Table of Contents
Introduction:
Influence of temperature and heating rate on the distribution of sugar cane cake pyrolysis products in a reactor with a heating plate. Influence of biomass particle size on the kinetics of slow pyrolysis and distribution of fast pyrolysis products.
Simulation of low-order internal heat transfer during pyrolysis of biomass particles. A review of computational fluid dynamics-based modeling methods for biomass pyrolysis systems. Complete simulation of heat transfer during cellulose pyrolysis with a detailed kinetic scheme. The role of heat transfer limitations in polymer pyrolysis at the microscopic level.
Effect of anisotropic porosity on heat transfer and gas release during biomass pyrolysis. Reaction mechanisms and multiscale modeling of lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis. Towards kinetic modelling based on the first principles of fast biomass pyrolysis. Particle scale model for the pyrolysis of municipal solid waste and waste fuels.
The effect of temperature and transport on the yield and composition of bio oil obtained from glucose pyrolysis.
Effect of pyrolysis temperature and sulfuric acid in the rapid pyrolysis of cellulose and Douglas fir in a wire mesh reactor at atmospheric pressure. Interaction of cellulose with hemicellulose during fast pyrolysis at different temperatures and mixing methods.
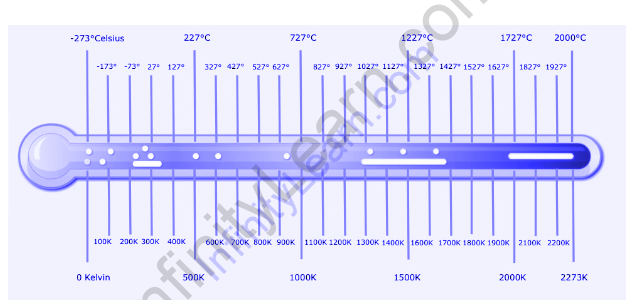
In a fundamental physical description using natural units, temperature can be directly measured in energy units. The ideal gas law allows you to measure temperature in degrees Kelvin using a gas thermometer.
In physics, the internationally accepted temperature scale is called the Kelvin scale. Most scientists measure temperature in Celsius and thermodynamic temperature in Kelvin, which is the offset of the Celsius scale so that the zero point of the Celsius scale is 0 K = -273.15 degrees Celsius, or absolute zero. Besides absolute zero temperature, the Kelvin temperature of a body in internal thermodynamic equilibrium is determined by suitably chosen measurements of physical properties, such as those having well-known theoretical explanations in terms of the Boltzmann constant.
The dimensional formula for entropy is equal to the dimensional formula for heat divided by the dimensional formula for temperature, and then the dimensional formulas for heat and temperature are arranged according to the laws of thermodynamics using the velocity equation to get the solution.
In the equation, dwpT is the difference in length between the workpiece (piston) and the reference at the temperature indicated by the measuring instrument. Where L is the length of the material at the reference temperature, DL is the change in length, CTE is the coefficient of thermal expansion, and DT is the temperature of the part minus the reference temperature; equals (Twp – exactly 68 degrees Fahrenheit or Twp – 20°C) when the reference temperature is the standard temperature.
If the instrument needs to be re-mastered, the temperature of the reference standard must be measured again and used to calculate the (EQ I) size at the temperature for the mastering step. The control approach simply means that the temperature of the workpiece, reference, and measuring instrument must be brought to an internationally recognized standard temperature before a measurement is taken. The three main elements of a measurement system that require attention when evaluating the effect of temperature are the measuring device, the standard, and the workpiece.
If all components are thermally stable in a 68°F environment, there will be no temperature-induced errors in dimensional measurements. Equation I can be used to determine the temperature-induced dimensional error that may occur in a temperature-controlled zone. Air Conditioning System.
Previously, since 1954, the International System of Units has defined the scale and unit of Kelvin as thermodynamic temperature, using the reliably reproducible triple point temperature of water as the second reference point and the first at absolute zero time 0K. . If the heat capacity is measured for a definite quantity of a substance, then the specific heat capacity is a measure of the amount of heat required per unit temperature to raise the temperature by that unit quantity. Heat is a measure of the thermal energy transferred when a system with a certain specific heat capacity and a certain mass is subjected to a temperature change. Temperature is an intensity property (one that depends on the amount of matter in the system).
FAQ’s
QUESTION: What is the dimensional formula of temperature?
ANS: M oL oT oθ
Is temperature a primary dimension?
Yes
What is dimension of absolute temperature?
None