Table of Contents
A mirror is a reflective surface that reflects light and creates either a real or a virtual picture. When an object is placed in front of a mirror, the mirror reflects the image of the same object. The incident rays are emitted by the object, and the image is generated by the reflected rays. The visuals are characterized as either genuine or virtual based on how light interacts with them. A true image is produced when rays of light actually intersect, but virtual images are formed when light rays appear to deviate from a point. Ray diagrams assist us in tracing the path of light for someone seeing a point on an image of an item.
A brief outline
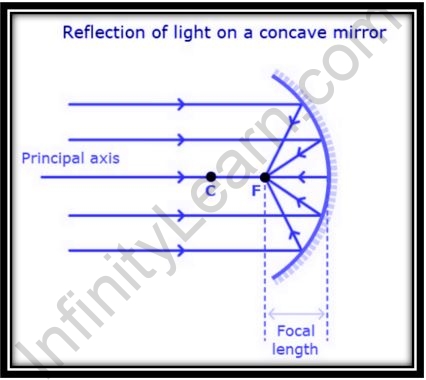
At the point when an empty round is isolated into parts and the outside surface of each cut piece is painted, it frames a mirror, with the inward surface mirroring the light. An inward mirror is a name for this kind of mirror.
Concave Mirror Characteristics
- Whenever light strikes and reflects back from the inward mirror’s reflecting surface, it meets at a point. Thus, it’s likewise called a merging mirror.
- An amplified and reenacted picture is produced when the curved mirror is put exceptionally near the thing.
- Whenever the distance between the thing and the mirror is expanded, notwithstanding, the size of the picture diminishes, and a genuine picture is created.
- The image made by the inward mirror can be controlled.
Important concepts
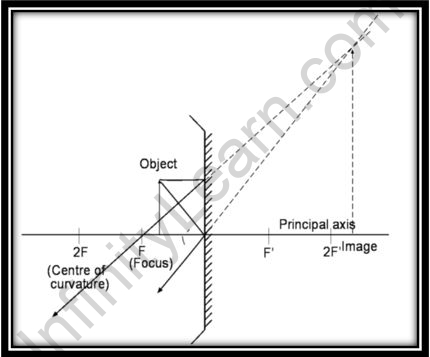
Concave mirror ray diagram steps
- When an object is positioned at infinity, a genuine image is generated at the focus, as shown in the Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. When compared to the large of the thing, the image is much smaller.
- An actual picture is produced between the centre of curvature and the focus when an object is positioned behind the center of curvature. When compared to the size of the thing, the image is smaller.
- The true picture is created at the centre of curvature when an object is put at the centre of curvature and focused. When compared to the size of the object, the image seems to be the same size.
- The genuine image is created behind the centre of curvature when an object is put between the centre of curvature and the focus. When compared to the size of the thing, the image is greater.
- The true image is produced at infinity when an object is placed at the focus. When compared to the size of the thing, the image is significantly larger.
- A virtual and erect picture is generated when an object is put between the focus and the pole. When compared to the size of the thing, the image is greater.
Concave Mirror in Real-Life Applications
Reflecting Telescopes:
In observational astronomy, concave mirrors are commonly utilized in various reflecting telescopes. The light from distant celestial objects is collected by the concave mirror in a reflecting mirror. The entering light rays are virtually parallel due to the great distance between the light sources. The light beams are focused on a flat mirror that is kept at its focal distance by the concave mirror. The intensity of the light increases as a result of the convergence. The flat mirror’s reflection is then visible through the eyepiece.
Magnifying lens
As a condenser, a curved mirror is utilized in the foundation of a magnifying instrument. In the wake of going through the mirror, light from an outer element is beamed on the example. The sunken mirror exclusively focuses light on the example to keep the environmental factors dull. The mirror’s direction can be adjusted by turning it. An eyepiece is utilized to see the example.
Headlights:
The focal point of a curved mirror is the bulb of a front light or a light. In the wake of being reflected at the sunken mirror, the light beams from the bulb show up as equal beams. Reflected beams can travel a significant distance and have extraordinary power.
Sunlight based Heater:
Sun-oriented heaters utilize exceptionally large curved mirrors to concentrate daylight. The sunken mirror gathers a lot of light and zeros in it on the point of convergence. Warming, cooking, making power, and dissolving metals all need centred energy.
The following are the properties of concave mirrors:
- They have the ability to create both real and virtual images.
- When they create a virtual image, they stand up.
- If the image creates an actual image, it is inverted.
- Based on the distance between the object and the mirror, the image of the object can be decreased, enlarged, or the same size as the object.
Significance of concave mirror in IIT JEE exam
Optics is a crucial chapter for the IIT JEE test, as well as future reference and competitive exam preparation. There are a few key points in the Chapter that you cannot afford to overlook. The chapter covers subjects such as light reflection, convex and concave mirrors, and more. In exams, questions from this chapter contain numerical and definitional problems. According to the chapter-by-chapter weighting distribution for the IIT JEE exam, Ray Optics has been asked about 5% of the total questions in the past eight years’ question papers.
FAQs
What are concave mirrors and how would they function?
The intelligent surface of a concave mirror is twisted internally and away from the light source. Light is reflected internally by curved mirrors to a solitary centre point. As opposed to raised mirrors, the picture created by a sunken mirror changes in view of the distance between the thing and the mirror.
What makes a concave mirror not the same as a convex mirror?
Inward mirrors are round mirrors with a reflecting internal surface. Raised mirrors are circular mirrors with a reflecting external surface.
Without touching them, can you tell the difference between concave and convex mirrors?
When you place an object in front of a concave mirror, it forms an enlarged image when kept close to the mirror, and an inverted picture when kept further away. A convex mirror constantly reflects the thing in a small, erect picture.








