Table of Contents
Important Topic Of Biology: Thyroid
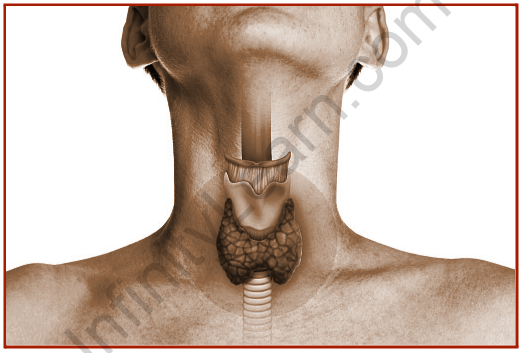
The thyroid gland in the human body is a system of glands and organs where these are found in front of the neck wrapped around the trachea. It helps to regulate all the functions of the human body and metabolism. As for how the nervous system creates connections through neurotransmitters and nerve impulses, the thyroid gland produces hormones to regulate many vital bodily functions.
When you talk about Biology topics, the thyroid gland is an important concept that stands out in everything. If you have studied biology in your previous classes, you are likely to know these words, their actions, and other related topics. Today, we will discuss the thyroid in more detail. Without wasting time, let’s get started!
The thyroid is a small organ in front of the neck, wrapped around the windpipe. It is butterfly-shaped, small in the middle with two broad wings extending to the side of your throat. The thyroid gland is starving. You have glands throughout your body when they create and release substances that help your body do something. Your thyroid makes hormones that help control many of the vital functions of your body.
Definition of the Thyroid
The thyroid gland, located in the cervical region, is a large non-pituitary gland that produces hormones itself to regulate growth and development, heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature.
Location and weight of Thyroid Gland:
The thyroid is a malignant disease in humans and animals. It is an endocrine-free gland and hides in the bloodstream. It is found in the anterior part of the neck. The thyroid gland is similar to that of a butterfly. A normal thyroid weighs 25-30 g. Among the endocrine glands present, the thyroid is said to be one of the major endocrine glands. On both sides of the trachea, the thyroid gland has two lobes. Each lobe is approximately 4-6 cm long and approximately 1.3-1.8 cm wide.
Thyroid Gland Activities:
The main functions of the thyroid gland include the production of two hormones. Two hormones are Triiodothyronine (T3) hormone and Thyroxine (T4). These hormones play a vital role and are needed in almost all tissues of the human body.
Triiodothyronine (T3) thyroid hormone is produced by the thyroid gland in the blood and is responsible for many important bodily functions such as growth, development, metabolism, etc.
Thyroxine (T4) is a thyroid hormone produced by the thyroid gland in the blood and is able to move to other parts of the human body such as the kidneys and liver. In these organs, they are converted to the active triiodothyronine.
Other thyroid gland functions include:
- Controlling vital bodily functions in humans and animals
- Controlling the respiratory process – inhaling and exhaling
- Maintaining an equal heart rate
- Development and control of the central and peripheral nervous systems
- Maintaining body weight
- It maintains muscle strength and helps keep the body against gravity
- Controls menstrual cycles
- Body temperature control
- Keeping cholesterol levels low
- To release hormones from a person’s bloodstream
- Maintaining hormone levels in the body
- Controlling physical growth and development
- Controlling lipid metabolism in our body
Why is the thyroid gland needed?
Triiodothyronine (T3) hormone and Thyroxine (T4) hormone are produced by the thyroid gland in the human blood. These hormones travel through the bloodstream. They reach almost every cell in the body. These hormones are needed to control the speed at which cells work; the rate of metabolism is controlled by these hormones. The hormone Triiodothyronine (T3) and the hormone Thyroxine (T4) regulate a person’s heartbeat and regulate the ability of the intestines to speed up the digestive process.
Levels of Triiodothyronine (T3) and the hormone Thyroxine (T4) are needed to maintain normal levels. When these hormones are lower than the required levels, the heart rate decreases slightly. A person with low levels of these hormones can have constipation-related problems and can gain weight. On the other hand, when the levels of Triiodothyronine (T3) and the hormone Thyroxine (T4) are high, the heart rate becomes faster. A person with high levels of these hormones can have problems related to diarrhea and can also lose weight. Too much or too little Triiodothyronine (T3) hormones and Thyroxine (T4) have side effects in the human body.
Thyroid Diseases and Disorders:
Some diseases and disorders are the results of the overproduction of hormones by the thyroid gland. A variety of causes can lead to the development of thyroid problems in humans. Pregnancy, injury, malnutrition, or any other disease can be the cause of developing thyroid problems in humans. The development of thyroid problems in humans can be from any age.
Some of the most common ways to develop thyroid problems in humans are as follows:
- Low or very low production of thyroid hormones – Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4) hormones
- Abnormal growth of thyroid cells and formation of a lump within the thyroid gland.
- Enlarged thyroid glands can cause lumps inside the thyroid which can lead to thyroid cancer.
Thyroid Gland
The thyroid is an endocrine gland. It is located at the front of the neck. It has a strong resemblance to the shape of a butterfly. In addition, it is one of the major endocrine glands, weighing between 25 – 30 g on average. The gland is divided into two lobes on either side of the trachea, each 4-6 cm long and 1.3-1.8 cm wide.
The main role of the thyroid gland is to produce two hormones, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Both the T3 and T4 hormones are important and affect almost all body tissues.
The thyroid is located between the C5 and T1 vertebrae in the anterior neck. It is made up of two lobes, each with parathyroid glands in the back.
Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones are divided into two types:
T4 stands for thyroxine (Tetraiodothyronine)
T3 represents triiodothyronine.
- T4: Thyroxine is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland in the blood. It is then converted into organs such as the kidneys and liver into the active triiodothyronine.
- T3: It is a thyroid hormone that influences various bodily processes, including growth, development, and metabolism.
Symptoms of Thyroid Disease
Sometimes symptoms of a thyroid problem are not so obvious. This is because a variety of other causes may cause similar symptoms, and treatment is usually determined by symptoms. Excessive fatigue, for example, maybe associated with asthma, narcolepsy, or other conditions, but the underlying symptoms may be related to the thyroid.
The following are some of the most common symptoms:
- Nervousness
- Inability to concentrate and store information
- Changes in the menstrual cycle
- Increased heart rate
- Muscle pain
- Weight gain
- High cholesterol level
- Thyroid Disorders
Many diseases and ailments can affect the thyroid gland. These problems can be caused by excessive hormone production, abnormal growth of hunger, or cancerous growth. Additionally, experts measure the link between stress and thyroid health. On the other hand, stress may aggravate the underlying thyroid disease.
Several common thyroid diseases include the following:
- Goiter
It is an abnormal growth of the thyroid gland that often blocks the esophagus or other organs in the neck and chest, making food and breathing difficult.
- Thyroid cancer
It is a type of cancer that is widespread. However, compared with other types of cancer, the chances of survival of a thyroid cancer patient are slim. Thyroid cancer is divided into four subtypes:
- Thyroid carcinoma with papillary growth
- Follicular for thyroid cancer
- Medulla cancer
- Thyroid cancer is anaplastic
- Hyperthyroidism
This disorder occurs when the thyroid gland produces an overdose of the hormone thyroxine. Anorexia nervosa, sudden weight loss, insomnia, fatigue, irritability, frequent urination, excessive sweating, and sensitivity to heat are some of the symptoms. However, with proper treatment and medication, the disease can usually be cured within a few months.
- Hypothyroidism
This condition is caused by a deficiency of thyroid hormones. It is a common occurrence that often goes unnoticed for years. One of the most common causes of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s disease, an autoimmune disease. In this condition, the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, causing the glands to produce fewer hormones.
Thyroid Treatment
The most commonly used treatment for thyroid issues such as hyperthyroidism is to replace another man-made synthetic hormone called levothyroxine (or L-thyroxine) with thyroxine. It is an injectable and oral medication that can help restore homeostasis of the thyroid gland. Patients will experience a reduction in the symptoms of hyperthyroidism a few weeks after starting treatment.
Radiation can be used effectively to treat thyroid cancer. Thyroid cancer can sometimes be difficult to diagnose because it does not show any signs or symptoms. Regular testing is important to prevent the spread of these diseases.
Also read: Important Topic Of Biology: Pineal
FAQs
What is Goitre?
Goitre is a term that refers to increasing the thyroid gland. Goiter can be a common diagnosis or warning of thyroid dysfunction. Goitre is very common in the present situation due to the widespread use of iodine-containing salts.
What is a Thyroid Storm?
Thyroid storms usually occur in a situation where hyperthyroidism is not diagnosed for a few weeks or months together. After the symptoms have worsened, undiagnosed hyperthyroidism affects an individual or the whole family may suffer from a thyroid storm.
Is Hypothyroidism more common than hyperthyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not function properly. Hypothyroidism is more common compared to hyperthyroidism. This is because there is a deficiency from the thyroid and congenital hypothyroidism present from birth.
What are the symptoms of thyroid problems?
Some of the symptoms of thyroid problems are difficulty in coping with temperature changes, weight loss, digestive problems, mood swings, skin problems, mood swings, memory problems.








