Table of Contents
Deviations from the complex order and periodic arrangement of particles in a crystal lattice are called crystal defects. In an ideal crystal, when there are irregularities at any point or around an atom in the crystal, it is called a deviated point defect. If there is any deviation in the position of the lattice points throughout the row, the defect will be a linear defect. Point defects distort the lattice and allow atoms to move inside the solid.
When the ideal solid arrangement is distorted around atoms/points in a crystalline solid, this is called a point defect. Point defects occur when one or more atoms of a crystalline solid leave their original positions in the crystal lattice and/or foreign atoms occupy interstitial positions in the crystal. Substitution defects occur when the original atoms at the lattice positions of a crystalline solid are replaced by atoms of a different type. In fact, a Frenkel defect occurs when an atom (more precisely an ion, or rather a cation) leaves its initial position in the crystal lattice and occupies a void in the same crystal.
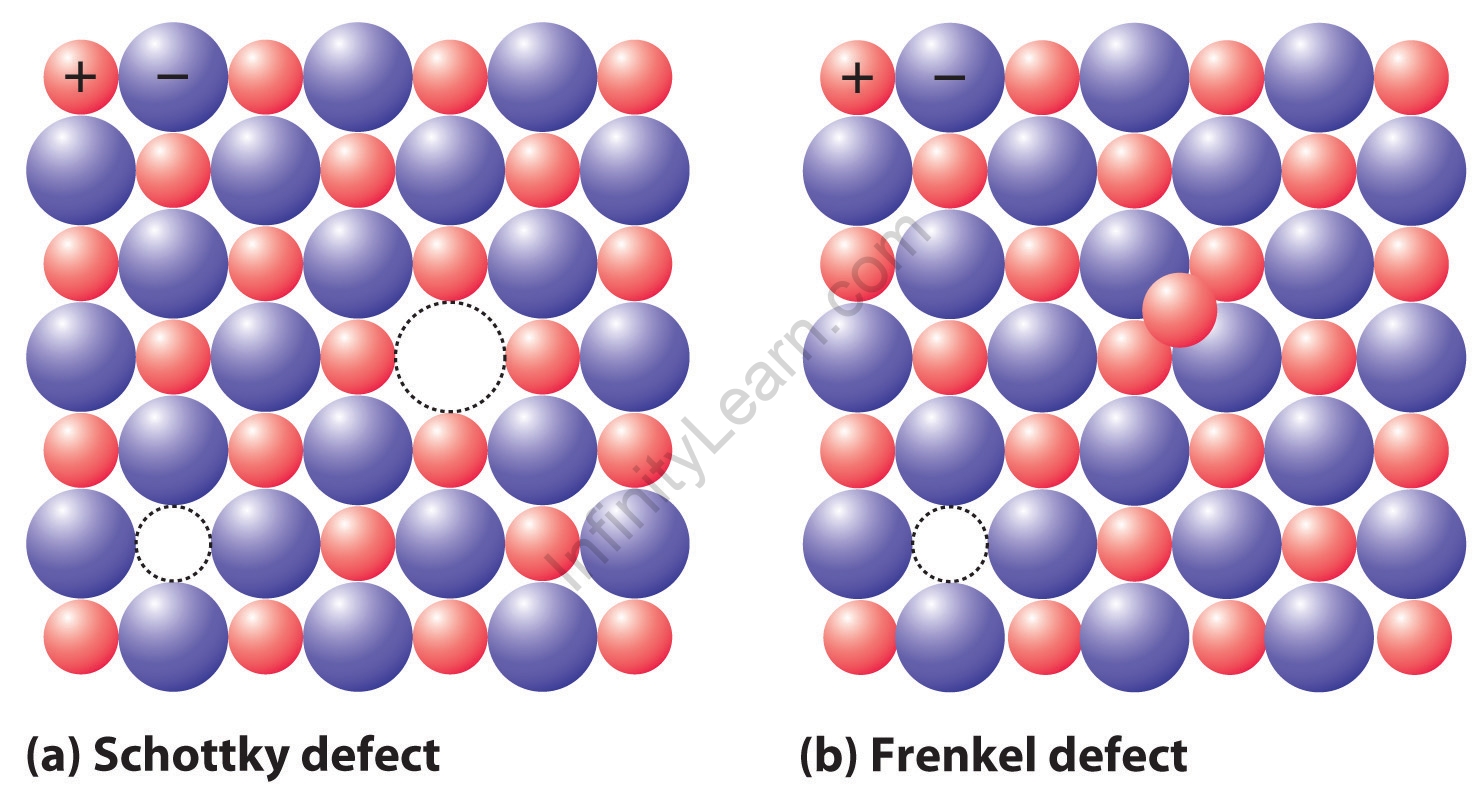
In a crystal, when an ion leaves its usual place and occupies an interstice, the defect is called a Frenkel defect.
A Frenkel defect is a type of dislocation defect or interstitial defect in which the smallest ion is usually displaced from its position to occupy an interstitial of the lattice or crystal. The Frenkel defect is usually observed in ionic solids, where the size of the anion substantially exceeds the size of the cation.
Stoichiometric defects occur when an anion is missing from its place and an electron occupies that space to keep the solid electrically neutral. In linear defects, the ratio of positive and negative ions (stoichiometric), while the electrical neutrality of the solid is not violated. The presence of stoichiometric defects provides a simple mechanism by which atoms can move within the crystal lattice.
In the case of ionic crystals (ceramic), Schottky defects and Frenkel defects can occur, which are nothing more than a combination of two different types of four groups. Point Defects Point defects can be divided into Frenkel defects and Schottky defects and are often found in ionic crystals. Point defects describe solid defects along with types of point defects.
Because point defects allow the planes of atoms in a solid to move one row at a time, dislocations weaken the metal. Linear defects or dislocations are lines in which entire rows of atoms are abnormally located in a solid. Crystal defects appear as point, line or surface defects, respectively called point, line or plane defects.
Crystal defects are common because in crystals with periodic crystal structures, the positions of atoms or molecules at repeating fixed distances determined by unit cell parameters are often imperfect.
The absence and deficiencies of atoms or ions in an ideal or hypothetical crystal structure or lattice, and the displacement of the unit cell in a real crystal, are called crystal defects or solid defects. Solid defects occur when the regular arrangement of atoms in a crystal structure is hindered in various ways. During the crystallization process, solid defects can occur due to the excessive or moderate rate of crystal formation.
Ionic solids that maintain the neutrality of the crystal are shown as Frenkel and Schottky defects. A Schottky defect is a type of vacancy defect in which an equal number of cations and anions is absent, but the crystal remains neutral.
Due to a decrease in the number of atoms in a crystalline solid, a vacancy defect leads to a decrease in density. What defects arise due to improper placement of atoms or ions and their vacancies in a crystalline material. For example, removing an atom from a crystal structure or replacing it with an atom of another element can be considered a crystal defect.
Point defects can change the physical and chemical properties of a solid, since they can turn an insulator into an electrically conductive one and increase the hardness of the material. Linear defects weaken the structure along with one-dimensional space, and the type and density of defects affect the mechanical properties of solids.
Previous studies only considered defects in one dimension, along chains of atoms, but real materials cannot be described in one dimension. Defects can also be defined as amorphous solids based on hollow or dense local atomic regions, and the nature of such defects can be evidenced by being analogous to normal vacancies and voids in crystals. Dislocations are one-dimensional defects caused by insufficient holes to become vacancies.
A similar phenomenon occurs when one atomic plane passes another atomic plane due to dislocation defects. Edge dislocations are additional half-planes of atoms that intersect parts of the solid structure.
Colour centres are imperfections in crystals that cause color (defects that cause color by absorbing light). Point defect – Imperfection of the crystal lattice due to the displacement of a particle from one position to another in the lattice. Stoichiometric defects occur when some sites in the crystal lattice remain vacant; that is, in some places, solid particles are missing. Impurity defects are foreign atoms that replace some of the atoms that make up a solid body, or are crushed in interstices; they are important for the electrical characteristics of semiconductors, materials used in computer chips and other electronic devices.
FAQs:
What is called imperfections in solids?
Crystal defects
What is defect type?
Zero dimensional defects
What are the various defects in solids explained with examples?
The missing and lacking atoms or ions in an ideal or imaginary crystal structure or lattice and the misalignment of unit cells in real crystals.


