Table of Contents
Introduction
In other words, ionic compounds are bonded together with ionic bonds as they are classified as ionic compounds. Elements can gain or lose electrons to achieve a respectable gas configuration nearby. The formation of ions (by gaining or losing electrons) to eliminate the octet helps them achieve stability.
In the transition between metals and non-metals, metals usually release electrons to complete their octet while non-metals acquire electrons to complete their octet. Metals and non-metals generally react to the formation of ionic compounds.
Ionic Compound Structure
The structure of ionic compounds depends on the relative sizes of cations and anions. Ionic compounds include salts, oxides, hydroxides, sulphides, and most of the inorganic compounds. Ionic solids are held together by electrostatic attraction between direct and negative ions.
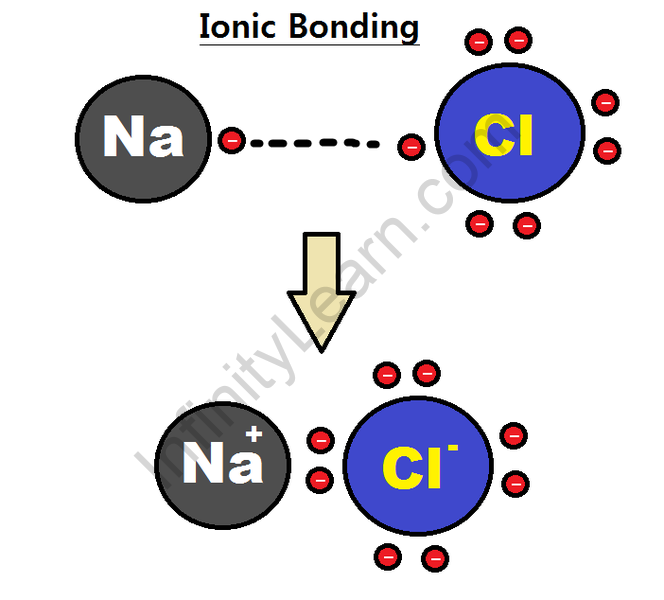
For example, sodium-ion attracts chloride ion and chloride ion absorbs sodium ion. The result is a three-dimensional structure of other Na+ and Cl– ions. This is a sodium chloride crystal. The crystal is not charged because the amount of sodium ion is equal to the number of chloride ions. The gravitational force between ions is trapped in the structures.
These ionic bonds between charged particles result in a large ion structure. Because ions are strongly bonded to these larger structures it takes a lot of energy to break all the bonds. As a result, ionic compounds have higher melting points and boiling points.
Examples of Ionic Compound
An example is a reaction between magnesium and chlorine. The magnesium atom has two electrons in its outer shell. By losing two electrons in its M shell its L-shell becomes a very outer shell with a stable octet. The nucleus of this magnesium atom still has 12 protons but the number of electrons has dropped to ten. Therefore, a positive Net charge is built on this magnesium atom, which provides the magnesium cation Mg2+.
On the other hand, the chlorine atom has seven electrons in its outer shell. Therefore, it only needs one electron to complete its octet. It can benefit from this one electron from one electron that lost a magnesium atom to a magnesium ion. Since two electrons lose the magnesium atom while one chlorine atom can receive only one electron, two chlorine atoms combine with one magnesium atom to form magnesium chloride.
The bond formed between them is known as the ionic bond. Due to the presence of ion-charged ions, ionic compounds are strongly absorbed by the electrostatic potential of attraction. The distinguishing features of ionic compounds are:
Ionic Compound Properties
1. Material of ionic compounds
Due to the presence of strong gravitational forces between direct and negative ions, ionic compounds are strong and difficult to break. They usually break down into pieces under pressure, which is why they are considered brittle.
2. Soluble and boiling points of ionic compounds
Due to the presence of attractive electrical energy between ions, a large amount of energy is required to break the ionic bonds between atoms. Therefore, ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points.
3. Melting of ionic compounds
Ionic compounds are usually soluble in polar solvents such as water and solubility is usually reduced in non-polar solvents such as gasoline, gasoline, etc.
4. Conducting Electricity
Ionic compounds do not carry electricity in a solid-state but are good conductors in a molten state. Electricity generation involves the flow of costs from one point to another. In a solid-state, as ion movements are not possible, ionic compounds do not conduct electricity. Although in the molten state, ionic compounds transmit electricity as electrostatic forces attract between ions that are resistant to heat emissions.
Ionic Character Formula
Another way to measure the ionic bond of a bond — that is, the magnitude of the charge difference in a polar covalent bond — is to calculate the difference in electron negativity between two atoms.
ΔX = Xß – XA
Bond polarity and ionic grains increase with increasing differences in electronegativity.
Ionic compounds contain ions and are bound together by gravitational forces between opposing charged ions. Common salt (sodium chloride) is one of the most popular ionic compounds. Combining molecules consisting of different molecules, held together by electrons (covalent bonding).
FAQ’s
What is an ionic compound?
Ionic compounds are ion compounds. These atomic ions gain or lose electrons, resulting in complete or incorrect charging. Metals often lose electrons, so they have a good amount of charge and become cations. Non-metals tend to gain electrons, resulting in a negative charge of anions.
What are the common ionic compounds?
Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points and appear solid and cracked. Ions may be single atoms, such as sodium and chlorine in common table salt (sodium chloride) or complex groups such as calcium carbonate.
What is an example of an ionic bond?
The concept of an ionic bond is when a well-charged ion forms a negatively charged ion bond and one atom transfers electrons to another. An example of an ionic bond is Sodium Chloride, a chemical compound.
Is MgO an ionic compound?
To have an octet, Mg loses two electrons. To have an octet, oxygen receives two electrons. The ionic bond between ions is the result of the opposite cost of electricity. The final formula for magnesium oxide is MgO.








