Table of Contents
Charles’s law is a test gas regulation. It makes sense of how gases will quite often extend when warmed. French physicist Charles concentrated on the impact of temperature on the amount of gas at steady tension. This regulation portrays how a gas extends on account of the temperature increments; on the other hand, a diminishing in temperature will cause a reduction in volume.
Charles’s Law Formula
Charles’s Law equation is composed as,
V1/T1=V2/T2
Where V1=Initial volume
V2=Final volume
T1= Initial outright temperature
T2=Final outright temperature
Here we ought to recollect that the temperatures are outright temperatures that are estimated in Kelvin, not in ⁰F or ⁰C.
Charles’s Law Derivation
In this segment, we will examine bit by bit deduction of the Charles regulation recipe.
Consider a framework whose underlying volume is V1 and starting temperature is T1.
Presently as per Charles’s regulation, the volume will be straightforwardly corresponding to temperature at consistent strain. So we can compose the connection among volume and temperature as follows:
V1 ∝ T1… … … … … … (1)
Since volume is straightforwardly corresponding to temperature, assuming that the temperature of the framework is expanded to T2the volume will likewise build relatively to V2. Presently the numerical articulation of Charles regulation at temperature T2 will be as per the following:
V2 ∝ T2… … … … … … (2)
Presently eliminating the proportionality sign by presenting the non zero consistent k we can compose conditions (1) and (2) as follows:
V1 = kT1
V1/T1=k… … … … … … … (3)
V2 = kT2
V2 /T2=k… … … … … … … … … … … (4)
The non zero consistent in conditions (3) and (4) are something very similar, so by contrasting conditions (3) and (4) we will get the numerical articulation of Charles regulation as follows:
V1/T1=V2 /T2 or
V1/V2 =T1/T2 or
V1/T2 = V2 /T1
This articulation gives the Charles regulation when a similar material is under two distinct arrangements of conditions.
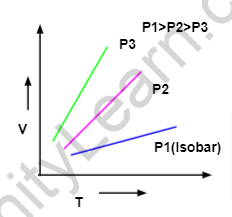
Graphical Representation Of Charles Law
ISOBAR-Graph among V and T at consistent tension is known as isobar or bioplastics and it generally gives a straight line. A plot of V versus T (°C) at steady tension is a straight line at – 273.15°C. – 273.15-degree Celcius is the most minimal conceivable temperature.
Charles Law Application In Real Life
- This regulation has a wide application in day to day existence. Some
- In a chilly climate or in a cool climate, helium inflatables recoil.
In winters when the weather conditions are cool, the limit of the human lung diminishes. This makes it harder for the competitors to perform on a freezing winter day and it additionally makes it challenging for individuals to go running.
FAQs
What is Charles Law in straightforward terms?
Charles' regulation, an explanation that the volume involved by a proper measure of gas is straightforwardly relative to its outright temperature, assuming the strain stays consistent.
How is Charles's regulation utilized in space?
Charle's Law in Space Charles regulation is actually utilized in space. At the point when we send off a rocket, they increment the temperature and the hotness, making the rocket go up and simultaneously speed up.
Is Charles's regulation an immediate relationship?
Charles Law is an immediate connection between temperature and volume. At the point when the temperature of the atoms builds the particles move quicker making more strain on the compartment of the gas expanding the volume, assuming that the tension remaining parts steady and the quantity of the atoms stay consistent.
Also Read For:
Charles Law – Definition and Examples | Charles Law in General Gas Equation
Charles’s Law Relationship Between Temperature Volume









