Table of Contents
An LC circuit is really a type of electric circuit that consists of an inductor denoted by the letter L and a capacitor denoted by the letter C. Both of these are connected in a single circuit in this case. An LC circuit is often known as a tank circuit, resonant circuit, or tuned circuit. LC circuits are important components in many electronic devices, including radio equipment, and can be found in circuits such as filters, oscillators, and tuners.
In many cases, an LC circuit is indeed a suitable model because it allows us to assume that there is no energy dissipation even if there is resistance. Even so, any practical implementation will result in loss due to the small electrical resistance in the connecting wires or components. Such a type of circuit is used because it can oscillate with minimal damping, resulting in the lowest possible resistance. Even so, the majority of the circuits operate with some loss.
An LC circuit can store electrical energy when it oscillates at its natural resonant frequency. The capacitor will store energy in the electric field (E) between its plates relying on the voltage it receives, whereas an inductor will accumulate energy in its magnetic field depending on the current (B).
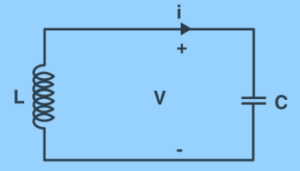
Nomenclature
The di elemental LC circuit is just a basic example of an inductor-capacitor network. Furthermore, it is referred to as a second-order LC circuit to distinguish it from more complicated LC networks with more capacitors and inductors. Such LC networks with more than two reactances can have multiple resonant frequencies.
A resonant frequency is really a system’s undamped or natural frequency. The resonant frequency of an LC circuit is usually determined by the impedance L and capacitance C. In the meantime, the network order would be a rational function order that describes the network in complex frequency variables s. In general, the order equals the number of L and C elements in the circuit and cannot be exceeded in any case.
Applications or Uses of LC Circuit
The resonance impacts of LC circuits have a wide range of applications, including communication systems and signal processing.
- LC circuits are being used to detect or generate a signal at a specific frequency.
- Tank circuits are most commonly used for tuning radio transmitters and receivers. When you tune a radio to a particular station, for example, the LC circuits establish a resonance for that carrier frequency.
- Current magnification has been produced by a parallel resonant circuit.
- Voltage magnification has been produced by a series resonant circuit.
- Induction heating employs both series and parallel resonant circuits.
FAQs
Where are LC circuits used?
LC circuits are being used to detect or generate a signal at a specific frequency. Tank circuits have been most commonly used for tuning radio transmitters and receivers. Once you tune a radio to a particular station, for example, the LC circuits establish a resonance for that carrier frequency.
Why do LC circuits produce oscillations?
Once we connect a charged capacitor to an inductor, the electric current and charge on the capacitor in the circuit oscillate. This pattern then repeats itself at a fixed frequency, and if no resistance is present in the LC circuit, the LC oscillations will continue indefinitely.






