Table of Contents
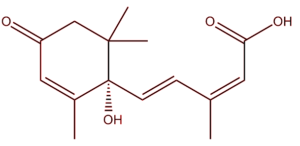
Definition:
ABA is one of the plant hormones(C15H20O4). The hormone was 1st isolated by ADDICOTT -from cotton balls. Produced- in many parts of the plants but more abundantly inside chloroplasts of the cells. Promotes- leaf abscission and dormancy and has an inhibitory effect on cell elongation.
ABA is the derivative of carotenoids. ABA -previously termed as ABSCISIN &DORMIN because of their regulatory effect on ABSCISSION and DORMANCY. ABSCISSION: The natural detachment of parts of a plant, like dead leaves and ripe fruits. DORMANCY: The state of normal functions slowed down for a period of time/temporarily inactive. Hormone formed from MEVALONIC ACID/XANTHOPHYLL. Transported to all parts of the plant through diffusion and through xylem and phloem. ABA is called STRESS HORMONES because it induces various responses in stress conditions and increases tolerance to various kinds of stresses.
Overview:
ABA is naturally present in fruits and vegetables and it plays an important role in managing glucose homeostasis in humans. According to the latest U.S survey, about 92 %of the population might have a deficient intake of ABA due to their deficient intake of fruits and vegetables.
Most of the plant’s responses to these abiotic conditions are mediated by abscisic acid. ABA plays important roles in seed development, maturation, synthesis of proteins, cuticular wax accumulation, leaf senescence, osmotic regulation, seed germination, etc. It is synthesized within the stem, leaves, fruits, and seeds of the plant. It acts as an antagonist to gibberellic acid. It is used as a spraying agent on trees to regulate the dropping of fruits. Favours in development and maturation of seeds. Unlike animals, plants cannot flee from potentially harmful conditions like:
- Drought
- The approach of winter
They must adapt or die
The plant hormone plays an important role in mediating the adaptation of plants to various stresses. ABA is a mobile signal, and its movement is mediated by the influx and efflux of carrier proteins. The movement of ABA is an important mechanism of plant responses to drought stresses. The best-characterized one is ABA, Which is chemically related to CYTOKININS. It is universally distributed in higher plants and has various actions; for example- it promotes abscission(leaf fall), the development of dormancy in buds, and the formation of potato tubers.
ABA is a phytohormone and it controls downstream responses to abiotic and biotic changes.ABA deficient mutants from various plants display reduced seed dormancy and wilty phenotypes. Exogenous ABA helps in the delay of wilting and allows plants to survive short periods of severe drought. Under drought conditions, ABA which is stored in guard cells of stomata helps in stomatal closures this helps in water loss from leaves. ABA Inhibits early germination.
The ABA mediates responses to environmental stresses such as the presence of nitrate in the soil, water stress, and salt, shaping the structure of the root system by regulating the production of lateral roots as well as controlling root elongation by modulating cell division. The addition of ABA to mature non-dominant seeds inhibits seed germination and thus ABA appears to inhibit seed germination by restricting the availability of energy and metabolites. ABA controls cell elongation and wall formation.
It is produced in matured leave, especially under stress. Roots, then are transported to shoots. It inhibits the maturation of seeds and embryogenesis. ABA Is sometimes applied to plants before they are shipped to enter dormancy, then gibberellins are sprayed and used for the commercial purposes of ABA.
ABA is discovered by 3 independent types of research separately, they are;
- Inhibitor B
- Abscission 2
- Dormin
These 3 are chemically identical.
ABA is produced in terminal buds in preparation for winter. This slows plant growth and protects dormant buds during the cold season. It also inhibits the division of cells in the vascular cambium, adjusting to cold conditions by suspending primary and secondary growth.
Functions:
- Acts as an inhibitor of plant growth & metabolism
- Inhibits -seed germination
- Stimulates- closure of stomata in the epidermis to reduce transpiration and thus prevent water loss from leaves.
- An important role in seed development, maturation & dormancy. Seed dormancy by ABA helps to withstand desiccation &other factors unfavorable for growth
- INDUCES-Bud dormancy in a variety of plants.
- CONTROLS-Geotropic responses of roots and stimulates positive geotropism in roots.
- IT is produced in roots in response to decreased soil water potential and other stresses.
- Important in plants in response to environmental stresses, including drought, soil salinity, cold tolerance, heat stress.
Biosynthesis:
ABA IS an isoprenoid plant hormone, synthesized in the 2-c-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate (MEP pathway). Zeaxanthin is 1st committed ABA precursor; a series of enzyme-catalyzed epoxidation & isomerizations, final cleavage of the C40 CAROTENOID by a deoxygenation reaction yields the proximal ABA precursor, xanthoxin, which is then further oxidized to ABA.
Effects:
- Antitranspirant
- Induces fruit ripening
- Downregulates enzymes for photosynthesis
- Inhibits the synthesis of kinetin nucleotide
- Delays cell division
- Acts on the epidermis to prevent the growth of roots when exposed to salty conditions
Among the 5 plant growth regulators, ABA is one of the plant regulators. In many tests, ABA Inhibits growth and metabolism and enhances the degradative changes as in senescence and ripening.
Importance of this chapter in NEET:
This chapter is containing information regarding plant growth regulators and the importance of the plant growth regulator abscisic acid. What are its functions and the process of its formation and all, as plant growth regulators are important in plant germination and its growth lifecycle? we can’t replace them with other plant growth regulators as specific ones are specific roles. so in the question paper, you can get questions regarding its functions and examples. paper won’t get over without asking about plant growth regulators. don’t avoid it as it is important and easy to get a high score.
Also read: Auxin Plant Hormone
FAQs
What is abscisic acid?
ABA is naturally present in fruits and vegetables and it plays an important role in managing glucose homeostasis in humans. According to the latest U.S survey, about 92 %of the population might have a deficient intake of ABA due to their deficient intake of fruits and v
Q. What are its functions?
Ans: Some of the functions of abscisic acid are: Acts as an inhibitor of plant growth & metabolism
- Inhibits – seed germination
- Stimulates – closure of stomata in the epidermis to reduce transpiration and thus prevent water loss from leaves.
- An important role in seed development, maturation & dormancy. Seed dormancy by ABA helps to withstand desiccation &other factors unfavourable for growth
- INDUCES -Bud dormancy in a variety of plants.
- CONTROLS-Geotropic responses of roots and stimulates positive geotropism in roots.
- IT is produced in roots in response to decreased soil water potential and other stresses.
- Important in plants in response to environmental stresses, including drought, soil salinity, cold tolerance, heat stress.
Q. What are its effects?
Ans: Effects are as follows:
- Antitranspirant
- Induces fruit ripening
- Downregulates enzymes for photosynthesis
- Inhibits the synthesis of kinetin nucleotide
- Delays cell division
- Acts on the epidermis to prevent the growth of roots when exposed to salty conditions
Among the 5 plant growth regulators, ABA is one of the plant regulators. In many tests, ABA Inhibits growth and metabolism and enhances the degradative changes as in senescence and ripening.








