Table of Contents
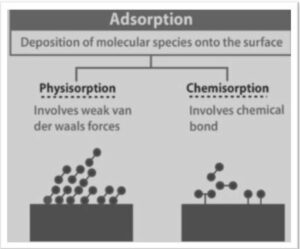
Physisorption: The exothermic process of physisorption is also known as physical adsorption. It has a modest enthalpy of adsorption, ranging from 20 to 40 kJ/mol. During physical adsorption, weak Van der Waals forces cause the gas to collect only on solid objects.
A brief outline of Physisorption
Physisorption suffers from some limitations since the adsorbent in the provided surface doesn’t really suggest any specific gas. It is reversible in nature, in the sense that gas physisorption by a solid could be reversed. It will be the adsorption of gases like hydrogen, nitrogen, and other gases just on the surface of adsorbents including charcoal.
Important concepts
The Van der Waals force is the primary interacting force in physisorption. It plays an essential role in nature, despite the low contact energy (10–100 meV). For example, geckos’ extraordinary ability to scale vertical walls is due to the van der Waals affinity between surfaces and foot-hairs. The interactions between induced, persistent, or transient electric dipoles produce Van der Waals forces.
In contrast to chemisorption, which alters the electronic structure of bonding atoms or molecules and results in the formation of covalent or ionic connections, physisorption does not alter the chemical bonding structure. In reality, determining whether adsorption is physical adsorption or chemisorption is based mostly on the adsorbate’s binding energy to the substrate, with physis-orption being significantly weaker on a per-atom basis than any sort of chemical bond.
Physical adsorption is reversible to some extent since the adsorbed substance is also quicker to desorb. Adsorbed gas on activated carbon, for example, can be easily extracted without causing any environmental impacts. Hydrogen physisorption on carbon nanostructures opens up the potential of low-pressure, rapid, and fully reversible hydrogen and other gas storage systems. The molecular interactions happening at a solid surface can be probed on a surface. Because the type of the adsorbing species could be determined, this gives a method for investigating the solid’s characteristics.
It does not change the chemical bonding structure, unlike chemisorption, which changes the electronic structure of bonding atoms or molecules and helps in the formation of covalent or ionic connections.
Significance of moment of inertia of a hollow cone in IIT JEE exam
Owing to the reduced weightage for the parts, this topic does have a weightage of around 3.33 per cent in all years. This suggests that there will be 1 or 2 questions on this topic, each with a point value of 4 points.
Join our specially curated JEE 2024 course to make your IIT dream come true in the upcoming JEE 2023 exam.
FAQs on Physisorption
Temperature and physisorption are mutually exclusive. As the temperature rises, the efficiency of physisorption decreases.
Physisorption is a type of adsorption in which the force between adsorbate and the adsorbent is a physical van der Waals force. Because the adsorbent and adsorbate have weak Van der Waals forces, this is the case.
Physical adsorption, but on the other hand, is inherently non-specific. What is the link between temperature and physisorption?
What type of forces exist between the adsorbate and the adsorbent during physisorption?
Is physical adsorption a common occurrence?