Table of Contents
Benzene (likewise called cyclohexatriene) is a natural substance compound with the sub-atomic recipe C6H6. The benzene particle is made out of six-carbon molecules participating in a planar ring with one hydrogen iota joined to each. Since it contains just carbon and hydrogen particles, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon.
Benzene is a characteristic constituent of raw petroleum and is one of the rudimentary petrochemicals. Because of the cyclic ceaseless pi connections between the carbon particles, benzene is classed as a sweet-smelling hydrocarbon. It is in some cases contracted PhH. Benzene is a boring and profoundly combustible fluid with a lovely smell, and is to some degree liable for the fragrance around petroleum (gas) stations. It is utilized fundamentally as an antecedent to the assembling of synthetic compounds with more intricate designs, for example, ethylbenzene and cumene, of which billions of kilograms are delivered yearly. Albeit a significant modern synthetic, benzene finds restricted use in shopper things due to its toxicity. The hybridization of benzene is supposed to be sp2 type. Benzene comprises of 6 carbon and 6 hydrogen iotas where the focal particle generally is hybridized. Here, carbon is the focal iota.
What is the Hybridization of Benzene?
Before we talk about the hybridization of C6H6 let us initially get the construction of benzene. This synthetic compound is produced using a few carbon and hydrogen particles. Notwithstanding, to shape benzene, the carbon particles will require one hydrogen and two carbons to frame bonds. Further, the carbon iota misses the mark on expected number of unpaired electrons to frame the bonds. At this stage its electronic design will be 1s2, 2s2, 2px1, 2py1. What occurs next is the advancement of one 2s2 electron pair to the void 2pz orbital.
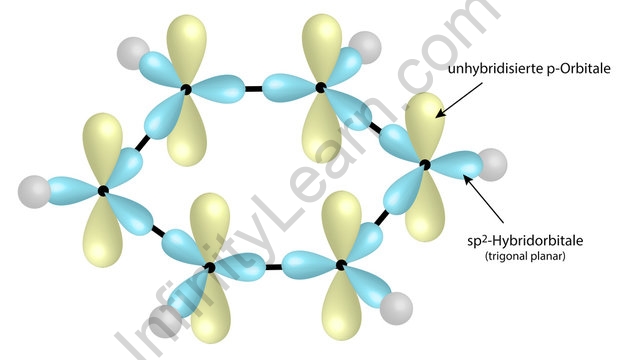 During this, the carbon iota will go into an invigorated state and the electron arrangement will likewise change to become 1s2, 2s1, 2px1, 2py1, 2pz1. Presently when the electron is elevated from the 2s to the void 2p orbital, we will get 4 unpaired electrons. These electrons will be utilized in the development of the bonds. For, hybridisation to happen the external orbitals are utilized. Three of the carbon orbitals are utilized rather than every one of the four. In this, 1 s orbital and two p orbitals are hybridized and structure three sp2 hybridized orbitals. Every one of the carbon particles will shape sigma bonds with two different carbons and one hydrogen atom.
During this, the carbon iota will go into an invigorated state and the electron arrangement will likewise change to become 1s2, 2s1, 2px1, 2py1, 2pz1. Presently when the electron is elevated from the 2s to the void 2p orbital, we will get 4 unpaired electrons. These electrons will be utilized in the development of the bonds. For, hybridisation to happen the external orbitals are utilized. Three of the carbon orbitals are utilized rather than every one of the four. In this, 1 s orbital and two p orbitals are hybridized and structure three sp2 hybridized orbitals. Every one of the carbon particles will shape sigma bonds with two different carbons and one hydrogen atom.
The state of benzene
Benzene is a planar customary hexagon, with bond points of 120°. This is effectively clarified. It is a customary hexagon since every one of the bonds are indistinguishable. The delocalisation of the electrons intends that there aren’t rotating twofold and single bonds. It is planar in light of the fact that that is the main way that the p orbitals can cover sideways to give the delocalised pi framework.
The fiery soundness of benzene
This is represented by the delocalisation. As an overall guideline, the more you can spread electrons around – at the end of the day, the more they are delocalised – the more steady the atom becomes. The additional security of benzene is frequently alluded to as “delocalisation energy”.
Derivatives of Benzene
Numerous significant substance compounds are gotten from benzene by supplanting at least one of its hydrogen molecules with another practical gathering. Instances of straightforward benzene subordinates are phenol, toluene, and aniline, condensed PhOH, PhMe, and PhNH2, separately. Connecting benzene rings gives biphenyl, C6H5-C6H5. Further loss of hydrogen gives “combined” fragrant hydrocarbons, like naphthalene, anthracene, phenanthrene, and pyrene. The restriction of the combination interaction is the without hydrogen allotrope of carbon, graphite.
In heterocycles, carbon particles in the benzene ring are supplanted with different components. The main varieties contain nitrogen. Supplanting one CH with N gives the compound pyridine, C5H5N. Despite the fact that benzene and pyridine are basically related, benzene can’t be changed over into pyridine. Substitution of a second CH bond with N gives, contingent upon the area of the subsequent N, pyridazine, pyrimidine, or pyrazine.
Where benzene is found and the way in which it is utilized
- Benzene is framed from both regular cycles and human exercises.
- Regular wellsprings of benzene incorporate volcanoes and woods fires. Benzene is likewise a characteristic piece of unrefined petroleum, gas, and tobacco smoke.
- Benzene is broadly utilized in the United States. It positions in the main 20 synthetic compounds for creation volume.
- A few businesses use benzene to make different synthetic compounds that are utilized to make plastics, gums, and nylon and manufactured filaments. Benzene is likewise used to make a few sorts of ointments, rubbers, colors, cleansers, medications, and pesticides.
How benzene functions
- Benzene works by causing cells not to work accurately. For instance, it can cause bone marrow not to create sufficient red platelets, which can prompt pallor. Likewise, it can harm the safe framework by changing blood levels of antibodies and causing the deficiency of white platelets.
- The reality of harming brought about by benzene relies upon the sum, course, and time allotment of openness, as well as the age and previous ailment of the uncovered individual.
FAQs
Q: What is Benzene?
Ans: • We realize that benzene is a natural substance compound with the synthetic equation C6H6.
• The benzene particle involves six-carbon molecules participating in a ring with one hydrogen iota joined to each. Since it contains both Carbon and Hydrogen molecules, we order benzene as a hydrocarbon.
• It has a sp2 hybridization.
• During the hybridization cycle, every carbon molecule structures various bonds with two other comparable carbon particles rather than only one.
• Benzene has a Trigonal Planar calculation having a bond point of 120°.
State the uses of Benzene.
The greater part of the benzene created every year is changed over to ethylbenzene, then, at that point, to styrene, and afterward to polystyrene. The following biggest utilization of benzene is in the arrangement of phenol. Different purposes incorporate the arrangement of aniline (for colors) and dodecylbenzene (for cleansers).





