Table of Contents
A periodic variable’s amplitude is indeed a measure of its change over a single period (such as time or spatial period). A non-periodic signal’s amplitude would be its magnitude in comparison to a reference value. There are a few definitions of amplitude (see below), all of which are functions of the magnitude of the differences between the extreme values of the variable. The phase of a periodic function is sometimes referred to as the amplitude in older texts.
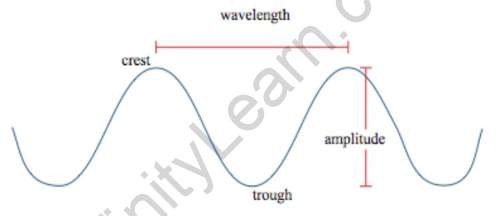
The units of amplitude vary according to the type of wave, but they are always the same as the oscillating variable. The role of amplitude remains analogous to this simple case in a more general representation of the wave equation.
The amplitude of waves on a string or in a medium such as water is a displacement.
In fact, the amplitude of sound waves and audio signals (which corresponds to volume) has been traditionally defined as the amplitude of the air pressure in the wave, but it is also used to describe the amplitude of displacement (movements of the air or the diaphragm of a speaker). Because the logarithm of the amplitude squared is usually expressed in decibels (dB), a null amplitude corresponds to −∞ dB. Loudness would be related to amplitude and intensity and is one of the most noticeable qualities of a sound, though it can be recognised independently of amplitude in most sounds. We can say that the intensity of the wave will be proportional to the square of the amplitude.
The amplitude of a photon in electromagnetic radiation relates to changes in the wave’s electric field. Even so, radio signals can be carried by electromagnetic radiation; the intensity (amplitude modulation) or frequency (frequency modulation) of the radiation oscillates, and then the individual oscillations are varied (modulated) to produce the signal.
Complex transient timbres could be achieved with waveforms containing many overtones by assigning each overtone to its own distinct transient amplitude envelope. Regrettably, it has the unintended consequence of modulating the loudness of the sound as well. It is more logical to separate loudness and harmonic quality as parameters that can be controlled independently of one another.
Dimensional Formula of Amplitude
The dimensional formula of the amplitude of a wave can be represented as:
[M0 L1 T0]
Here,
M = Mass
L = Length
T = Time
Derivation
We have, the amplitude of wave = Maximum displacement
Because the dimensional formula of displacement = [M0 L1 T0]
Thus, the amplitude of a wave has been dimensionally represented as [M0 L1 T0].
FAQs
What determines amplitude?
The amplitude of a wave is really a measure of its strength or intensity. While looking at a sound wave, for example, the amplitude measures the loudness of the sound. The wave's energy differs in direct proportion to the wave's amplitude.
What is the dimension of SHM?
The one-dimensional projection of uniform circular motion has always been simple harmonic motion. Whenever an object moves with angular speed ω around a circle with radius r centred at the origin of the XY-plane, its motion along each coordinate is simple harmonic motion with amplitude r and angular frequency ω.






