Table of Contents
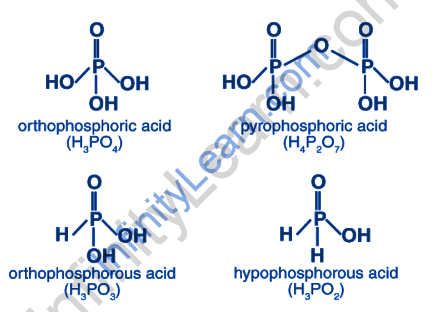
In layman’s terms, oxoacids are acids that contain oxygen. Phosphorus is one such element that can be used to create a variety of oxoacids. H3PO4, H3PO3, and other common oxyacids The phosphorus atom is tetrahedrally surrounded by other atoms in phosphorus oxoacids. In general, it is clear that these acids contain at least one P=O bond and one P–OH bond. In addition to P=O and P–OH bonds, phosphorus oxoacids contain P–P or P–H bonds. In these cases, the phosphorus oxidation state is less than +5. ese acids are known to jump between higher and lower oxidation states. When heated, phosphorous acid, for example, disproportionates to form phosphoric acid and phosphine.
The P-H bonds in oxoacids cannot be ionised to produce H+ ions. The H atoms attached to oxygen in P-OH form, on the other hand, are ionisable. As a result, we can say that basicity is a property exhibited by H atoms attached to oxygen. As a result of the two P-OH bonds, phosphorous acid, H3PO3, is dibasic. Similarly, phosphoric acid, H3PO4, is tribasic due to the presence of three P-OH bonds. Phosphorus oxoacids with P-H bonds have strong reducing properties. Hypophosphorous acid, which contains two P-H bonds, is an excellent reducing agent.
4AgNO3 + 2H2O + H3PO2 → 4Ag + 4HNO3 + H3PO4
Basicity of Oxoacids of Phosphorus
The basicity of phosphorus oxoacids is defined as the number of ionizable H+ ions or protons in that acid. The structure of Phosphorus Oxoacids (H3PO3) is shown below. Although the structure of Phosphorus Oxoacids contains three H atoms, only those directly attached to the Oxygen (O) atom are easily ionised. There are, however, only two such H atoms.
Uses of Oxoacids of Phosphorus
Phosphorus oxoacids have a wide range of applications, including:
- Phosphorus is used as a sulphuric acid substitute in the production of HI and HBr.
- It is used in the preparation of soft drinks as a souring agent.
- It is used in the production of sodium, ammonium, and potassium phosphate salts.
- It’s used in the production of phosphatic fertilisers.
Few popular oxoacids of phosphorus
H3PO3 phosphoric acid: Phosphoric acid is a diprotic acid, which means it ionises two protons. The structural formula describes it better. HPO(OH)2 The hydrolysis of phosphorus trichloride with acid or steam yields phosphoric acid.
PCl3+ 3H2O → HPO(OH)2 + 3HCl
H3PO4 (phosphoric acid)
Phosphoric acid is classified as a tricrotic acid. This means it has the ability to ionise three protons. When pure, it is a non-toxic acid. At room temperature and pressure, it is solid. Sulfuric acid can be used to make phosphoric acid by combining it with tricalcium phosphate rock:
Ca5(PO4)3X + 5H2SO4 +10H2O → 3H3PO4 + 5CaSO4.2H2O + HX
HPO3 (Polymetaphosphoric Acid)
We can get it by heating orthophosphoric acid to around 850 degrees Celsius. As a monomer, it does not exist. It comes in the form of a cyclic trimer, cyclic tetramer, or polymer.
FAQs
Which phosphorus oxoacid is the most acidic?
In the first case, all of the hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom as an OH group, allowing hydrogen to be easily released as protons. As a result, the acidity will be the highest.
What is the chemistry of oxoacids?
A ternary acid, oxyacid, oxoacid, or oxyacid is an acid that contains oxygen. It is a compound containing hydrogen, oxygen, and at least one other element, with at least one hydrogen atom bonded to oxygen that can dissociate to produce the acid's H+ cation and anion.






