Table of Contents
Introduction:
The word “taxonomy” comes from two words, “taxis” meaning planning and “nomos” meaning laws. Plant taxonomy deals with the classification of plants according to certain established rules. The term taxonomy was coined by the Swiss botanist A. P. de Candolle in his book “Théorie élémentaire de la botanique”.
Plant taxonomy can be defined as a branch of plant science responsible for the classification of plants, identification, classification, and classification of plants based on their similarities and differences.
The principles of plant taxonomy are:
- Identification: identify unknown species based on their characteristics and compare them with existing species
- Feature: describe all the features of the newly identified species
- Classification: classifying and classifying known species into different groups or taxa according to similarities and differences
- Nomenclature: to give a scientific name in a meeting
TAXONOMY AND SYSTEMATICS
The Taxonomic Hierarchy is the process of arranging biodiversity into successive ecosystems by decreasing or evolving from one empire to another and vice versa. ” Each of these levels of royalty is called the taxonomic class or rank.
The term systematics comes from the word ‘system’, which means the orderly arrangement of living organisms. It takes into account the evolutionary relationship of living things. Plant systematics discusses the relationship between plants and their evolution. Systematics studies biological diversity and organizes information into phases.
Living things are categorized on the basis of similarity, intimacy, or relationships between them. It shows phylogenetic relationships between different organisms and shows their lineage. Individual similarities suggest that they may have descended from a common ancestor. It shows the evolutionary process of modern living things. Biologically related organisms are grouped into groups, which share the same genes.
Organisms are categorized into different taxonomic categories according to their specific characteristics.
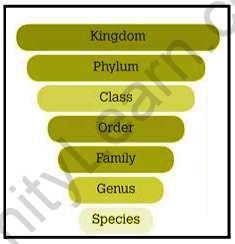
The different taxonomic categories respectively are:
- Kingdom
- Phylum
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
The number of common characteristics decreases as we move from species to the kingdom, where species having fundamental similarities and organisms in the same kingdom have the least common features.
NUMERICAL SYSTEMATICS
Numerical taxonomy is a classification system in biological systematics that deals with the classification of numbers of taxonomic units based on the characteristics of their characters. It aims to create a taxonomy using numerical algorithms as a group analysis rather than using an independent assessment of their properties. The concept was first developed by Robert R. Sokal and Peter H. A. Sneath in 1963 and later described by similar authors. They have divided the field into phenetics where classification is formed based on patterns of overall similarity and cladistics where classification is based on branch patterns of the limited evolutionary history of taxonomy.
Although intended as a method of objective, the actual selection and specificity of the symptoms are influenced by the available data and the research interests of the researcher. The goal was to introduce specific steps that should be used to create dendrograms and cladograms using numerical methods rather than independent data combinations.
MOLECULAR SYSTEMATICS
Molecular systematics is the use of molecules to determine systems of separation and relationships. For centuries botanists have used morphology, or the appearance of all of them, to identify and classify plants. Morphological systematics was important in understanding basic plant origins and relationships; however, it has its limitations. Another limitation in morphology in plants is homology. Homology assumes that two identical buildings have the same origin of evolution. In other words, this trait was inherited from the ancestor and was passed on to his offspring. Homology in plant morphology is often very difficult to resolve as plant structures can be transformed into other species (e.g., spine leaves of cacti are altered).
ANGIOSPERM SYSTEMATICS
Angiosperm, also called flowering plant, or any other species of about 300,000 flowering plants, is the largest and most diverse group within the Plantae kingdom. Angiosperms represent about 80 percent of all known green plants now living. Angiosperms are vascular seed plants in which the egg (egg) fertilizes and grows into a seed in an empty, empty uterus. The ovary itself is usually closed in flower, that part of the angiospermous plant that contains the male or female reproductive organs or both. The fruit is found in the growing parts of the flowers of the angiospermous plant and is therefore a feature of angiosperms. In contrast, in gymnosperms (e.g., conifers and cycads), another large group of vascular sperm plants, the sperm do not develop trapped inside the ovary but are often transported to the surface of reproductive structures, such as cones.
Also read: Important Topic Of Biology: Lichens
FAQs
What Is the Importance of Taxonomy?
Humans are a part of nature and plants, animals, and other living things play a vital role in human life. Whether our food needs, medical needs, industrial needs are all accomplished by the diversity of life on earth. Both the useful and the harmful aspects of biodiversity must be clear to us in order to be used effectively and thus the orderly planning (taxonomy) of biodiversity becomes a necessity. And compounding and integrating taxonomical breeding is very helpful in finding similarities and differences between different species.
Explain the Principles of Taxonomy.
Taxonomy is part of systematics but both terms are used in the same way.
The principles of systematics or taxonomy are-
- Diagnosis- This refers to the identification of an organism, looking at its morphological and anatomical features, studying it using various key points.
- Classification- On the basis of research on biological identification assigned a different level of tax based on its characteristics.
- Nomenclature- This refers to the invention of a living thing with a scientific name that remains the same all over the world to avoid any confusion. The scientific name contains the name of the species and species of animals.
- Eg. Mangifera indica (Genus) – mango (Species)








