Table of Contents
Introduction
The oxidation state, also known as the oxidation number, is the charge that an atom would have if all of its links to other atoms were entirely ionic. It refers to how much an atom in a chemical compound has been oxidized (lost electrons). The oxidation state can theoretically be positive, negative, or zero.
A brief outline
Antoine Lavoisier used the term “oxidation” to describe the reaction of a material with oxygen. Much later, it was discovered that the substance loses electrons when oxidized, and the definition was expanded to include any reaction in which electrons are lost, irrespective of whether oxygen is present.
Important concepts
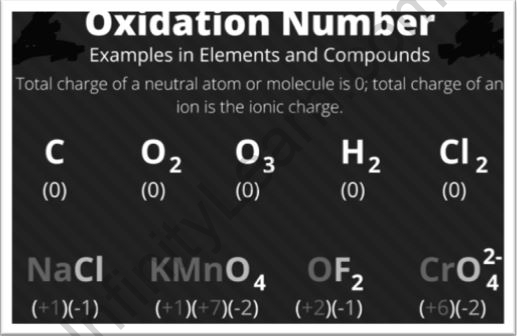
The oxidation state, or number, aids in the description of electron transmission. However, students should be aware that this is not the same as a formal charge, which determines atom configuration. In redox reactions, the oxidation number/state is also employed to determine the changes that occur. In the meanwhile, it’s very similar to valence electrons.
The charge that an atom seems to have when forming ionic connections with other heteroatoms is described by its oxidation number. A negative oxidation number is ascribed to an atom with higher electronegativity.
The definition gives an atom’s oxidation state based on whether or not the atom
- Bonds with heteroatoms.
- Ionic bonding is always formed by either receiving or losing electrons, regardless of the nature of the bonding.
Atoms or ions lose or gain electrons in redox reactions, resulting in various oxidation states before and after the process.
- The number of oxidations might be positive, zero, or negative.
- Because the number of electrons can only be an integer, the oxidation number must be an integer.
Significance of oxidation number in IIT JEE exam
Every aspect of a subject’s chapter should be approached holistically. The most significant chapter in chemistry is weighted at 13.3 per cent, while the remaining chapters are weighted at 3.3 per cent and 6.6 per cent. The topic of oxidation number, which is part of the redox reaction chapter, contributes to 3.3 per cent of the exam with 1 to 2 questions.
FAQs
In terms of significance, usage, representation, and charge indication, oxidation states and oxidation numbers are not interchangeable.
The highest oxidation state that may be set to an element is +9, and it cannot go higher than that.
Oxidation state is important in determining the strength of acids and bases, as well as determining the charge of an atom in a chemical reaction. While a rise in oxidation state implies that an acid's strength is increasing, it also shows that a base's strength is decreasing. What are the similarities and differences between the Oxidation States and numbers?
What is the maximum positive oxidation state that an element can have?
What may the oxidation state be used for?






