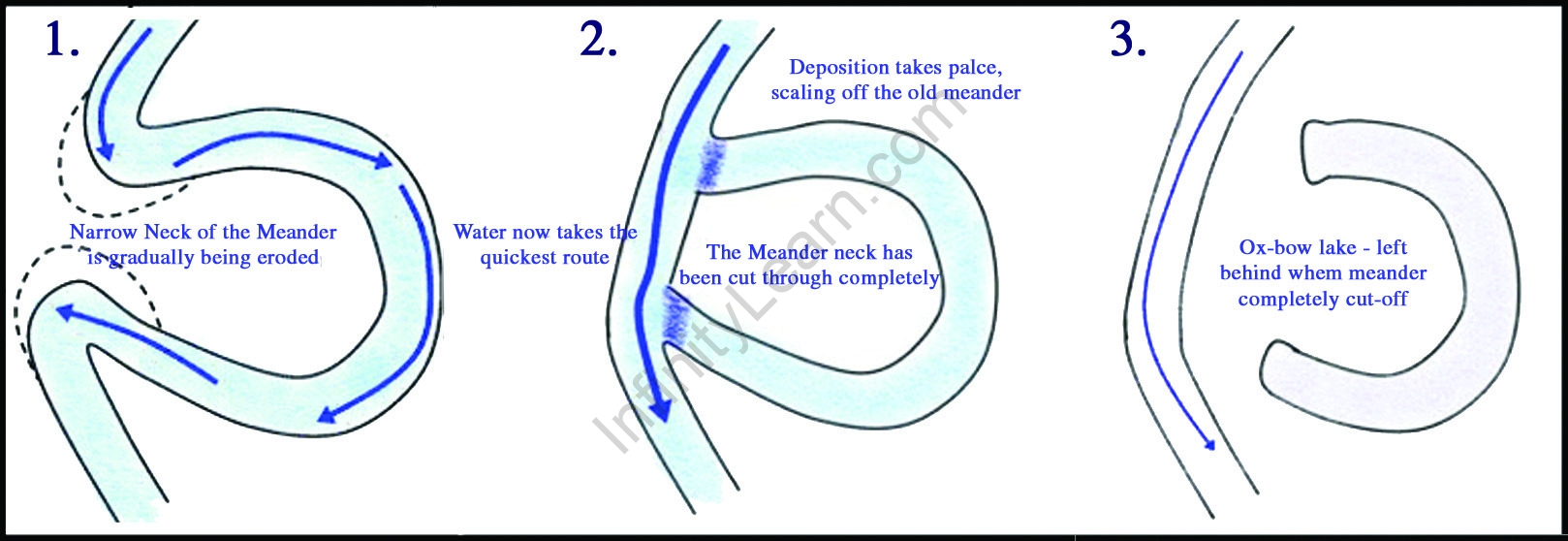
Ques 7. What are ox-bow lakes?
Ans. An ox-bow lake is a crescent-shaped lake formed by a meandering river. During its journey through a plain, a river twists and turns to form meanders. Erosion and deposition occur constantly along the sides of a meander, thereby causing the ends of its loop to come closer and closer. In due course of time, the meander loop cuts off from the river and forms a cut-off, crescent-shaped ox-bow lake.
(i) Which is not an erosional feature of sea waves?
(a) Cliff
(b) Beach
(c) Sea cave
Answer: b
(ii) The depositional feature of a glacier is:
(a) Flood plain
(b) Beach
(c) Moraine
Answer: c
(iii) Which is caused by the sudden movements of the earth?
(a) Volcano
(b) Folding
(c) Flood plain
Answer: a
(iv) Mushroom rocks are found in:
(a) Deserts
(b) River valleys
(c) Glaciers
Answer: a
(v) Oxbow lakes are found in:
(a) Glaciers
(b) River valleys
(c) Deserts
Answer: b
| (i) Glacier | (a) Seashore |
| (ii) Meanders | (b) Mushroom rock |
| (iii) Beach | (c) River of ice |
| (iv) Sand dunes | (d) Rivers |
| (v) Waterfall | (e) Vibrations of earth |
| (vi) Earthquake | (f) Seacliff |
| (g) Hard bedrock | |
| (h) Deserts |
Answer:
| (i) Glacier | (c) River of ice |
| (ii) Meanders | (d) Rivers |
| (iii) Beach | (a) Seashore |
| (iv) Sand dunes | (h) Deserts |
| (v) Waterfall | (g) Hard bedrock |
| (vi) Earthquake | (e) Vibrations of earth |
Some rocks have the shape of mushrooms.
As we know that wind in deserts is an active agent of erosion and deposition. Winds erode the lower section of the rock more than the upper section. So, such rocks have a narrower base and wider top, which gives them a mushroom-like appearance. Hence, some rocks in deserts have mushroom-like shapes.
Flood plains are very fertile.
Flood deposits layers of fine soil and other materials called sediments along its banks. This leads to the formation of fl at fertile flood plain. Hence, these flood plains have fertile soil.
Sea caves are turned into stacks.
As the sea caves’ cavities become bigger and bigger only the roof of the caves remain, thus forming sea arches. Again, erosion even breaks the roof and only walls are left. These wall-like features are called stacks. In this way, sea caves change into stacks.
Buildings collapse due to earthquakes.
i) Earthquakes are the sudden vibrations caused within the Earth’s surface as a result of the movement of the Lithospheric plates.
ii) Such vibrations, when they are of high intensity, cause damage to the things on the Earth’s
iii) Various human-made (e.g., buildings) and natural (e.g., trees) constructions can break down and collapse under the effect of the vibrations because they are situated on the Earth’s surface.
Our Changing Earth Summary
This part from the NCERT Social Science Geography book gives definite data about:
Our Environment is the NCERT Social Science Geography book for students in Class 7. For NCERT Solutions for 7th Class Social Science, visit the connected article.
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 7 PDF from Here
No courses found
The topics that are canvassed in the 3rd Chapter of NCERT Solutions for 7th Class Social Science Geography are –
Before launching with test arrangements, students really should be aware of the total prospectus first. Afterward, a strong report plan designating time for every one of the subjects must be made. The NCERT Solutions at INFINITY LEARN give replies to every one of the reading material inquiries to hone the applied information and critical thinking abilities of students. Every one of the arrangements PDF can be gotten to involving the download choice for nothing with no time limitations.
At the point when the breeze blows, it lifts and transports sand starting with one spot then onto the next. At the point when the breeze quits blowing, the sand falls and gets saved in the low slope-like constructions. These are called sand rises. They are generally found in desert regions. To get more familiar with the principle points and accomplish a solid hold over them, students ought to allude to the NCERT Solutions made by individual informed authorities at Infinity Learn.
The chapter talks about physical, chemical, and biological weathering that break or change rocks in different ways.
The focus is to help students understand how the Earth's surface keeps changing due to natural forces.
Rivers erode rocks and soil, carry them away, and deposit them in other places to form valleys and plains.
An earthquake is a sudden shaking of the Earth’s surface caused by movements inside the Earth.
Glaciers move slowly and carve the land, creating valleys and changing landforms over time.
They give correct answers, save time, and help in better understanding of important concepts.
Deposition is the process where rivers or wind drop the soil and rocks they carry, forming new land.
It helps us know how mountains, valleys, and earthquakes form and how they affect life on Earth.