Table of Contents
Introduction
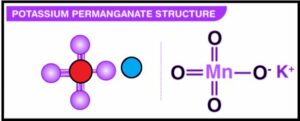
KMnO4 is the chemical formula for potassium permanganate, an inorganic molecule. It’s a crystalline purplish-black salt. Potassium permanganate is extensively used as a strong oxidizing agent in the chemical sector and labs, as well as a treatment for dermatitis, wound cleansing, and general disinfection.
A brief outline
The solution created when potassium permanganate crystals are exposed to water is purple. It’s a potent oxidizing agent that doesn’t produce any hazardous by-products. Other minerals, such as manganese oxide, are frequently used to make it.
Important concepts
- KMnO4 – Potassium Permanganate Preparation
Commercial potassium permanganate is made by combining a solution of potassium hydroxide and granular manganese oxide with oxidizing agents such as potassium chlorate. The mixture is cooked until it has evaporated, then heated in iron pans till it acquires a pasty consistency.
- 6KOH + 3MnO2 + 6KClO3 → 3K2MnO4 + 6KCl + 3H2O
The potassium manganate (green) is then heated with a huge amount of water and a current of chlorine, CO2, and ozonized air is circulated through the liquid until permanganate is created. To prevent the MnO2 from breaking down the permanganate, it is continually removed.
- 6K2MnO4 + 3Cl2 → 6KMnO4 (Potassium Permanganate) + 6KCl
The KMnO4 solution is extracted from any concentrated and crystalline MnO2 precipitate. The crystals are dried after centrifugation.
Potassium Permanganate – KMnO4 Physical Properties
- It’s a crystalline substance that’s odourless and ranges from purple to magenta in colour.
- Water, acetone, acetic acid, methanol, and pyridine are all soluble in it.
- In ethanol and organic liquids, it dissolves.
Potassium Permanganate Chemical Properties
- Because potassium permanganate is a powerful oxidising agent, it can be utilised as an oxidant in a wide range of chemical reactions.
- When initiating a redox reaction with potassium permanganate, the dark purple solution will turn colourless and eventually into a brown solution, demonstrating its oxidising power.
Significance of potassium permanganate in IIT JEE exam
Organic chemistry, which covers compounds and their structures, accounts for about 8.33 per cent of the overall 120 marks on the JEE test. The NCERT textbook is used to solve the majority of the questions on this topic. There will undoubtedly be a few queries about this organic chemistry topic.
FAQs
Elements grow more electronegative as their oxidation states increase. As a result, permanganate is an excellent oxidising agent.
The physical state of potassium permanganate is an odourless solid that resembles dark purple or bronze crystals. The solution turns purple when these crystals are dissolved in water.
When all of the permanganate ions were being used up in the reaction, the solution sheds its pink colour. Potassium permanganate is a self-indicator because it acts as an indication in addition to being one of the reactants. Permanganate is an excellent oxidizer. Why?
What colour does potassium permanganate have?
What makes KMnO4 a self-indicator?








