Table of Contents
Boric acid is a boron-based monobasic Lewis acid that is also known as hydrogen borate, boracic acid, and orthoboric acid. Some of its behaviour in certain chemical reactions, however, suggests that it is also tribasic acid in the Bronsted sense. Boric acid is a common antiseptic, insecticide, flame retardant, neutron absorber, and precursor to other chemical compounds. It has a chemical formula and exists as colourless crystals or a white powder that dissolves in water. It is known as sassolite when it occurs as a mineral.
Boric acid, also known as sassolite, is found mostly in its free form in volcanic areas, such as the Italian region of Tuscany, the Lipari Islands, and the US state of Nevada. It erupts from fissures in the ground, mixed with steam, in volcanic settings. It is also found in a variety of naturally occurring minerals, including borax, boracite, ulexite (boronatrocalcite), and colemanite. Seawater contains boric acid and its salts. It is also present in plants, including nearly all fruits. Boric acid is a naturally occurring water-soluble white compound. It is made up of oxygen, boron, and hydrogen. It has antifungal and antimicrobial properties, according to the claims. Before applying boric acid to any part of your body, always consult your doctor. It is irritant to the skin and can result in severe reactions. Boric acid and its sodium borate salts are pesticides found in nature and a variety of products. One of the most common products is borax. Boric acid and its sodium salts each have a unique way of combining boron with other elements. In general, their toxicity is proportional to the amount of boron they contain. Boric acid and its sodium salts are effective pesticides that can be used to control a wide range of pests. Insects, spiders, mites, algae, moulds, fungi, and weeds are examples. Since 1948, products containing boric acid have been registered for use in the United States.
Overview
It is an acid with four oxygen atoms, one phosphorus atom, and three hydrogen atoms. Boric acid also goes by the names acidum boricum, hydrogen borate, boracic acid, and orthoboric acid. It is a weak acid that is antiviral, antifungal, and antiseptic. Boric acid is water-soluble and does not have a distinct odour. Under normal conditions, this compound exists as a colourless crystal or as a white powdery substance. Boric acid can be made by combining borax and hydrochloric acid. It should be noted that Wilhelm Homberg was the first to create boric acid from borax. Boric acid is an inorganic compound that is a boron-based weak monobasic Lewis acid. Although it acts as a tribasic acid in some chemical reactions. Hydrogen borate, boracic acid, and orthoboric acid are other names for it. Trihydrooxidoboron is its IUPAC name. Sassolite is the name given to boric acid when it occurs naturally as a mineral. At room temperature, it is a crystalline solid. It is found in a variety of naturally occurring minerals, including borax, boracite, ulexite, and colemanite. Seawater contains its salts. It can also be found in all fruits and vegetables, as well as many plants. In 1702 Wilhelm Homberg created the first crystals of boric acid. He named it sal sedativum Hombergi (sedative salt of Homberg). Although boric acid compounds have been used for cleaning, preserving food, and other purposes since the time of the ancient Greeks. Boric acid is commonly used as an antiseptic to treat minor cuts and burns. This compound is also found in medical dressings and salves. As an eyewash, very dilute solutions of boric acid can be used. Because of its antibacterial properties, boric acid can also be used to treat acne in humans. It can also be sprinkled into socks and shoes in powdered form to prevent the athlete’s foot (tinea pedis). It is important to note that large amounts of boric acid can be poisonous if consumed or inhaled. Furthermore, long-term exposure to boric acid can cause severe kidney damage.
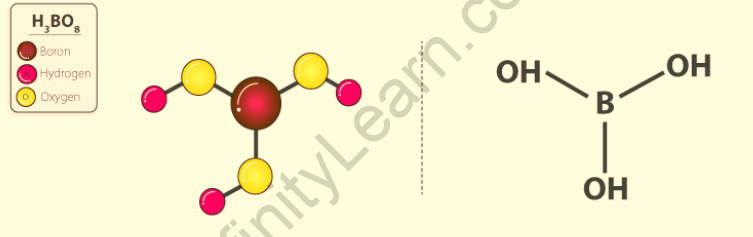
Anomalous properties of boric acid
Boric acid’s physical properties are as follows.
- At room temperature, it is a colourless or white crystalline solid.
- It has a molecular mass of 61.83 g/mol.
- It has a melting point of 170.9 degrees Celsius.
- It has a boiling point of 300°C.
- It dissolves in water.
Boric acid’s chemical properties are as follows.
Boric acid exists as a white, crystalline solid that is fairly soluble in water under standard temperature and pressure (STP). The solubility of water varies with temperature. The solubility of boric acid in water at 25 degrees Celsius is 57 grammes per litre. When water is heated to 100 degrees Celsius, the solubility of this compound increases to about 275 grammes per litre. It is also worth noting that boric acid is only marginally soluble in pyridine and only slightly soluble in acetone. The borate anion is the conjugate base of boric acid.
The acidity of boric acid solutions is known to increase with polyols containing cis-vicinal diols (like mannitol and glycerol). Under different mannitol concentrations, the pK of is known to vary by five orders of magnitude (from 9 to 4). It is worth noting that in the presence of mannitol, the solution of boric acid with increased acidity is known as mannitoboric acid.
Boric acid powder
Boric acid is a chemical compound made up of borax and glycerin. Borax is primarily useful for clearing up acne on the skin, but it also has antibacterial properties. The glycerin present hydrates the skin and aids in the repair of skin damage caused by acne and dryness. It also aids in the removal of acne scars by clarifying the affected area.
Use of boric acid
The following are some of the applications for boric acid.
- It is used in the production of textile fibreglass.
- It is used in the manufacture of flat panel displays.
- It is employed in the neutralization of active hydrofluoric acid.
- Blacksmiths use it as welding flux.
- It is used in electroplating and the jewellery industry.
- It is used in the production of silly putty.
- It is employed as an insecticide.
- It’s an antiseptic and antibacterial agent.
- It is used as a dry lubricant on carrom boards and as a neutron poison in some nuclear power plants.
- It is used to store grains such as wheat and rice.
It is not uncommon to find boric acid on the list of chemical additives used in hydraulic fracturing (also known as fracking). This compound is also used as a cross-linking and gelling agent in conjunction with guar gum, and it is known to regulate the viscosity and rheology of drilling fluid that is pumped at high pressure into wells. Furthermore, it is critical to regulate the fluid viscosity to keep the grains of the propping agents suspended over long transport distances in order to keep the cracks in the shales sufficiently open to facilitate gas extraction after hydraulic pressure is relieved.
Borax and boric acid
Borax and boric acid are different forms of the same compound. Borax is a mineral extracted from the ground (a form of the element Boron) that is used in cleaning products. Boric acid is its extracted, processed, and refined form, which can be found in a wide range of chemical products.
Some of the most common applications for borax are as follows:
- Detergent for laundry
- Fertilizer Hand Soap
Some of the most common applications for boric acid are as follows:
- Drops for the eyes
- Pesticide/insecticide
Only when ingested are borax and boric acid toxic. They will be labelled for external use only on products containing them, but they can be hazardous to children and pets.
Also read: Anomalous Properties of Boron Hydrides
FAQs
Is boric acid synonymous with borax?
In fact, borax and boric acid are the same thing and are commonly used to make homemade laundry soap. Boron is present in all of these materials. Borax is commonly extracted and refined from tourmaline, kernite, and colemanite. Boric acid is used to extract the mineral sassolite.
What is the purpose of boric acid?
Boric acid is also used as an antiseptic, insecticide, flame retardant, neutron absorber, and precursor in many chemical products.
What is boric acid, exactly?
Boric acid, also known as hydrogen borate, boracic acid, orthoboric acid, or acid boricum, is a weak boron acid that is occasionally used as an antiseptic, insecticide, flame retardant, or neutron absorber, as well as a precursor to other chemical compounds.








