Table of Contents
Introduction:
Cardiac output: The quantity of blood the heart pumps through the circulatory system in a minute. The stroke volume is the amount of blood put out by the heart’s left ventricle in one contraction. The attack volume and the heart rate specify the cardiac output. An average adult has a cardiac output of 4.7 liters (5 quarts) of blood per minute. The cardiac progression is all the heart’s actions were through one complete heartbeat; it is through one contraction and relaxation of both atria and ventricles. The contraction event is called systole, and the relaxation event is diastole.
Overview:
Cardiac output (Q) is the quantity of blood pumped by the heart each minute. Resting cardiac output in trained and sedentary individuals is approximately 4 to 5 L/min. Still, during exercise, the maximal cardiac output can reach 20 L/min. Maximum cardiac output in an individual depends on many factors, including age, posture, body size, presence of cardiac disease, and physical conditioning. During dynamic exercise, cardiac output initially increases with increasing exercise intensity by increases in SV and HR. Increases in cardiac output initially beyond 40% to 50%, however, is accounted for only by increases in HR.77,119,124
Cardiac output definition:
The procedure of the heart is to drive blood through the circulatory system in a cycle that transmits oxygen, nutrients, and chemicals to the body’s cells and removes cellular trash. Because it throws out whatever blood attains back into it from the venous system, the quantity of blood returning to the heart determines the amount of blood the heart pumps out – its cardiac output, Q. Cardiac output is classically distinguished alongside stroke volume (SV) and the heart rate (HR).
Factors affecting the cardiac output
Factors affect cardiac happenings by changing heart rate and stroke volume. Primary factors include blood volume revulsions, autonomic innervation, and hormones. Secondary factors include extracellular fluid ion attention, body temperature, feelings, coitus, and age.
Cardiac output classification:
- Cardiac output (CO), also comprehended as heart output denoted by the symbols {Q}is a term used in the cardiac study that describes the volume of blood pumped by the heart, left and right ventricle, per unit time.
- Cardiac output (CO) is the outcome of the heart rate (HR), i.e. the number of heartbeats per minute (bpm) and the stroke volume (SV), which is the magnitude of blood pumped from the ventricle per beat; thus, CO = HR × SV.
- The importance of cardiac output is usually denoted as L/min. For a fit person weighing 70 kg, the cardiac production at rest averages about 5 L/min; Because cardiac output pertains to the quantity of blood delivered to various parts of the body, it is a crucial component of how efficiently the heart can meet the body’s demands to maintain adequate tissue perfusion.
- Body tissues compel continuous oxygen delivery, which imposes the sustained transport of oxygen to the tissues by the systemic circulation of oxygenated blood at an adequate pressure from the heart’s left ventricle via the aorta and arteries.
- Oxygen delivery (DO2 mL/min) is the result of blood flow (cardiac output CO) times the blood oxygen content (CaO2).
Mathematically this is computed as follows:
Oxygen delivery = cardiac output × arterial oxygen content
DO2 = CO × CaO2
With a resting cardiac outcome of 5-liter min−1, ‘normal’ oxygen delivery is 997.5 ml min. The amount of the /percentage of the circulated oxygen consumed (VO2) per minute through metabolism differs depending on the activity level but at rest is circa 25% of the DO2. Manual exercise requires a higher than resting level of oxygen consumption to benefit increased muscle activity. In the case of heart failure, actual CO may be insufficient to sustain even an adequate daily living training camp and I, nor can it increase sufficiently to meet the higher metabolic demands stemming from even moderate workouts.
Cardiac output is an accepted blood flow parameter of interest in hemodynamics, the study of blood flow. The components affecting stroke volume and heart rate also affect cardiac production.
Importance of chapter for JEE primary, Neet, and Board Exams:
The unit has a vital part to play in the different examination syllabus. It makes us aware why Keeping track of your heart rate can give you insight into your fitness level, heart health, and emotional health, and many people are walking around with a resting heart rate that is too high due to factors such as too much caffeine, dehydration, inactivity, and persistent stress. That extra heartbeats over time can be taking years off your life. Learning about cardiac output makes the person aware of a healthy lifestyle and makes them know about the importance of measuring the heart rate and why staying fit is a crucial part of daily living.
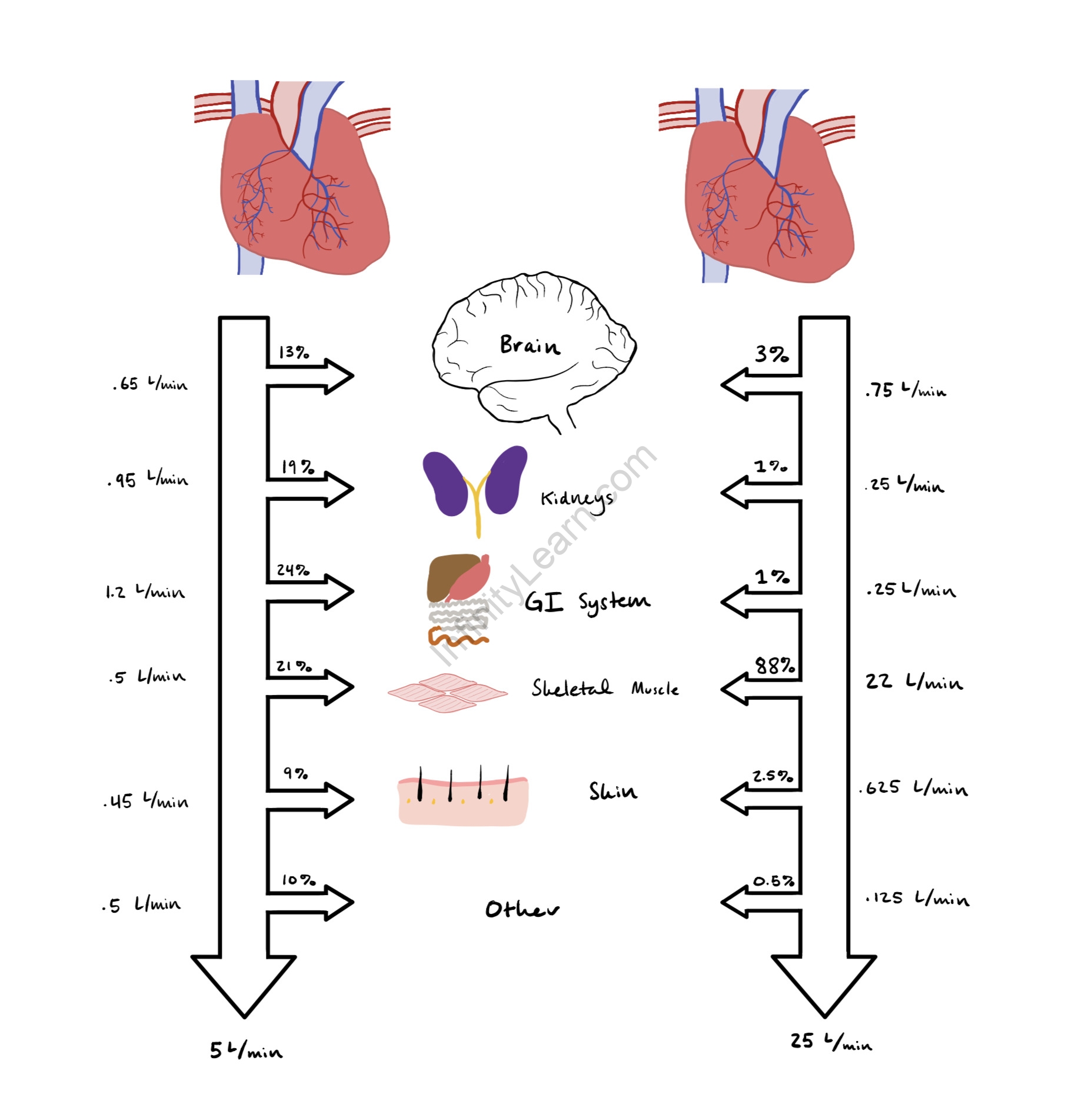
Various cardiac output, including the detailed analysis of heart function and its importance in the human body, is available here. There are many materials and quantities in bio. Distinct units can be used to express different amounts in biology. Students who want to flourish in bio can get a good knowledge of specific topics from the article. The comprehensive unit of cardiac output is provided here to assist students in effectively understanding the respective issue. Continue to visit our website for additional biology help.
Also read: Structure Of The Human Heart
FAQs:
What do you understand by cardiac output?
Cardiac output: The quantity of blood the heart pumps through the circulatory system in a minute. The stroke volume is the amount of blood put out by the heart's left ventricle in one contraction.
Who has introduced the concept of measuring cardiac output?
In 1628 William Harvey proved the existence of blood circulation by calculating the cardiac output in half an hour.
What are the factors that affect the heart rate of human beings?
Factors affect cardiac happenings by changing heart rate and stroke volume. Primary factors include blood volume revulsions, autonomic innervation, and hormones. Secondary factors include extracellular fluid ion attention, body temperature, feelings, coitus, and age.
Why is it essential to keep track of cardiac output?
It makes us aware why Keeping track of your heart rate can give you insight into your fitness level, heart health, and emotional health, and many people are walking around with a resting heart rate that is too high due to factors such as too much caffeine, dehydration, inactivity, and persistent stress. That extra heartbeats over time can be taking years off your life. Learning about cardiac output makes the person aware of a healthy lifestyle and makes them know about the importance of measuring the heart rate and why staying fit is a crucial part of daily living.
What regulates cardiac output?
Cardiac output is regulated and affected by many factors, such as atrial and ventricular reflexes, including the autonomic nervous system, hormones, blood ion concentration, and emotions.








