Table of Contents
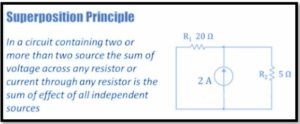
Electrical circuits with two or more sources are subjected to the Superposition Principle. The superposition technique is used to calculate the current or voltage flowing through any resistor or component in a multi-item network.
A Brief Outline
Summing the effects of individual sources can be used to get the total current through a resistor or the total voltage across a resistor. To use the superposition theorem, each source is examined individually, with other sources being substituted by a short or open circuit. A short circuit is used to replace a voltage source, while an open circuit is used to substitute a current source.
Important Concepts
According to the concept of superposition, every charge in space generates an electric field at a specific spot, regardless of the presence of additional charges in the medium. The resulting electric field is a vector sum of the individual charges’ electric fields. The net flux, net field, and net potential energy of the system are estimated using the superposition concept. When there are a lot of changes in a system, the superposition principle comes in handy.
Superposition Theorem and how does it work
- The initial step is to choose one source among the many available in the bilateral network. Any one of the circuit’s multiple sources can be taken into consideration initially.
- All sources should be substituted by their internal impedance, with the exception of the specified source.
- Evaluate the current that flows through or the voltage drop across a specific network node using a network simplification approach.
- The same applies to all other sources in the circuit when evaluating a single source.
- After you’ve gotten the replies for each individual source, add them all up to get the voltage level drop or current via the circuit element.
The theorem of Superposition’s Limitations
Non-linear circuits are not covered by the theorem. Because linearity is required, the Superposition Theorem can only be used to calculate voltage and current, but not power. When only one source is considered at a time, power dissipation is a nonlinear function that does not add up to an accurate total algebraically.
Significance of superposition principle in IIT JEE exam
The Oscillations and Waves chapter covers a wide range of topics and comprises 10% of the exam questions. All you have to do is understand each topic’s concepts. If you stick to this approach, your Physics preparation will be flawless, and you will breeze through this part. Basic and medium-level questions make up around 83 percent of the JEE paper, according to the allocation of levels of difficulty in the previous year’s tests.
FAQs
What is the superposition theorem, and how does it work?
The superposition theorem is a circuit simulation theorem that is used to solve a network with two or more connected sources.
Is the superposition theory true for AC circuits as well?
For AC circuits, the superposition theorem holds true.
We apply the superposition theorem for a variety of reasons.
Because it reduces a complex circuit into a Norton or Thevenin equivalent circuit, the superposition theorem is crucial in circuit analysis.








