Table of Contents
Linear Equation: All equations are the type of algebraic expression and equation. you know very well that algebraic expressions it is those which is connected with variable. let us take some examples of algebraic expression
5x, 2x – 3, 4xy + 3x + 6
some example of equation are , 2x =3, 3x + 5y = 4
A linear equation is an equation in which the highest power of the variable is one. It is also called a one-degree equation. those type of polynomial whose variable power is one is known as mono-polynomial. Let us discuss the method of linear equation, formula, standard form, and how we can draw the linear equation graph.
Linear Equation:-
It is that equation in which the variable highest power is 1. so we can say that the exponent is not more than 1. The linear equation’s graph is always a straight line. The standard form of expressing a linear equation is ax + b = 0. Here, a is the coefficient, b is a constant term, and x is the variable. Now, the standard form of a linear equation in two variables is ax + by = c. Here x and y are variables, a and b are coefficients of x and y, and c is constant.
Form of Linear equation or formula:-
liner equation has three important forms also; they are called the formula of expressing the linear equation.
- Standard form
- Slope Intercept form
- Point slope form
The standard form of a linear equation:-
Linear is made up of the combination of constant and variable. The standard form of linear in one variable can be represented as
![]()
The standard form of a linear equation in two variables can be represented as
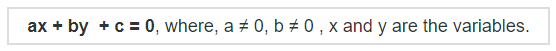
The standard form of three variable linear equation in three variables can be represented as:

Slope Intercept form:-
Linear equation important and most common is slope-intercept form, which can be represented as;
y = mx + b;
above equation is the equation of a line in which
The slope of this line is m,
b is the intercept of
the Coordinates of the x-axis and y-axis are x and y
Let us give an example for this, y = 4x + 5
slope, m = 4 and intercept = 5
The x-coordinate becomes zero if the above equation’s graph is parallel to the x-axis. Therefore,
y=b
The y-coordinate becomes zero if the above equation’s graph is parallel to the y-axis.
mx + b = 0
x=-b/m
Point slope form:-
In this form of linear equation, a straight line equation is formed if taking the point in the x-y plane,
y – y1 = m(x – x1 )
In which the coordinates of the point are (x1, y1).
We can be represented as:
y = mx + y1 – mx1
Method of solving linear equation in one variable:-
Firstly do both sides balance the linear equation? the equal sign shows that a given statement is an equation. If the given equation infraction then clears the fraction. then do isolate one side variable term and another side constant term. solve this equation with the mathematical operation. after that, give the value of a variable.
We can explain through an example
Example: Solve (2x – 10)/2 = 3(x – 1)
Step 1: Clear the fraction
x – 5 = 3(x – 1)
Step 2: Simplify Both side’s equations
x – 5 = 3x – 3
x = 3x + 2
Step 3: Isolate x
x – 3x = 2
-2x = 2
x = -1
Method of solving a linear equation in two variables:-
Solving linear equation in two variables have a different method:-
To solve the linear equation in two variables, firstly, take a pair of equations to resolve the values of 2 variables. Let ax + by + c = 0 and dx + ey + f = 0, known as a system of equations in two variables, where x and y are two variables and a, b, c, d, e, f are constants, and also note be that a, b, d and e are not zero. Otherwise, a single equation gives many solutions.
- Graphical Method:- This method solves linear equations by drawing the graph. then we get an intercept point
- Substitution Method:-In this method, we solve the set of linear equations by substituting the value from one equation to another. then we get the required solution.
- Elimination Method:-In this method, we solve linear equations by eliminating or cancelling one variable.
- Cross multiplication Method:-In this method, we solve the equation by taking the variable coefficient term and constant term and equating it with a variable, then do the cross multiply. we get the solution of the linear equation.
Solution of Linear Equations in Three Variables:-
To solve linear equations in 3 variables, we required a set of 3 equations, as given below, to find the values of unknown variables. For solving linear equations with 3 variables Matrix method is an important method.
a1x + b1 y + c1z + d1 = 0
a2x + b2 y + c2 z + d2 = 0 and
a3x + b3 y + c3 z + d3 = 0
Let us take an example
Example:- Solve x – y = 12 and 2x + y = 22 by the substitution method.
Solution:
Let us take the equations
x – y = 12 …(1)
2x + y = 22 …(2)
from Equation (1) for x,
x = y + 12…….(3)
Substitute eq.(3) in equation (2)
2x + y = 22
2(y+12) + y = 22
2y + 24 +y = 22
3y + 24 = 22
3y = -2
or y = -2/3
Substitute the value of y in eq.(3)
x = y + 12
x = -2/3 + 12
x = 34/3
So, the required solution, x = 34/3 and y = -2/3
Important Points for Linear Equation:-
- solution of the linear equation after that, which gives the value of the variable, is known as the roots of the linear equation.
- The equation will be unaffected if any number is added, subtracted, multiplied, or divided into both sides.
- Graph of linear equation in one or two variables form a straight line.
FAQ’s
Question: What is the method of solving a linear equation in two variables?
Answer:
- Graphical Method
- Substitution Method
- Elimination Method
- Cross Multiplication Method
Define linear equation.
A linear equation is an equation in which the highest power of the variable is 1. It is also called a one-degree equation. graph of the linear equation always is a straight line. A linear equation can be expressed in one variable, two variables, three variables and so on. the standard form of a linear equation is one and two variable such. ax + b = 0, where x is a variable, a is the coefficient of x, and b is a constant term. And for two variables ax + by = c . Here x and y are variables, a and b are the coefficient of x and y, and c is a constant term.
What is the slope-intercept form of a linear equation?
The slope-intercept form of the linear equation is y = mx + b; where m is the slope of the line, and b is the y-intercept.








