Table of Contents
Introduction
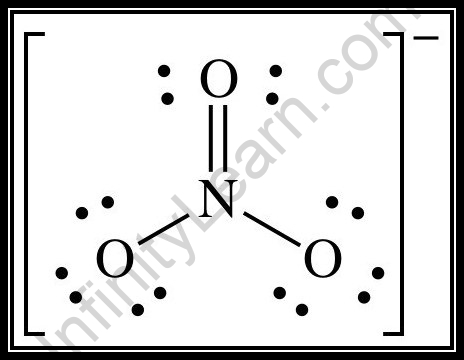
The simplest method for deciding the hybridization of nitrate is by drawing the Lewis structure. In the wake of drawing the construction, we really want to count the number of electron sets, and the bonds that exist in the focal nitrogen particle. On the off chance that we see NO–3, the focal particle is reinforced with three oxygen molecules, and there exist no solitary sets. Also, on the off chance that we check the Lewis structure further, one of the nitrogen-oxygen bonds is a twofold bond other than the other two are of single bonds.
The three sp2 orbitals of nitrogen cross over with one s orbital of the oxygen particle during holding. The p orbital of nitrogen creates a twofold bond with three oxygen particles where the three electron sets are divided among the p orbital of the nitrogen and one p orbital of oxygen molecule each. The oxygen iotas will likewise have two p orbitals that will oblige a solitary pair of electrons.
NO3 Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles
There is one focal particle in nitrate which is encircled by 3 indistinguishably reinforced oxygen molecules that lie at the triangle corners and a comparable one-layered plane. Basically, nitrate has 3 electron spaces with zero solitary sets. Consequently, NO–3 atomic calculation is three-sided planar and is somewhat bowed. The bond point is 120°.
Hybridization of the Central Atom in NO–3
To know the focal particle’s hybridization in NO–3, let us adopt the strategy of drawing the Lewis design of it, which looks like follows.
Presently, without forgetting the ‘−,’ we want to ascertain the number of electrons present in the NO–3. We should then position the bonds with the right number of electrons and fill in the solitary sets around the iotas to get the right number of absolute electron count (electrons, addressed as dabs).
Presently, by utilizing the accompanying table, we really want to track down the hybridization.
Presently, we should count the number of connections between the particles on the Lewis construction and afterwards really take a look at the table. In the Lewis structure, we can see 3 connections between the molecules (the specks shown between iotas are the bonds).
- Alluding to the table under ‘kind of half and half orbital’, this is the place where the hybridization ought to be. That is to say, for ‘the number of bonds’ = 3 and the hybridization is sp2. Thus, the outcome is sp2.
- Bond Lengths Order For NO+2, NO–2, And NO–3
- Allow us to ascertain the bond orders prior to going to track down the request. The higher the bond request results, the more limited the bond length.
- Along these lines, Bond order= (Number of holding electrons – Number of antibonding electrons)/2.
- Presently, to compute these, we ought to consider the sub-atomic request of a heteronuclear diatomic particle NO first. Presently, the NO atom has 6 electrons in the holding orbitals and 1 electron in the antibonding orbital. Accordingly, it has the bond request of (6-1)/2 = 2.5.
- Then, at that point, NO+2 has 2 electrons, which is lesser than NO. It has 6 electrons in the fourth holding orbitals and zero electrons in antibonding. Along these lines, it has the bond request of (6-0)/2 = 3.
- For NO–2, the bond request is given by, (6-3)/2=1.5, and
- For NO–3 the bond request is given by (6-4)/2=1
- The request for the bond request can be given by, NO+2 > NO–2 > NO–3
- In this manner, the request for bond length becomes NO–3 > NO–2> NO+2
Sub-atomic Structure of NO–3
Since the nitrate particle comes from the nitric corrosive, so let us start from the construction of nitric corrosive.
Assuming we notice the holding around the nitrogen cautiously, we will see that one of the bonds is totally framed from the solitary pair on the nitrogen. That is known as the direction bond. The nitrate particle structures by the deficiency of the hydrogen particle as its design looks as underneath.
There are 4 sets of shared electrons around the focal nitrogen and no solitary pair remaining. Presently, the first solitary pair has turned into a holding pair. Along these lines, two of those sets structure a twofold bond. The two single bonds and the twofold bond unit organize themselves as far separated in a three-sided planar course of action as could be expected – unequivocally like the carbonate particle, which is given underneath.
The territory of Hybridization of N In NO–3
Allow us to examine the sp3 half breed orbitals of the focal molecule N. Here, the three sp2 orbitals present in a plane and structure a course of action of a three-sided plane. Every one of these N-O bonds is created by covering a nitrogen sp2 half and half orbital and the oxygen 2p orbital. Along these lines, the atom, NO–3 is planar, and all the ONO points become 120°.
Utilizations of NO3
- A portion of the purposes of nitrate is recorded underneath.
- The nitrate (NO3 ) can be utilized as a natural or inorganic ester or salt of nitric corrosive, containing the (NO–3 ) particle.
- Of all salts, nitrates are the most dissolvable in water and assume a huge part in the nitrogen cycle and nitrate contamination also.
- The inorganic nitrates are shaped by microorganisms and are fundamental parts of farming soil.
- Nitrate is a fundamental synthetic in the agrarian business.
- Likewise, a fundamental plant supplement aids the plants’ development and cycles, like photosynthesis.
Nitrate
The sub-atomic equation of nitrate is NO3 and nitrate is one of the types of nitrogen. Nitrate can be begun by normal as well as counterfeit means. The most well-known utilization of nitrate is that they help in plant development. Aside from this nitrate is even utilized in making inorganic manures and explosives. Nitrate is additionally utilized as a food additive. An excessive number of nitrates in water can cause a natural awkwardness of water and can cause eutrophication. Nitrites are likewise present in the follow levels of soil, normal waters, plants, and creature tissues.
Utilizations of Nitrate NO3
Underneath referenced are a few purposes of nitrates:
- The nitrate (NO3 ) is utilized as a natural as well as an inorganic ester.
- Of all salts present on the earth, nitrate is the most dissolvable in water and assumes a huge part in the nitrogen cycle and nitrate contamination also.
- The inorganic nitrates are framed by microorganisms and are fundamental parts of agrarian soil.
- Nitrate is a fundamental substance in the horticultural business.
- A fundamental plant supplement helps in the plants’ development and cycles like photosynthesis, photosynthesis is an interaction through which green plants make their own food within the sight of daylight, chlorophyll, water, and supplements like nitrate, and so on
- Nitrates are likewise utilized as food additives.
- Aside from this nitrate is even utilized in making inorganic manures and explosives.
Compound Properties of Nitrate
Beneath referenced is a portion of the super synthetic properties of nitrate:
- Nitrate is especially potassium nitrate and it is otherwise called nitre or nitre and saltpetre.
- The hybridization kind of nitrate is sp2 and the security point of nitrate is 120 degrees.
- The sub-atomic load of Nitrate is 62.005.
Hybridization of Nitrate
Hybridization is a prevalently involved term in science, in any case, hybridization implies intermixing of two nuclear circles to foster another sort of circle. The new circle which is the essential aftereffect of this intermixing hybridization process has altogether unique energy, shape, size, and mass.
Hybridization of Nitrate NO3
During holding, nitrogen’s three sp2 orbitals cross over with one s orbital of the oxygen molecule. Concerning the p orbital of nitrogen, it shapes a twofold bond with three oxygen particles where three sets of electrons are divided among the p orbital of the nitrogen and one p orbital of every oxygen molecule. The oxygen iotas will likewise have two p orbitals which will oblige a solitary pair of electrons.
FAQs
Clarify the Structure of Nitrate Ions.
The anion is the nitric corrosive's form base with one focal nitrogen molecule encompassed by 3 indistinguishably reinforced oxygen iotas in a course of action of a three-sided planar. As a rule, the nitrate particle conveys a proper charge of −1. This charge results from a conventional charge blend in which every one of the three oxygens conveys a charge of − 2⁄3.
Clarify the Occurrence and Production of Nitrate.
Nitrate salts are normally found on earth as huge stores, explicitly of nitratine, which is a huge wellspring of sodium nitrate. A few nitrifying microscopic organisms species structure nitrates and the nitrate compounds for explosive were delivered by and large, without even a trace of mineral nitrate sources and utilizing different ageing cycles utilizing waste and pee.
What is the Hybridization of Nitrate NO3?
During the holding system nitrogen's three sp2 orbitals cross over with one s orbital of the oxygen molecule. Concerning the p orbital of nitrogen, it shapes a twofold bond with three oxygen molecules where three sets of electrons are divided among the p orbital of the nitrogen and one p orbital of every oxygen particle. The oxygen iotas will likewise have two p orbitals which will oblige a solitary pair of electrons.








