Table of Contents
Introduction
The force of electricity EMF, for example, is a concept that most students are unfamiliar with. However, it is inextricably linked to the more familiar concept of voltage. Understanding the difference between these two and what EMF means provides us with the tools we need to solve many physics and electronics problems. It will also introduce the concept of a battery’s internal resistance. EMF describes the voltage of a battery without accounting for internal resistance, which reduces the value. The electric potential produced by an electrochemical cell or by changing the magnetic field is referred to as electromotive force. EMF is an abbreviation for electromotive force. The conversion of energy from one form to another is accomplished through the use of a generator or a battery. One terminal in these devices becomes positively charged, while the other becomes negatively charged. As a result, work done on a unit electric charge is characterized as an electromotive force. Electromotive force is used in the electromagnetic flowmeter, which is based on Faraday’s law.
Negative electromotive forces are possible. Consider the case where an inductor generates an EMF that opposes the incoming power. The produced EMF is then interpreted as negative because the flow direction is opposite to the real power. As a result, the electromotive force may be negative.
Overview
The electromotive force of a cell, also known as the electromotive force of a cell, is the maximum potential difference between two electrodes of a cell. It is also known as the net voltage between the oxidation and reduction halves of the reaction. A cell’s EMF is primarily used to determine whether or not an electrochemical cell is galvanic. An electrochemical cell is a device that uses a chemical reaction to generate electricity.
It is essentially a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. An electrochemical cell requires a chemical reaction that involves the exchange of electrons in order to function. Such reactions are referred to as redox reactions. The voltage of a cell defines it. Regardless of cell size, a specific type of cell generates the same voltage. Given ideal operating conditions, the only thing that depends on cell voltage is the chemical composition of the cell.
Normally, the cell voltage will deviate from this ideal value due to a variety of factors such as temperature differences, concentration changes, and so on. The Nernst equation, developed by Walther Nernst, can be used to calculate the EMF value of a given cell if the cell’s standard cell potential is known.
An electrochemical cell is a device that uses a chemical reaction to generate electricity. It’s a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. An electrochemical cell requires a chemical reaction that involves the exchange of electrons in order to function. These types of reactions are known as redox reactions. The voltage of a cell defines it. Regardless of cell size, a specific type of cell generates the same voltage.
If the cell is operated under ideal conditions, the chemical composition of the cell is determined by the cell voltage. The cell voltage can vary due to a variety of factors such as temperature differences, concentration changes, and so on.
Emf of leclanche cell
A Leclanche cell is made up of a carbon electrode packed in a porous pot with manganese dioxide and charcoal powder. The porous pot is immersed in an outer glass vessel containing a saturated solution of ammonium chloride (electrolyte). In an electrolytic solution, a zinc rod is immersed.
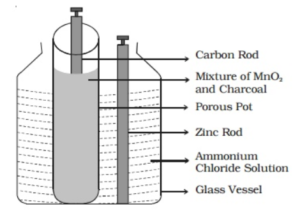
The oxidation reaction at the zinc rod converts Zn atoms into Zn++ ions and 2 electrons. Zinc chloride and ammonia gas are produced when Zn++ ions react with ammonium chloride.
Zn++ + 2 NH4Cl – 2NH3 + ZnCl2 + 2 H+ + 2e–
The ammonia gas leaks. Hydrogen ions diffuse through the porous pot’s pores and react with manganese dioxide. The positive charge of a hydrogen ion is transferred to a carbon rod during this process. When a zinc rod and a carbon rod are externally connected, the two electrons from the zinc rod move towards the carbon rod and neutralize the positive charge. As a result, current flows from carbon to zinc. The Leclanche cell is useful for supplying sporadic current. The cell has an emf of about 1.5 V and can supply a current of 0.25 A.
Emf of dry cell
A paste electrolyte is used in a dry cell, with just enough moisture to allow current to flow. A dry cell, unlike a wet cell, can operate in any orientation without spilling because it contains no free liquid, making it ideal for portable equipment. In comparison, the first wet cells were typically fragile glass containers with lead rods hanging from the open top that required care to avoid spillage. Until the development of the gel battery, lead-acid batteries did not achieve the safety and portability of the dry cell. Because inhibiting the electrolyte flow tends to reduce the current capability, wet cells have continued to be used for high-drain applications such as starting internal combustion engines. The zinc-carbon cell, also known as the dry Leclanché cell, has a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts, which is the same as the alkaline cell (because both use the same zinc–manganese dioxide combination).
Emf of a galvanic cell
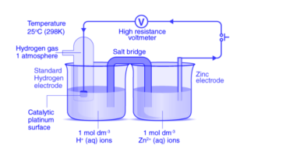
The Galvanic Cell is named after the Italian scientist Luigi Galvani. A galvanic cell is a type of electrochemical cell that serves as the foundation for many other electrochemical cells, such as the Daniell cell. It is made up of two different metallic conductors known as electrodes that are immersed in their own ionic solutions. Each of these configurations is a half cell. A half cell cannot generate a potential difference on its own. However, when they are combined, they have the potential to make a difference. A salt bridge is used to chemically connect the two cells. It provides electrons to the electron-deficient half cell and accepts electrons from the electron-rich half cell as needed.
Also Check: Relation between Gibbs energy change and EMF of a cell
FAQ’s
What is the primary distinction between an electrochemical cell and an electrolytic cell?
Chemical energy is converted to electrical energy in electrochemical cells, whereas electrical energy is converted to chemical energy in electrolytic cells.
What are the parallels between the Galvanic Cell and the Daniel Cell?
Both the Galvanic Cell and the Daniel Cell are electrolytic half cells made up of electrodes and electrolytes.
Explain a cell's EMF.
When no current is present, the electromotive force (EMF) is equal to the potential difference across the terminals of the cell. EMF is the amount of energy provided by a cell or battery per coulomb of charge passing through it, measured in volts (V).








